GANT61GLI antagonist CAS# 500579-04-4 |
- Cyclopamine
Catalog No.:BCN2964
CAS No.:4449-51-8
- Purmorphamine
Catalog No.:BCC3641
CAS No.:483367-10-8
- GANT 58
Catalog No.:BCC1587
CAS No.:64048-12-0
- GDC-0449 (Vismodegib)
Catalog No.:BCC1285
CAS No.:879085-55-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 500579-04-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 421610 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C27H35N5 | M.Wt | 429.6 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | GANT 61; GANT-61; NSC136476; GNT61 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 25 mg/mL (58.19 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
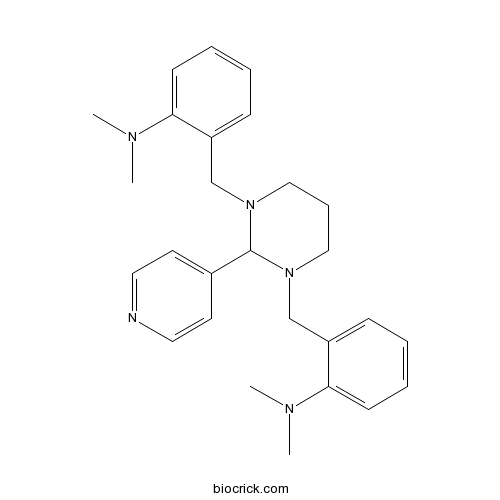
| Chemical Name | 2-[[3-[[2-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methyl]-2-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-diazinan-1-yl]methyl]-N,N-dimethylaniline | ||
| SMILES | CN(C)C1=CC=CC=C1CN2CCCN(C2C3=CC=NC=C3)CC4=CC=CC=C4N(C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KVQOGDQTWWCZFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C27H35N5/c1-29(2)25-12-7-5-10-23(25)20-31-18-9-19-32(27(31)22-14-16-28-17-15-22)21-24-11-6-8-13-26(24)30(3)4/h5-8,10-17,27H,9,18-21H2,1-4H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | GLI antagonist that inhibits GLI1 and GLI2-induced transcription (IC50 ~ 5 μM). Inhibits the hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway downstream of SMO and SUFU causing GLI1 nuclear accumulation. Displays antiproliferative and antitumor activity in vivo. Inhibits the pluripotency factors Oct4, Sox-2, Nanog and c-Myc in pancreatic cancer stem cells. |

GANT61 Dilution Calculator

GANT61 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3277 mL | 11.6387 mL | 23.2775 mL | 46.5549 mL | 58.1937 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4655 mL | 2.3277 mL | 4.6555 mL | 9.311 mL | 11.6387 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2328 mL | 1.1639 mL | 2.3277 mL | 4.6555 mL | 5.8194 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0466 mL | 0.2328 mL | 0.4655 mL | 0.9311 mL | 1.1639 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0233 mL | 0.1164 mL | 0.2328 mL | 0.4655 mL | 0.5819 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
GANT61 is a selective inhibitor of GLI with IC50 value of 13.56 μM (NBL-W-S cells, 48 hours) [1].
GLI genes, GLI1 and GLI2, are transcription activator and regulate target genes at the distal end of the canonical Hedgehog (HH) signaling pathway (SHH->PTCH->SMO-
>GLI). It is well known that HH signaling plays a pivotal role in normal cellular processes, like embryonic development, tissue patterning and differentiation. As oncogenes, GLI1 and GLI2 are found to be constitutively activated in a variety types of human cancers [2].
GANT61 is a potent GLIs inhibitor. In SK-N-EB(2) cells expressing MYCN, GANT61 treatment reduced the cell viability with the IC50 value of 10.9μM and 7.96μM at 48 hours and 72 hours, respectively [1]. When tested with human RMS cell lines—RD and RH30, GANT-61 treatment exhibited anti-proliferative effects and induced cell death in a dose-dependent manner (5-25 μM) via decreasing GLI1/2 expression which resulted in the arrest of cell cycle at Go/G1 phase [3].
In nude mice model with RD or RH30 cells xenograft, intraperitoneal injected GANT-61 (50mg/kg, body weight in 200μl PBS; three times a week) markedly reduced tumor growth [3].
References:
[1].Wang, J., et al., Inhibition of autophagy potentiates the efficacy of Gli inhibitor GANT-61 in MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma cells. BMC Cancer, 2014. 14: p. 768.
[2].Agyeman, A., et al., Mode and specificity of binding of the small molecule GANT61 to GLI determines inhibition of GLI-DNA binding. Oncotarget, 2014. 5(12): p. 4492-503.
[3].Srivastava, R.K., et al., GLI inhibitor GANT-61 diminishes embryonal and alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma growth by inhibiting Shh/AKT-mTOR axis. Oncotarget, 2014. 5(23): p. 12151-65.
- Rilpivirine
Catalog No.:BCC1897
CAS No.:500287-72-9
- 3,5-Dimethoxyphenol
Catalog No.:BCN7198
CAS No.:500-99-2
- Olivetol
Catalog No.:BCN4629
CAS No.:500-66-3
- Rhapontigenin
Catalog No.:BCN3515
CAS No.:500-65-2
- Kawain
Catalog No.:BCN3564
CAS No.:500-64-1
- Yangonin
Catalog No.:BCN3565
CAS No.:500-62-9
- Convolamine
Catalog No.:BCN1905
CAS No.:500-56-1
- Apoatropine
Catalog No.:BCN1869
CAS No.:500-55-0
- L-Mimosine
Catalog No.:BCC5450
CAS No.:500-44-7
- Nordihydroguaiaretic acid
Catalog No.:BCC1805
CAS No.:500-38-9
- D-(+)-Glucose
Catalog No.:BCN1259
CAS No.:50-99-7
- Ephedrine Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8322
CAS No.:50-98-6
- Securinol A
Catalog No.:BCN6987
CAS No.:5008-48-0
- Trans-caffeic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3462
CAS No.:501-16-6
- Cardanol (C15:1)
Catalog No.:BCN3751
CAS No.:501-26-8
- Kojic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6543
CAS No.:501-30-4
- 8-Azabicyclo-3.2.1-octan-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN1888
CAS No.:501-33-7
- Resveratrol
Catalog No.:BCN5607
CAS No.:501-36-0
- Hydrocinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4057
CAS No.:501-52-0
- 2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethanol
Catalog No.:BCN5608
CAS No.:501-94-0
- Rhododendrol
Catalog No.:BCN5609
CAS No.:501-96-2
- Phloretic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2950
CAS No.:501-97-3
- 2,3-Di-O-methylthiomethyleuscaphic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5610
CAS No.:
- Pilosol A
Catalog No.:BCC9121
CAS No.:501086-15-3
Anti-cancer stem cell activity of a hedgehog inhibitor GANT61 in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells.[Pubmed:28211214]
Cancer Sci. 2017 May;108(5):918-930.
Estradiol (E2) increases not only the cell growth but also the cancer stem cell (CSC) proportion in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer cells. It has been suggested that the non-canonical hedgehog (Hh) pathway activated by E2 plays an important role in the regulation of CSC proportion in ER-positive breast cancer cells. We studied anti-CSC activity of a non-canonical Hh inhibitor GANT61 in ER-positive breast cancer cells. Effects of GANT61 on the cell growth, cell cycle progression, apoptosis and CSC proportion were investigated in four ER-positive breast cancer cell lines. CSC proportion was measured using either the mammosphere assay or CD44/CD24 assay. Expression levels of pivotal molecules in the Hh pathway were measured. Combined effects of GANT61 with antiestrogens on the anti-cell growth and anti-CSC activities were investigated. E2 significantly increased the cell growth and CSC proportion in all ER-positive cell lines. E2 increased the expression levels of glioma-associated oncogene (GLI) 1 and/or GLI2. GANT61 decreased the cell growth in association with a G1-S cell cycle retardation and increased apoptosis. GANT61 decreased the E2-induced CSC proportion measured by the mammosphere assay in all cell lines. Antiestrogens also decreased the E2-induced cell growth and CSC proportion. Combined treatments of GANT61 with antiestrogens additively enhanced anti-cell growth and/or anti-CSC activities in some ER-positive cell lines. In conclusion, the non-canonical Hh inhibitor GANT61 inhibited not only the cell growth but also the CSC proportion increased by E2 in ER-positive breast cancer cells. GANT61 enhanced anti-cell growth and/or anti-CSC activities of antiestrogens in ER-positive cell lines.
GANT61, a GLI inhibitor, sensitizes glioma cells to the temozolomide treatment.[Pubmed:27894350]
J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Nov 28;35(1):184.
BACKGROUND: The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of downregulating Hedgehog pathway by GANT61 on human glioma cells, examine the consequent changes of temozolomide (TMZ)-induced effects and explore the molecular mechanisms. METHODS: The cytotoxicity of a Gli1/2 inhibitor, GANT61 was examined both alone and in combination with TMZ in human glioma cell lines. The mRNA and protein expression alterations were determined by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blot, respectively. CCK-8 assay detected the cell proliferative capability. Apoptotic cell number was measured by flow cytometry. The transwell assay was used to test the cell invasive capability. DNA damage effect was identified by COMET assay and gammaH2AX expression. RESULTS: Proliferation of tumor cells treated with GANT61 in combination with TMZ was significantly suppressed compared with those treated with either drug used alone. The combination treatment induced a higher rate of apoptosis, DNA damage and reduced the invasive capability of glioma cells. DNA damage repair enzyme MGMT and the Notch1 pathway increased in the cells treated by TMZ treatment. However, GANT61 could abrogated the protein increasing. CONCLUSIONS: GANT61 sensitizes glioma cells to TMZ treatment by enhancing DNA damage effect, decreasing MGMT expression and the Notch1 pathway.
The Effect of Metformin and GANT61 Combinations on the Radiosensitivity of Prostate Cancer Cells.[Pubmed:28208838]
Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Feb 13;18(2). pii: ijms18020399.
The anti-diabetes drug metformin has been shown to have anti-neoplastic effects in several tumor models through its effects on energy metabolism and protein synthesis. Recent studies show that metformin also targets Hedgehog (Hh) signaling, a developmental pathway re-activated in several tumor types, including prostate cancer (PCa). Furthermore, we and others have shown that Hh signaling is an important target for radiosensitization. Here, we evaluated the combination of metformin and the Hh inhibitor GANT61 (GLI-ANTagonist 61) with or without ionizing radiation in three PCa cell lines (PC3, DU145, 22Rv1). The effect on proliferation, radiosensitivity, apoptosis, cell cycle distribution, reactive oxygen species production, DNA repair, gene and protein expression was investigated. Furthermore, this treatment combination was also assessed in vivo. Metformin was shown to interact with Hh signaling by inhibiting the effector protein glioma-associated oncogene homolog 1 (GLI1) in PCa cells both in vitro and in vivo. The combination of metformin and GANT61 significantly inhibited PCa cell growth in vitro and enhanced the radiation response of 22Rv1 cells compared to either single agent. Nevertheless, neither the growth inhibitory effect nor the radiosensitization effect of the combination treatment observed in vitro was seen in vivo. Although the interaction between metformin and Hh signaling seems to be promising from a therapeutic point of view in vitro, more research is needed when implementing this combination strategy in vivo.
Anti-cell growth and anti-cancer stem cell activities of the non-canonical hedgehog inhibitor GANT61 in triple-negative breast cancer cells.[Pubmed:28144905]
Breast Cancer. 2017 Sep;24(5):683-693.
BACKGROUND: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) exhibits biologically aggressive behavior and has a poor prognosis. Novel molecular targeting agents are needed to control TNBC. Recent studies revealed that the non-canonical hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway plays important roles in the regulation of cancer stem cells (CSCs) in breast cancer. Therefore, the anti-cell growth and anti-CSC effects of the non-canonical Hh inhibitor GANT61 were investigated in TNBC cells. METHODS: The effects of GANT61 on cell growth, cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and the proportion of CSCs were investigated in three TNBC cell lines. Four ER-positive breast cancer cell lines were also used for comparisons. The expression levels of effector molecules in the Hh pathway: glioma-associated oncogene (GLI) 1 and GLI2, were measured. The combined effects of GANT61 and paclitaxel on anti-cell growth and anti-CSC activities were also investigated. RESULTS: Basal expression levels of GLI1 and GLI2 were significantly higher in TNBC cells than in ER-positive breast cancer cells. GANT61 dose-dependently decreased cell growth in association with G1-S cell cycle retardation and increased apoptosis. GANT61 significantly decreased the CSC proportion in all TNBC cell lines. Paclitaxel decreased cell growth, but not the CSC proportion. Combined treatments of GANT61 and paclitaxel more than additively enhanced anti-cell growth and/or anti-CSC activities. CONCLUSIONS: The non-canonical Hh inhibitor GANT61 decreased not only cell growth, but also the CSC population in TNBC cells. GANT61 enhanced the anti-cell growth activity of paclitaxel in these cells. These results suggest for the first time that GANT61 has potential as a therapeutic agent in the treatment of patients with TNBC.
Blocking Hedgehog survival signaling at the level of the GLI genes induces DNA damage and extensive cell death in human colon carcinoma cells.[Pubmed:21747117]
Cancer Res. 2011 Sep 1;71(17):5904-14.
Canonical Hedgehog (HH) signaling is characterized by Smoothened (Smo)-dependent activation of the transcription factors Gli1 and Gli2, which regulate HH target genes. In human colon carcinoma cells, treatment with the Gli small-molecule inhibitor GANT61 induces extensive cell death in contrast to the Smo inhibitor cyclopamine. Here we elucidate cellular events upstream of cell death elicited by GANT61, which reveal the basis for its unique cytotoxic activity in colon carcinoma cells. Unlike cyclopamine, GANT61 induced transient cellular accumulation at G(1)-S (24 hours) and in early S-phase (32 hours), with elevated p21(Cip1), cyclin E, and cyclin A in HT29 cells. GANT61 induced DNA damage within 24 hours, with the appearance of p-ATM and p-Chk2. Pharmacologic inhibition of Gli1 and Gli2 by GANT61 or genetic inhibition by transient transfection of the Gli3 repressor (Gli3R) downregulated Gli1 and Gli2 expression and induced gammaH2AX, PARP cleavage, caspase-3 activation, and cell death. GANT61 induced gammaH2AX nuclear foci, while transient transfection of Gli3R showed expression of Gli3R and gammaH2AX foci within the same nuclei in HT29, SW480, and HCT116. GANT61 specifically targeted Gli1 and Gli2 substantiated by specific inhibition of (i) direct binding of Gli1 and Gli2 to the promoters of target genes HIP1 and BCL-2, (ii) Gli-luciferase activity, and (iii) transcriptional activation of BCL-2. Taken together, these findings establish that inhibition of HH signaling at the level of the GLI genes downstream of Smo is critical in the induction of DNA damage in early S-phase, leading to cell death in human colon carcinoma cells.
Inhibition of GLI-mediated transcription and tumor cell growth by small-molecule antagonists.[Pubmed:17494766]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 May 15;104(20):8455-60.
The developmentally important Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway has recently been implicated in several forms of solid cancer. Current drug development programs focus on targeting the protooncogene Smoothened, a key transmembrane pathway member. These drug candidates, albeit promising, do not address the scenario in which pathway activation occurs downstream of Smoothened, as observed in cases of medulloblastoma, glioma, pericytoma, breast cancer, and prostate cancer. A cellular screen for small-molecule antagonists of GLI-mediated transcription, which constitutes the final step in the Hh pathway, revealed two molecules that are able to selectively inhibit GLI-mediated gene transactivation. We provide genetic evidence of downstream pathway blockade by these compounds and demonstrate the ineffectiveness of upstream antagonists such as cyclopamine in such situations. Mechanistically, both inhibitors act in the nucleus to block GLI function, and one of them interferes with GLI1 DNA binding in living cells. Importantly, the discovered compounds efficiently inhibited in vitro tumor cell proliferation in a GLI-dependent manner and successfully blocked cell growth in an in vivo xenograft model using human prostate cancer cells harboring downstream activation of the Hh pathway.


