GM 6001Broad spectrum MMP inhibitor CAS# 142880-36-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 142880-36-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 132519 | Appearance | Powder |
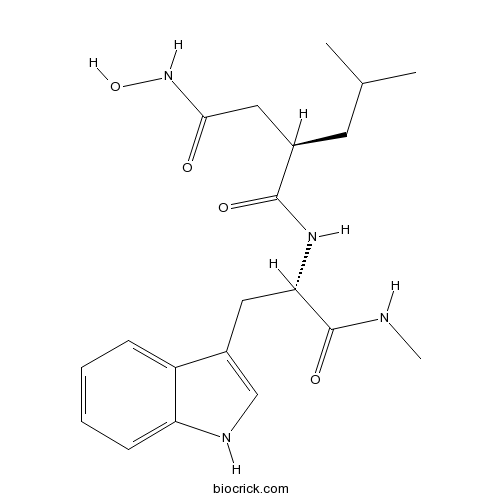
| Formula | C20H28N4O4 | M.Wt | 388.46 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Galardin, Ilomastat | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 47 mg/mL (120.99 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2R)-N'-hydroxy-N-[(2S)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-(methylamino)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]-2-(2-methylpropyl)butanediamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)CC(CC(=O)NO)C(=O)NC(CC1=CNC2=CC=CC=C21)C(=O)NC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NITYDPDXAAFEIT-DYVFJYSZSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H28N4O4/c1-12(2)8-13(10-18(25)24-28)19(26)23-17(20(27)21-3)9-14-11-22-16-7-5-4-6-15(14)16/h4-7,11-13,17,22,28H,8-10H2,1-3H3,(H,21,27)(H,23,26)(H,24,25)/t13-,17+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Broad spectrum MMP inhibitor. Reduces infarct volume following middle cerebral artery occlusion in an ischemic mouse model. Also inhibits human skin fibroblast collagenase (Ki = 0.4 nM). |

GM 6001 Dilution Calculator

GM 6001 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5743 mL | 12.8713 mL | 25.7427 mL | 51.4854 mL | 64.3567 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5149 mL | 2.5743 mL | 5.1485 mL | 10.2971 mL | 12.8713 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2574 mL | 1.2871 mL | 2.5743 mL | 5.1485 mL | 6.4357 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0515 mL | 0.2574 mL | 0.5149 mL | 1.0297 mL | 1.2871 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0257 mL | 0.1287 mL | 0.2574 mL | 0.5149 mL | 0.6436 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
GM 6001 is a broad-spectrum inhibitor of MMP with Ki values of 0.4nM, 0.5nM, 27nM, 0.1nM and 0.2nM, respectively for MMP-1,2,3,8 and 9 [1].
MMPs are divided into 4 subfamilies: stromelysins, gelatinases, membrane-type MMPs, and collagenases. They play major roles in mediating the effects of IL-1 during meniscal healing. As an inhibitor of MMP, GM 6001 is reported to enhance the repair of meniscal lesions in an inflammatory microenvironment. MMPs also play roles in the transactivation of EGFR induced by GPCR agonists. It is reported that treatment of GM 6001 inhibits the phosphorylation of EGFR as well as the activation of ERK induced by bombesin or LPA. The DNA synthesis induced by bombesin or LPA is also attenuated by GM 6001 since the activity of MMP is required for the GPCR-induced late response mitogenic signaling [1, 2].
References:
[1] McNulty AL, Weinberg JB, Guilak F. Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases enhances in vitro repair of the meniscus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009 Jun;467(6):1557-67.
[2] Santiskulvong C, Rozengurt E. Galardin (GM 6001), a broad-spectrum matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, blocks bombesin- and LPA-induced EGF receptor transactivation and DNA synthesis in rat-1 cells. Exp Cell Res. 2003 Nov 1;290(2):437-46.
- U 73343
Catalog No.:BCC8091
CAS No.:142878-12-4
- Toddacoumaquinone
Catalog No.:BCN3640
CAS No.:142878-03-3
- N-Acetyl-N-acetoxy-4-chlorobenzenesulfonamide
Catalog No.:BCC6762
CAS No.:142867-52-5
- Clausine D
Catalog No.:BCN4707
CAS No.:142846-95-5
- L-Sulforaphane
Catalog No.:BCN8449
CAS No.:142825-10-3
- Clinopodiside A
Catalog No.:BCN2621
CAS No.:142809-89-0
- Preapiodionene
Catalog No.:BCN1854
CAS No.:142808-39-7
- Apiodionene
Catalog No.:BCN1829
CAS No.:142808-38-6
- DPN
Catalog No.:BCC7088
CAS No.:1428-67-7
- 5,7-Dimethoxyluteolin
Catalog No.:BCN8167
CAS No.:90363-40-9
- Silybin B
Catalog No.:BCN7898
CAS No.:142797-34-0
- 4-Chlorophenylguanidine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2382
CAS No.:14279-91-5
- 1-O-Ethylpiptocarphin F
Catalog No.:BCN6448
CAS No.:142891-12-1
- 8alpha-Methacryloyloxy-13-ethoxyvernojalcanolide
Catalog No.:BCN7445
CAS No.:142891-14-3
- Petunidin chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3018
CAS No.:1429-30-7
- OXF BD 02
Catalog No.:BCC5598
CAS No.:1429129-68-9
- Mutant IDH1 inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC4144
CAS No.:1429180-08-4
- Triptoquinone B
Catalog No.:BCN6238
CAS No.:142937-50-6
- Triptoquinone A
Catalog No.:BCN6781
CAS No.:142950-86-5
- HPOB
Catalog No.:BCC5574
CAS No.:1429651-50-2
- UNC2025
Catalog No.:BCC8062
CAS No.:1429881-91-3
- Fmoc-D-Phe(4-Cl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3177
CAS No.:142994-19-2
- Fmoc-D-Ala(3-pyridyl)-OH.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3324
CAS No.:142994-45-4
- Salvianolic acid E
Catalog No.:BCN8194
CAS No.:142998-46-7
Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor GM 6001 attenuates keratinocyte migration, contraction and myofibroblast formation in skin wounds.[Pubmed:15350544]
Exp Cell Res. 2004 Oct 1;299(2):465-75.
In this study, we examined the impact of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) on epithelialization, granulation tissue development, wound contraction, and alpha-smooth muscle actin (ASMA) expression during cutaneous wound repair through systemic administration of the synthetic broad-spectrum MMP inhibitor GM 6001 (N-[(2R)-2-(hydroxamidocarbonylmethyl)-4-methylpentanoyl]-L-tryptophan methylamide). Four full-thickness excisional wounds (50 mm2) on the back of 22 young female Sprague-Dawley rats, 12 treated with GM 6001 100 mg/kg and 10 with vehicle, were allowed to heal by secondary intention. GM 6001-treated wounds were minimally resurfaced with neoepithelium, despite unaltered keratinocyte proliferation in wound edges, whereas control wounds were completely covered with 3-7 cell layers of parakeratinized epithelium on post-wounding day 7. Hydroxyproline concentration, a marker of collagen, and cell proliferation in granulation tissue did not differ significantly between GM 6001-treated and control groups. Impaired wound contraction (P < 0.01) was associated with a dramatic reduction of ASMA-positive myofibroblasts in granulation tissue of GM 6001 wounds. This was not due to GM6001 blocking transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1)-induced myofibroblast differentiation since GM 6001 did not inhibit TGF-beta1-induced ASMA expression and force generation in cultured rat dermal fibroblasts. The profound impairment of skin repair by the nonselective MMP inhibitor GM 6001 suggests that keratinocyte resurfacing, wound contraction, and granulation tissue organization are highly MMP-dependent processes.
Galardin (GM 6001), a broad-spectrum matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, blocks bombesin- and LPA-induced EGF receptor transactivation and DNA synthesis in rat-1 cells.[Pubmed:14568001]
Exp Cell Res. 2003 Nov 1;290(2):437-46.
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) have been implicated in the transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) induced by G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) agonists. Although EGFR phosphorylation and downstream signaling have been shown to be dependent on MMP activity in many systems, a role for MMPs in GPCR-induced DNA synthesis has not been studied in any detail. In this study we utilized the broad-spectrum matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, galardin (Ilomastat, GM 6001), to study the mechanism of bombesin- or LPA-induced EGFR transactivation and the role of MMPs in early and late response mitogenic signaling in Rat-1 cells stably transfected with the bombesin/GRP receptor (BoR-15 cells). Addition of galardin to cells stimulated with bombesin or LPA specifically inhibited total EGFR phosphorylation, as well as site-specific phosphorylation of tyrosine 845, a putative Src phosphorylation site, and tyrosine 1068, a typical autophosphorylation site. Galardin treatment also inhibited extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation induced by bombesin or LPA, but not by EGF. In addition, galardin inhibited bombesin- or LPA-induced DNA synthesis in a dose dependent manner, when stimulated by increasing concentrations of bombesin, and when added after bombesin stimulation. Furthermore, addition of galardin post-bombesin stimulation indicated that by 3 h sufficient accumulation of EGFR ligands had occurred to continue to induce transactivation despite an inhibition of MMP activity. Taken together, our results suggest that MMPs act as early as 5 min, and up to around 3 h, to mediate GPCR-induced EGFR transactivation, ERK activation, and stimulation of DNA synthesis.
[Experimental study on the treatment of corneal melting after alkali burn with GM 6001].[Pubmed:12410973]
Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2002 Sep;38(9):539-42.
OBJECTIVE: To eva1uate the effect of synthetic inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases (GM 6001) on the prevention of melting of rabbit corneas after alkali burn. METHODS: Severe and moderate rabbit alkali burns were made by different concentrations of NaOH. Corneas with severe or moderate alkali injuries were topically treated with 400 mg/L or 200 mg/L GM 6001 for 30 days. Vehicle was used as control. All corneas were evaluated for melting, opacity and other pathological changes. RESULTS: After severe alkali burns, all of the 8 corneas of the control group melted in 13 +/- 5 days, and 2 corneas perforated. Only did 2 corneas melt in 19 +/- 4 days after burn and not perforate in 400 mg/L GM 6001 group. The rates of corneal melting and perforation in 400 mg/L GM 6001 group were lower than that of the control (P < 0.05), and the initial time of melting was later than that of the control (P < 0.0l). After moderate alkali burn, all of the 6 corneas of control melted in 14 +/- 6 days, and 1 cornea perforated. Only did 2 of 200 mg/L GM 6001 treated corneas melt in 19 +/- 4 days without perforation after burn. The rate of corneal melting and the degree of corneal opacity were lower in 200 mg/L GM 6001 treated than that of the control, the difference being significant (P < 0.0l). Histologic section of GM 6001 treated corneas revealed much less collagen fiber destruction and inflammatory cell infiltration than that of the control. CONCLUSION: GM 6001 not only can prevent and delay the corneal melting after alkali burn, but also can reduce the destruction of corneal collagen fibers and infiltration of inflammatory cells in the corneal tissue.
Involvement of matrix metalloproteinase-mediated proteolysis of neural cell adhesion molecule in the development of cerebral ischemic neuronal damage.[Pubmed:21602423]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Aug;338(2):701-10.
Neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) is a membrane protein abundantly expressed in the central nervous system. Recently, it has been reported that dysfunction of NCAM is linked to human brain disorders. Furthermore, NCAM is one of the proteolysis targets of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP), whose activation is implicated in neuronal damage. The aim of this study was to elucidate the involvement of MMP-mediated proteolysis of NCAM in the development of ischemic neuronal damage. Male ddY and MMP-9 knockout (KO) C57BL/6J mice were subjected to 2 h of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). In MCAO model mice, development of infarction and behavioral abnormality were clearly observed on days 1 and 3 after MCAO. Protein levels of MMP-2 and MMP-9 were significantly increased on days 1 and 3 after MCAO. In addition, full-length NCAM (180 kDa) was significantly decreased, but its metabolite levels increased on day 1 by ischemic stress per se. NCAM small interfering RNA significantly increased the neuronal damage induced by MCAO. MMP inhibition or MMP-9 gene KO attenuated the infarction, behavioral abnormalities, and decrease of NCAM (180 kDa) observed after MCAO in mice. The present findings clearly suggest that MMP-2/MMP-9-mediated NCAM proteolysis is implicated in the exacerbation of ischemic neuronal damage.
Leptin stimulates endothelin-1 expression via extracellular signal-regulated kinase by epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation in rat aortic smooth muscle cells.[Pubmed:17678888]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Nov 14;573(1-3):49-54.
Obesity is a major risk factor for the development of hypertension. Recent studies have suggested that leptin, a 167-amino acid peptide hormone produced by white adipose tissue, is related to the pathogenesis of obesity-related hypertension. However, the signaling mechanisms underlying the effects of leptin remain to be extensively examined. In this study, we found that leptin induced extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation and endothelin-1 expression in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Both PD98059 and U0126, inhibitors of the upstream activator of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, inhibited augmentation of endothelin-1 expression stimulated with leptin. Leptin induced significant tyrosine phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor, which was significantly attenuated by two inhibitors, an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, AG1478, and a broad-spectrum matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, GM6001. This indicates that the pathway of epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation induced by leptin is dependent on proteolytically released epidermal growth factor receptor ligands. Pretreatment of cells with AG1478 significantly reduced the degree of phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and endothelin-1 expression. Our results reveal that epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation is involved in the leptin signaling pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells, which may be related to the increased risk of hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases in obese subjects.
Inhibition of human skin fibroblast collagenase, thermolysin, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase by peptide hydroxamic acids.[Pubmed:1322694]
Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 11;31(31):7152-4.
The hydroxamic acid HONHCOCH2CH(i-Bu)CO-L-Trp-NHMe, isomer 6A (GM 6001), inhibits human skin fibroblast collagenase with Ki of 0.4 nM using the synthetic thiol ester substrate Ac-Pro-Leu-Gly-SCH(i-Bu)CO-Leu-Gly-OEt at pH 6.5. The other isomer, 6B, which has the opposite configuration at the CH2CH(i-Bu)CO alpha-carbon atom, has a Ki of 200 nM for this enzyme. GM 6001 is one of the most potent inhibitors of human skin fibroblast collagenase yet reported. GM 6001 has a Ki of 20 nM against thermolysin and Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase. Isomer 6B has a Ki of 7 nM against thermolysin and 2 nM against the elastase. 6A and 6B are the most potent hydroxamate inhibitors reported for these bacterial enzymes. The pattern of inhibition for all three enzymes suggests that isomer 6A is the (R,S) compound, stereochemically analogous to the L,L-dipeptide, and isomer 6B is the (S,S) compound, analogous to the DL-dipeptide. The tolerance of the D configuration by thermolysin and the elastase allows these inhibitors to discriminate between the human and bacterial enzymes simply by inversion of configuration at the CH2CH(i-Bu)CO alpha-carbon atom. Substitution of the potential metal liganding groups carboxylate and hydrazide for the hydroxamate group yields much weaker inhibitors for all three enzymes.


