Helioxanthin 8-1inhibitor of HBV and HIV virus CAS# 840529-13-7 |
- Romidepsin (FK228, depsipeptide)
Catalog No.:BCC3597
CAS No.:128517-07-7
- Vorinostat (SAHA, MK0683)
Catalog No.:BCC2145
CAS No.:149647-78-9
- Trichostatin A (TSA)
Catalog No.:BCC3605
CAS No.:58880-19-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 840529-13-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6320331 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H12N2O6 | M.Wt | 376.32 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Helioxanthin analogue 8-1 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 10 mg/mL (26.57 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
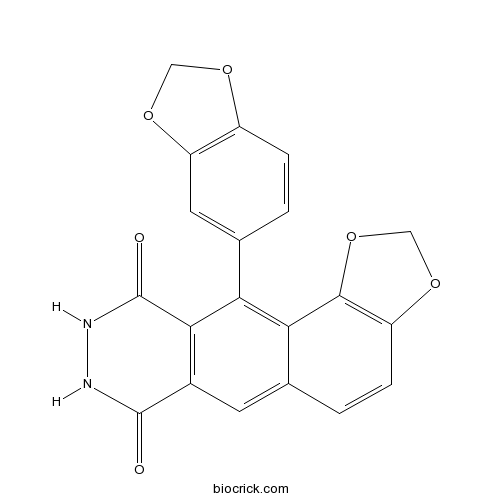
| Chemical Name | 11-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-8,9-dihydro-[1,3]benzodioxolo[7,6-g]phthalazine-7,10-dione | ||
| SMILES | C1OC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)C3=C4C(=CC5=C3C(=O)NNC5=O)C=CC6=C4OCO6 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PXSPEYYAEFFUMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H12N2O6/c23-19-11-5-9-2-4-13-18(28-8-26-13)16(9)15(17(11)20(24)22-21-19)10-1-3-12-14(6-10)27-7-25-12/h1-6H,7-8H2,(H,21,23)(H,22,24) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Helioxanthin 8-1 is an analogue of helioxanthin, exhibites significant in vitro anti-HBV/HCV/HSV-1/HIV activity with EC50 of >5/10/1.4/15 uM.
IC50 value: >5/10/1.4/15 uM(HBV/HCV/HSV-1/HIV) [1]
Target: Antiviral agent
The cyclic hydrazide 28(Helioxanthin 8-1) showed the most potent antiHBV activity among those helioxanthin analogues tested. In addition, compound 28 exhibited moderately potent activity against HIV. It would therefore be promising to study helioxanthin analogues that contain a six-membered ring instead of the five-membered ring found in the lactam [1]. 8-1 exhibited effective inhibition on DHBV replication. The combination of 8-1 with 3TC resulted in additional anti-DHBV activity. Viral induced cells displayed higher susceptibility to 8-1 treatment than non-induced cells. HBV X protein might not be an essential factor in the initiation of the biological activity of 8-1, as demonstrated by its absence in DHBV [2]. References: | |||||

Helioxanthin 8-1 Dilution Calculator

Helioxanthin 8-1 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6573 mL | 13.2866 mL | 26.5731 mL | 53.1463 mL | 66.4328 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5315 mL | 2.6573 mL | 5.3146 mL | 10.6293 mL | 13.2866 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2657 mL | 1.3287 mL | 2.6573 mL | 5.3146 mL | 6.6433 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0531 mL | 0.2657 mL | 0.5315 mL | 1.0629 mL | 1.3287 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0266 mL | 0.1329 mL | 0.2657 mL | 0.5315 mL | 0.6643 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Helioxanthin 8-1, an analogue of helioxanthin (ACH126447), is an inhibitor of HBV and HIV virus with EC50 values of 0.03 μM and 2.7 μM, respectively [1].
Helioxanthin 8-1 is the cyclic hydrazide derivative of helioxanthin and has shown significant in vitro antivirus activity with EC50 values of 0.03 μM and 2.7 μM for HBV and HIV, respectively [1]. In the ds-tet5 cells, helioxanthin 8-1 can inhibit duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) DNA synthesis with a mean IC50 value of 0.25±0.05 μM. Besides, in induced cells and non-induced ds-tet5 cells, helioxanthin 8-1 has cytotoxic effect with CC50 values of 18±2 μM and 45±3 μM, respectively, by using an MTT assay [2].
References:
[1] Yeo H1, Li Y, Fu L, Zhu JL, Gullen EA, Dutschman GE, Lee Y, Chung R, Huang ES, Austin DJ, Cheng YC. Synthesis and antiviral activity of helioxanthin analogues. J Med Chem. 2005 Jan 27;48(2):534-46.
[2] Ying C1, Tan S, Cheng YC. Helioxanthin analogue 8-1 inhibits duck hepatitis B virus replication in cell culture. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2010;21(2):97-103.
- Fmoc-N-Me-Val-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3358
CAS No.:84000-11-3
- Fmoc-N-Me-Ala-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3210
CAS No.:84000-07-7
- Xanthoxyletin
Catalog No.:BCN6579
CAS No.:84-99-1
- Vitamin K1
Catalog No.:BCN2209
CAS No.:84-80-0
- Lapachol
Catalog No.:BCN4391
CAS No.:84-79-7
- Dibutyl Phthalate
Catalog No.:BCC8411
CAS No.:84-74-2
- Diisobutyl phthalate
Catalog No.:BCN7148
CAS No.:84-69-5
- Anthraquinone
Catalog No.:BCC8832
CAS No.:84-65-1
- Anthraflavic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8831
CAS No.:84-60-6
- Tectoquinone
Catalog No.:BCN3481
CAS No.:84-54-8
- Stylopine
Catalog No.:BCN3715
CAS No.:84-39-9
- Syrosingopine
Catalog No.:BCN5365
CAS No.:84-36-6
- Lamotrigine
Catalog No.:BCC5051
CAS No.:84057-84-1
- Roquinimex
Catalog No.:BCC5355
CAS No.:84088-42-6
- 1-Benzhydrylpiperazine
Catalog No.:BCC8453
CAS No.:841-77-0
- Wilforlide A
Catalog No.:BCN4383
CAS No.:84104-71-2
- Wilforlide A acetate
Catalog No.:BCN4384
CAS No.:84104-80-3
- Triptotriterpenic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN6780
CAS No.:84108-17-8
- R406 (free base)
Catalog No.:BCC2553
CAS No.:841290-80-0
- R406
Catalog No.:BCC3876
CAS No.:841290-81-1
- 6-Fluoro-3-(4-piperidinyl)-1,2-benzisoxazole hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8772
CAS No.:84163-13-3
- Ac-Glu(OtBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2921
CAS No.:84192-88-1
- 7 8-Dihydroxy-4-Phenylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCC8289
CAS No.:842-01-3
- Sudan I
Catalog No.:BCN8378
CAS No.:842-07-9
Helioxanthin analogue 8-1 inhibits duck hepatitis B virus replication in cell culture.[Pubmed:21107018]
Antivir Chem Chemother. 2010;21(2):97-103.
BACKGROUND: Current approved anti-HBV treatment cannot completely eliminate HBV infection, and emergence of resistant virus is an important treatment issue. Effective anti-HBV agents with different mechanisms of action on novel target sites are needed for the treatment of HBV infection and for combating the resistant virus, alone or in combination with current anti-HBV strategies. Helioxanthin analogue 8-1 displayed potent anti-HBV activity in human HBV in vitro and in animal models, with a unique antiviral mechanism. Its antiviral activity in other HBV system needs further study. METHODS: The anti-duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) activity of 8-1, an analogue of a natural product, helioxanthin, was studied in the DHBV inducible cell line, dstet5, in comparison to and in combination with the nucleoside analogue, lamivudine (3TC). RESULTS: Helioxanthin analogue 8-1 exhibited anti-DHBV activity as demonstrated by quantification of viral DNA, RNA, covalently closed circular DNA and protein synthesis. Analogue 8-1 did not affect the stability of cellular macromolecules and did not have a sustained antiviral effect after drug removal. When DHBV replication was induced, virus-harbouring cells were more susceptible to the cytotoxicity of 8-1 than non-induced cells. CONCLUSIONS: 8-1 exhibited effective inhibition on DHBV replication. The combination of 8-1 with 3TC resulted in additional anti-DHBV activity. Viral induced cells displayed higher susceptibility to 8-1 treatment than non-induced cells. HBV X protein might not be an essential factor in the initiation of the biological activity of 8-1, as demonstrated by its absence in DHBV. These findings warrant further development of 8-1 for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B and its associated diseases.


