Hyperxanthone ECAS# 819860-76-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 819860-76-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11151593 | Appearance | Powder |
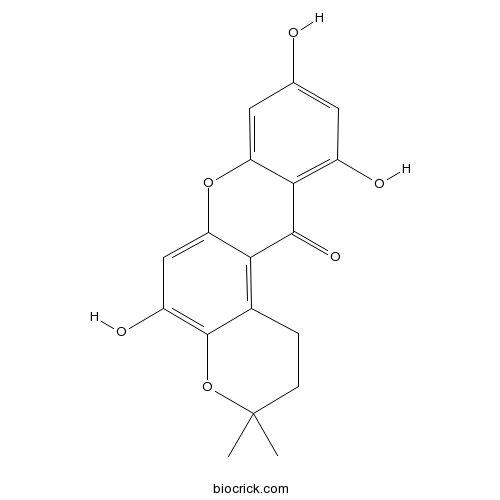
| Formula | C18H16O6 | M.Wt | 328.32 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 5,9,11-trihydroxy-3,3-dimethyl-1,2-dihydropyrano[3,2-a]xanthen-12-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1(CCC2=C3C(=CC(=C2O1)O)OC4=CC(=CC(=C4C3=O)O)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JXBWMJZDYVJVIV-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H16O6/c1-18(2)4-3-9-14-13(7-11(21)17(9)24-18)23-12-6-8(19)5-10(20)15(12)16(14)22/h5-7,19-21H,3-4H2,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Hyperxanthone E is a phytoalexin from Hypericum calycinum cell cultures. |
| In vitro | Cinnamate:CoA ligase initiates the biosynthesis of a benzoate-derived xanthone phytoalexin in Hypericum calycinum cell cultures.[Pubmed: 22992510]Plant Physiol. 2012 Nov;160(3):1267-80.Although a number of plant natural products are derived from benzoic acid, the biosynthesis of this structurally simple precursor is poorly understood.
Hypericum calycinum cell cultures accumulate a benzoic acid-derived xanthone phytoalexin, Hyperxanthone E, in response to elicitor treatment. |
| Structure Identification | Molecules. 2015 Aug 27;20(9):15616-30.Molecular Cloning and Characterization of a Xanthone Prenyltransferase from Hypericum calycinum Cell Cultures.[Pubmed: 26343621 ]In plants, prenylation of metabolites is widely distributed to generate compounds with efficient defense potential and distinct pharmacological activities profitable to human health.
|

Hyperxanthone E Dilution Calculator

Hyperxanthone E Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0458 mL | 15.229 mL | 30.4581 mL | 60.9162 mL | 76.1452 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6092 mL | 3.0458 mL | 6.0916 mL | 12.1832 mL | 15.229 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3046 mL | 1.5229 mL | 3.0458 mL | 6.0916 mL | 7.6145 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0609 mL | 0.3046 mL | 0.6092 mL | 1.2183 mL | 1.5229 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0305 mL | 0.1523 mL | 0.3046 mL | 0.6092 mL | 0.7615 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- KW-2478
Catalog No.:BCC2127
CAS No.:819812-04-9
- Clovin
Catalog No.:BCN7817
CAS No.:81970-00-5
- Splendoside
Catalog No.:BCN6647
CAS No.:81969-41-7
- 4(15),5,10(14)-Germacratrien-1-ol
Catalog No.:BCN4354
CAS No.:81968-62-9
- Z-Ligustilide
Catalog No.:BCC9193
CAS No.:81944-09-4
- Zofenopril calcium
Catalog No.:BCC5229
CAS No.:81938-43-4
- Polyphyllin H
Catalog No.:BCN2834
CAS No.:81917-50-2
- Momordicoside I aglycone
Catalog No.:BCN4353
CAS No.:81910-41-0
- 5,19-Epoxy-25-methoxycucurbita-6,23-dien-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN1341
CAS No.:81910-39-6
- Ganoderic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN3033
CAS No.:81907-62-2
- Ganoderic acid B
Catalog No.:BCN3034
CAS No.:81907-61-1
- Forskolin J
Catalog No.:BCN4352
CAS No.:81873-08-7
- Vitedoin A
Catalog No.:BCN6741
CAS No.:819861-40-0
- Lancerin
Catalog No.:BCN2803
CAS No.:81991-99-3
- Khellin
Catalog No.:BCN4356
CAS No.:82-02-0
- Benzanthrone
Catalog No.:BCC8845
CAS No.:82-05-3
- Rottlerin
Catalog No.:BCC7127
CAS No.:82-08-6
- Alpha-Toxicarol
Catalog No.:BCN6467
CAS No.:82-09-7
- 1-Amino-2-methylanthraquinone
Catalog No.:BCC8451
CAS No.:82-28-0
- Visnagin
Catalog No.:BCN4367
CAS No.:82-57-5
- Peri acid
Catalog No.:BCC9116
CAS No.:82-75-7
- 8-Anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8785
CAS No.:82-76-8
- Daurichromenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4355
CAS No.:82003-90-5
- 10Z-Hymenialdisine
Catalog No.:BCC5773
CAS No.:82005-12-7
Molecular Cloning and Characterization of a Xanthone Prenyltransferase from Hypericum calycinum Cell Cultures.[Pubmed:26343621]
Molecules. 2015 Aug 27;20(9):15616-30.
In plants, prenylation of metabolites is widely distributed to generate compounds with efficient defense potential and distinct pharmacological activities profitable to human health. Prenylated compounds are formed by members of the prenyltransferase (PT) superfamily, which catalyze the addition of prenyl moieties to a variety of acceptor molecules. Cell cultures of Hypericum calycinum respond to elicitor treatment with the accumulation of the prenylated xanthone Hyperxanthone E. A cDNA encoding a membrane-bound PT (HcPT) was isolated from a subtracted cDNA library and transcript preparations of H. calycinum. An increase in the HcPT transcript level preceded Hyperxanthone E accumulation in cell cultures of H. calycinum treated with elicitor. The HcPT cDNA was functionally characterized by expression in baculovirus-infected insect cells. The recombinant enzyme catalyzed biosynthesis of 1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxy-8-prenylxanthone through regiospecific C-8 prenylation of 1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxyxanthone, indicating its involvement in Hyperxanthone E formation. The enzymatic product shared significant structural features with the previously reported cholinesterase inhibitor gamma-mangostin. Thus, our findings may offer a chance for semisynthesis of new active agents to be involved in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Cinnamate:CoA ligase initiates the biosynthesis of a benzoate-derived xanthone phytoalexin in Hypericum calycinum cell cultures.[Pubmed:22992510]
Plant Physiol. 2012 Nov;160(3):1267-80.
Although a number of plant natural products are derived from benzoic acid, the biosynthesis of this structurally simple precursor is poorly understood. Hypericum calycinum cell cultures accumulate a benzoic acid-derived xanthone phytoalexin, Hyperxanthone E, in response to elicitor treatment. Using a subtracted complementary DNA (cDNA) library and sequence information about conserved coenzyme A (CoA) ligase motifs, a cDNA encoding cinnamate:CoA ligase (CNL) was isolated. This enzyme channels metabolic flux from the general phenylpropanoid pathway into benzenoid metabolism. HcCNL preferred cinnamic acid as a substrate but failed to activate benzoic acid. Enzyme activity was strictly dependent on the presence of Mg(2)(+) and K(+) at optimum concentrations of 2.5 and 100 mM, respectively. Coordinated increases in the Phe ammonia-lyase and HcCNL transcript levels preceded the accumulation of Hyperxanthone E in cell cultures of H. calycinum after the addition of the elicitor. HcCNL contained a carboxyl-terminal type 1 peroxisomal targeting signal made up by the tripeptide Ser-Arg-Leu, which directed an amino-terminal reporter fusion to the peroxisomes. Masking the targeting signal by carboxyl-terminal reporter fusion led to cytoplasmic localization. A phylogenetic tree consisted of two evolutionarily distinct clusters. One cluster was formed by CoA ligases related to benzenoid metabolism, including HcCNL. The other cluster comprised 4-coumarate:CoA ligases from spermatophytes, ferns, and mosses, indicating divergence of the two clades prior to the divergence of the higher plant lineages.


