VisnaginCAS# 82-57-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 82-57-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6716 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
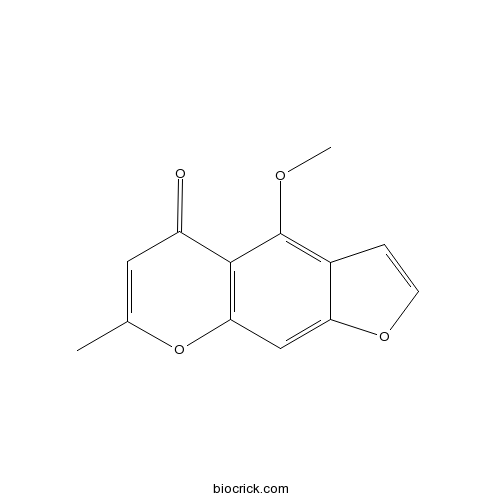
| Formula | C13H10O4 | M.Wt | 230.2 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-methoxy-7-methylfuro[3,2-g]chromen-5-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC(=O)C2=C(O1)C=C3C(=C2OC)C=CO3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NZVQLVGOZRELTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H10O4/c1-7-5-9(14)12-11(17-7)6-10-8(3-4-16-10)13(12)15-2/h3-6H,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Visnagin has acute hypotensive, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects, it protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy through modulation of mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase. Visnagin can relax aortae previously contracted by noradrenaline, and weakly inhibit the hydrolytic activity of the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) isozymes (PDE5, PDE4, PDE3, cyclic GMP activated PDE2 and PDE1). |
| Targets | IL Receptor | TNF-α | COX | P450 (e.g. CYP17) | NOS | AP-1 | NF-kB | IFN-γ | PDE |
| In vitro | Khellin and visnagin differentially modulate AHR signaling and downstream CYP1A activity in human liver cells.[Pubmed: 24069365]PLoS One. 2013 Sep 19;8(9):e74917.Khellin and Visnagin are two furanochromones that can be frequently found in ethnomedical formulations in Asia and the Middle East. Both compounds possess anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, therefore modern medicine uses these compounds or structurally related derivatives for treatment of vitiligo, bronchial asthma and renal colics. Despite their frequent usage, the potential toxic properties of Visnagin and khellin are not well characterized up-to-now. |
| In vivo | Neuroprotective Effect of Visnagin on Kainic Acid-induced Neuronal Cell Death in the Mice Hippocampus.[Pubmed: 21165322 ]Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010 Oct;14(5):257-63.Visnagin (4-methoxy-7-methyl-5H-furo[3,2-g][1]-benzopyran-5-one), which is an active principle extracted from the fruits of Ammi visnaga, has been used as a treatment for low blood-pressure and blocked blood vessel contraction by inhibition of calcium influx into blood cells. However, the neuroprotective effect of Visnagin was not clearly known until now. Cardiovascular effects of visnagin on rats.[Pubmed: 10705731]Planta Med. 2000 Feb;66(1):35-9.The present article describes the effects of Visnagin on systolic blood pressure and heart rate in the anaesthetized rat. |
| Kinase Assay | Effects of visnagin on cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases and their role in its inhibitory effects on vascular smooth muscle contraction.[Pubmed: 9888257]Anti-inflammatory effect of visnagin in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV-2 microglial cells.[Pubmed: 21116788]Arch Pharm Res. 2010 Nov;33(11):1843-50.Visnagin, which is found in Ammi visnaga, has biological activity as a vasodilator and reduces blood pressure by inhibiting calcium influx into the cell. Gen Pharmacol. 1999 Jan;32(1):71-4.
|
| Cell Research | An aqueous extract of Ammi visnaga fruits and its constituents khellin and visnagin prevent cell damage caused by oxalate in renal epithelial cells。[Reference: WebLink]Phytomedicine. 2010 Jul; 17(0): 653–658.Teas prepared from the fruits of Ammi visnaga L. (syn. “Khella”) have been traditionally used in Egypt as a remedy to treat kidney stones. It was the aim of our study to evaluate the effect of a Khella extract (KE) as well as the two major constituents khellin and Visnagin on renal epithelial injury using LLC-PK1 and Madin-Darby-canine kidney (MDCK) cells. |
| Animal Research | Visnagin protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy through modulation of mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase.[Pubmed: 25504881]Sci Transl Med. 2014 Dec 10;6(266):266ra170.Doxorubicin is a highly effective anticancer chemotherapy agent, but its use is limited by its cardiotoxicity. |

Visnagin Dilution Calculator

Visnagin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.344 mL | 21.7202 mL | 43.4405 mL | 86.881 mL | 108.6012 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8688 mL | 4.344 mL | 8.6881 mL | 17.3762 mL | 21.7202 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4344 mL | 2.172 mL | 4.344 mL | 8.6881 mL | 10.8601 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0869 mL | 0.4344 mL | 0.8688 mL | 1.7376 mL | 2.172 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0434 mL | 0.2172 mL | 0.4344 mL | 0.8688 mL | 1.086 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 1-Amino-2-methylanthraquinone
Catalog No.:BCC8451
CAS No.:82-28-0
- Alpha-Toxicarol
Catalog No.:BCN6467
CAS No.:82-09-7
- Rottlerin
Catalog No.:BCC7127
CAS No.:82-08-6
- Benzanthrone
Catalog No.:BCC8845
CAS No.:82-05-3
- Khellin
Catalog No.:BCN4356
CAS No.:82-02-0
- Lancerin
Catalog No.:BCN2803
CAS No.:81991-99-3
- Vitedoin A
Catalog No.:BCN6741
CAS No.:819861-40-0
- Hyperxanthone E
Catalog No.:BCN8072
CAS No.:819860-76-9
- KW-2478
Catalog No.:BCC2127
CAS No.:819812-04-9
- Clovin
Catalog No.:BCN7817
CAS No.:81970-00-5
- Splendoside
Catalog No.:BCN6647
CAS No.:81969-41-7
- 4(15),5,10(14)-Germacratrien-1-ol
Catalog No.:BCN4354
CAS No.:81968-62-9
- Peri acid
Catalog No.:BCC9116
CAS No.:82-75-7
- 8-Anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8785
CAS No.:82-76-8
- Daurichromenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4355
CAS No.:82003-90-5
- 10Z-Hymenialdisine
Catalog No.:BCC5773
CAS No.:82005-12-7
- Boc-Leucinol
Catalog No.:BCC2724
CAS No.:82010-31-9
- Loteprednol etabonate
Catalog No.:BCC4916
CAS No.:82034-46-6
- NSC 33994
Catalog No.:BCC2441
CAS No.:82058-16-0
- JNJ 17203212
Catalog No.:BCC7668
CAS No.:821768-06-3
- CMK
Catalog No.:BCC1489
CAS No.:821794-90-5
- FMK
Catalog No.:BCC1580
CAS No.:821794-92-7
- Andropanoside
Catalog No.:BCN4570
CAS No.:82209-72-1
- Andrographiside
Catalog No.:BCN4569
CAS No.:82209-76-5
Khellin and visnagin differentially modulate AHR signaling and downstream CYP1A activity in human liver cells.[Pubmed:24069365]
PLoS One. 2013 Sep 19;8(9):e74917.
Khellin and Visnagin are two furanochromones that can be frequently found in ethnomedical formulations in Asia and the Middle East. Both compounds possess anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, therefore modern medicine uses these compounds or structurally related derivatives for treatment of vitiligo, bronchial asthma and renal colics. Despite their frequent usage, the potential toxic properties of Visnagin and khellin are not well characterized up-to-now. Many natural compounds modulate the expression and activity of cytochrome P450 1A1 (CYP1A1), which is well-known to bioactivate pro-carcinogens. The expression of this enzyme is controlled by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR), a ligand-activated transcription factor and regulator of drug metabolism. Here, we investigated the influence of both furanochromones on AHR signaling in human HepG2 hepatocarcinoma cells and primary human hepatocytes. Both compounds transactivated xenobiotic response element (XRE)-driven reporter gene activity in a dose-dependent manner and induced CYP1A1 transcription in HepG2 cells and primary hepatocytes. The latter was abolished in presence of a specific AHR antagonist. CYP1A enzyme activity assays done in HepG2 cells and primary hepatocytes revealed an inhibition of enzyme activity by both furanochromones, which may become relevant regarding the metabolism of xenobiotics and co-administered therapeutic drugs. The observed induction of several other members of the AHR gene battery, whose gene products are involved in regulation of cell growth, differentiation and migration, indicates that a further toxicological characterization of Visnagin and khelllin is urgently required in order to minimize potential drug-drug interactions and other toxic side-effects that may occur during therapeutic usage of these furanochromones.
Anti-inflammatory effect of visnagin in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV-2 microglial cells.[Pubmed:21116788]
Arch Pharm Res. 2010 Nov;33(11):1843-50.
Visnagin, which is found in Ammi visnaga, has biological activity as a vasodilator and reduces blood pressure by inhibiting calcium influx into the cell. The present study demonstrates the anti-inflammatory effect of Visnagin on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated BV-2 microglial cells. When cells were treated with Visnagin prior to LPS stimulation, production of nitric oxide and expression of iNOS were attenuated in a dose-dependent manner. Visnagin also caused a significant decrease of mRNA expression and release of TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and IFNgamma. In addition, Visnagin reduced LPS-induced IL-6 and MCP-1 mRNA level. We further found that Visnagin dose-dependently inhibited LPS-induced AP-1 and NF-kappaB luciferase activities. Taken together, our results for the first time suggest that the anti-inflammatory effect of Visnagin might result from the inhibition of transcription factors, such as AP-1 and NF-kappaB.
Neuroprotective Effect of Visnagin on Kainic Acid-induced Neuronal Cell Death in the Mice Hippocampus.[Pubmed:21165322]
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010 Oct;14(5):257-63.
Visnagin (4-methoxy-7-methyl-5H-furo[3,2-g][1]-benzopyran-5-one), which is an active principle extracted from the fruits of Ammi visnaga, has been used as a treatment for low blood-pressure and blocked blood vessel contraction by inhibition of calcium influx into blood cells. However, the neuroprotective effect of Visnagin was not clearly known until now. Thus, we investigated whether Visnagin has a neuroprotective effect against kainic acid (KA)-induced neuronal cell death. In the cresyl violet staining, pre-treatment or post-treatment Visnagin (100 mg/kg, p.o. or i.p.) showed a neuroprotective effect on KA (0.1 microg) toxicity. KA-induced gliosis and proinflammatory marker (IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, IL-6, and COX-2) inductions were also suppressed by Visnagin administration. These results suggest that Visnagin has a neuroprotective effect in terms of suppressing KA-induced pathogenesis in the brain, and that these neuroprotective effects are associated with its anti-inflammatory effects.
Visnagin protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy through modulation of mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase.[Pubmed:25504881]
Sci Transl Med. 2014 Dec 10;6(266):266ra170.
Doxorubicin is a highly effective anticancer chemotherapy agent, but its use is limited by its cardiotoxicity. To develop a drug that prevents this toxicity, we established a doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy model in zebrafish that recapitulates the cardiomyocyte apoptosis and contractility decline observed in patients. Using this model, we screened 3000 compounds and found that Visnagin (VIS) and diphenylurea (DPU) rescue the cardiac performance and circulatory defects caused by doxorubicin in zebrafish. VIS and DPU reduced doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in cultured cardiomyocytes and in vivo in zebrafish and mouse hearts. VIS treatment improved cardiac contractility in doxorubicin-treated mice. Further, VIS and DPU did not reduce the chemotherapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin in several cultured tumor lines or in zebrafish and mouse xenograft models. Using affinity chromatography, we found that VIS binds to mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase (MDH2), a key enzyme in the tricarboxylic acid cycle. As with VIS, treatment with the MDH2 inhibitors mebendazole, thyroxine, and iodine prevented doxorubicin cardiotoxicity, as did treatment with malate itself, suggesting that modulation of MDH2 activity is responsible for VIS' cardioprotective effects. Thus, VIS and DPU are potent cardioprotective compounds, and MDH2 is a previously undescribed, druggable target for doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy.
Effects of visnagin on cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases and their role in its inhibitory effects on vascular smooth muscle contraction.[Pubmed:9888257]
Gen Pharmacol. 1999 Jan;32(1):71-4.
1. Visnagin relaxed aortae previously contracted by noradrenaline. This effect was unalterated by endothelium removal and potentiated, at high concentrations, by the previous incubation with sodium nitroprusside. 2. Visnagin weakly inhibited the hydrolytic activity of the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) isozymes (PDE5, PDE4, PDE3, cyclic GMP activated PDE2 and PDE1). 3. The present results indicate an involvement of PDE inhibition in the relaxant effect of Visnagin at high concentration (>5x10(-5) M).
Cardiovascular effects of visnagin on rats.[Pubmed:10705731]
Planta Med. 2000 Feb;66(1):35-9.
The present article describes the effects of Visnagin on systolic blood pressure and heart rate in the anaesthetized rat. Intravenous administration of Visnagin (0.3-5 mg kg-1) produced dose-related decreases in blood pressure with no significative changes in heart rate. Under nitric oxide synthase inhibition (L-NAME, 50 mg kg-1) the hypotensive effects of Visnagin (5 mg kg-1) were not affected. Visnagin (5 x 10(-6) M-10(-4) M) produced a weak decrease in the rate and amplitude of spontaneous contractions in right atria. Visnagin also caused a weak decrease in peak contractile force and the df/dtmax with no significant changes in the time to peak tension or the time for total contraction in left atria driven at a basal rate of 1 Hz. Visnagin (10(-5) M, 5 x 10(-5) M and 10(-4) M) concentration-dependently decreased pressor response to KCl (IC50 = 5.1 +/- 2.5 x 10(-5) M) and noradrenaline (IC50 = 2.6 +/- 0.9 x 10(-5) M) in rat isolated mesenteric beds. Visnagin (3 x 10(-7) M-10(-4) M) induced a concentration-dependent relaxation of isolated mesenteric arteries contracted by noradrenaline (IC50 = 1.7 +/- 0.8 x 10(-5) M). The relaxant effects in the absence of functional endothelium were not significantly different (IC50 = 1.5 +/- 0.3 x 10(-5) M, P > 0.05) from those observed in segments with intact endothelium. In conclusion, the main mechanism responsible for the acute hypotensive effect of Visnagin is the vasorelaxant response induced by this drug in resistance arteries.


