IcaritinCAS# 118525-40-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 118525-40-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5318980 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
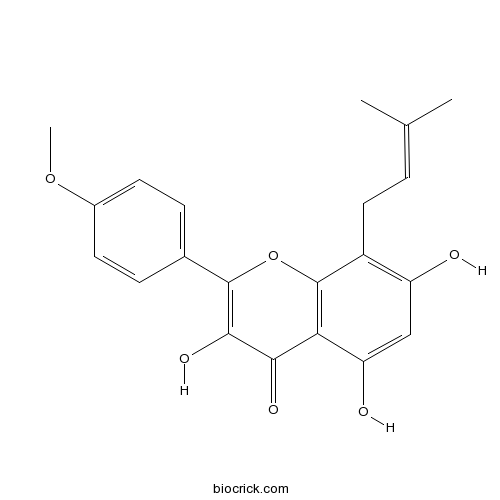
| Formula | C21H20O6 | M.Wt | 368.38 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Anhydroicaritin | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 14 mg/mL (38.00 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) | ||
| Chemical Name | 3,5,7-trihydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-8-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)chromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | CC(=CCC1=C(C=C(C2=C1OC(=C(C2=O)O)C3=CC=C(C=C3)OC)O)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | TUUXBSASAQJECY-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H20O6/c1-11(2)4-9-14-15(22)10-16(23)17-18(24)19(25)20(27-21(14)17)12-5-7-13(26-3)8-6-12/h4-8,10,22-23,25H,9H2,1-3H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Icaritin, a potent inhibitor of transcription factor SREBPs, which exhibits a variety of biological activities, such as activation of cancer cell apoptosis and inhibition of growth, hormone regulation, protection against beta amyloid-induced neurotoxicity, and promotion of neuronal and cardiac cellular differentiation. Icaritin shows potent anti-leukemia activity on chronic myeloid leukemia in vitro and in vivo by regulating MAPK/ERK/JNK and JAK2/STAT3 /AKT signalings. |
| Targets | IL Receptor | JAK | STAT | Bcl-2/Bax | Caspase | Estrogen receptor | JNK | ERK | Akt | p38MAPK | Bcr-Abl | Beta Amyloid | Progestogen receptor |
| In vitro | Icaritin suppresses multiple myeloma, by inhibiting IL-6/JAK2/STAT3.[Pubmed: 25865044]Oncotarget. 2015 Apr 30;6(12):10460-72.Icaritin is an active prenylflavonoid derived from Epimedium genus, a traditional Chinese medicine. Icaritin has a wide range of pharmacological and biological activities, including cardiovascular function improvement, hormone regulation and antitumor activity. Proliferation-stimulating effects of icaritin and desmethylicaritin in MCF-7 cells.[Pubmed: 15541416 ]Eur J Pharmacol. 2004 Nov 19;504(3):147-53.Icariin, Icaritin and desmethylIcaritin are constituents of Epimedium with a similar structure to genistein and daidzein. Synergistic inhibitory effect of Icariside II with Icaritin from Herba Epimedii on pre-osteoclastic RAW264.7 cell growth.[Pubmed: 25442270]Phytomedicine. 2014 Oct 15;21(12):1633-7.Increasing evidence shows the therapeutic superiority of herbal extracts in comparison to isolated single constituents. One of the reasons may be attributed to the synergy effect of compound combinations. Flavonoids from Herba Epimedii have been shown to have therapeutic effect against bone loss. Our previous study showed that Icariside II inhibited pre-osteoclast RAW264.7 growth. The aim of this study was to investigate whether the activity of Icariside II is synergized by other components of Herba Epimedii. |
| Kinase Assay | Neuroprotective effects of icaritin against beta amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in primary cultured rat neuronal cells via estrogen-dependent pathway.[Pubmed: 17321691]Anticancer agent icaritin induces apoptosis through caspase-dependent pathways in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.[Pubmed: 25434584 ]Mol Med Rep. 2015 Apr;11(4):3094-100.
Icaritin is an active ingredient derived from the plant Herba epimedium, which exhibits various pharmacological and biological activities. However, the function, and the underlying mechanisms of Icaritin on the growth of SMMC‑7721 human hepatoma cells have yet to be elucidated. Neuroscience. 2007 Mar 30;145(3):911-22.Beta-amyloid protein (Abeta) is the hallmark of pathogenic neurotoxins which contribute greatly to Alzheimer's disease (AD)-associated cascade including severe neuronal loss. |
| Cell Research | Icaritin shows potent anti-leukemia activity on chronic myeloid leukemia in vitro and in vivo by regulating MAPK/ERK/JNK and JAK2/STAT3 /AKT signalings.[Pubmed: 21887305]A study on the effect of icaritin on rat chondrocytes.[Pubmed: 26032072]Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2015 May;40(5):517-21.To investigate the eff ect of Icaritin on proliferation and apoptosis in rat chondrocytes and to provide new theory for osteochondropathy treatment.
PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23720.To explore the effects of Icaritin on chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cells and underlying mechanisms.
|

Icaritin Dilution Calculator

Icaritin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7146 mL | 13.5729 mL | 27.1459 mL | 54.2918 mL | 67.8647 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5429 mL | 2.7146 mL | 5.4292 mL | 10.8584 mL | 13.5729 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2715 mL | 1.3573 mL | 2.7146 mL | 5.4292 mL | 6.7865 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0543 mL | 0.2715 mL | 0.5429 mL | 1.0858 mL | 1.3573 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0271 mL | 0.1357 mL | 0.2715 mL | 0.5429 mL | 0.6786 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Icaritin(Anhydroicaritin) is a component of Epimedium flavonoid isolated from Herba Epimedii; enhances osteoblastic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) while it inhibits adipogenic differentiation of MSCs by inhibiting PPAR-g pathway. IC50 value: Target: in vitro: Icaritin was unable to promote proliferation, migration and tube like structure formation by human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) in vitro [1]. Icaritin potently inhibited proliferation of K562 cells (IC50 was 8 μM) and primary CML cells (IC50 was 13.4 μM for CML-CP and 18 μM for CML-BC), induced CML cells apoptosis and promoted the erythroid differentiation of K562 cells with time-dependent manner. Furthermore, Icaritin was able to suppress the growth of primary CD34+ leukemia cells (CML) and Imatinib-resistant cells, and to induce apoptosis [2]. icaritin strongly inhibited the growth of breast cancer MDA-MB-453 and MCF7 cells. At concentrations of 2-3 μM, icaritin induced cell cycle arrest at the G(2)/M phase accompanied by a down-regulation of the expression levels of the G(2)/M regulatory proteins such as cyclinB, cdc2 and cdc25C. Icaritin at concentrations of 4-5 μM, however, induced apoptotic cell death characterized by the accumulation of the annexin V- and propidium iodide-positive cells, cleavage of poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) and down-regulation of the Bcl-2 expression [3]. in vivo: In mouse leukemia model, Icaritin could prolong lifespan of NOD-SCID nude mice inoculated with K562 cells as effective as Imatinib without suppression of bone marrow. Icaritin could up-regulate phospho-JNK or phospho-C-Jun and down-regulate phospho-ERK, phospho-P-38, Jak-2, phospho-Stat3 and phospho-Akt expression with dose- or time-dependent manner [2].
References:
[1]. Yao D, et al. Icaritin, an exogenous phytomolecule, enhances osteogenesis but not angiogenesis--an in vitro efficacy study. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e41264.
[2]. Zhu Jf, et al. Icaritin shows potent anti-leukemia activity on chronic myeloid leukemia in vitro and in vivo by regulating MAPK/ERK/JNK and JAK2/STAT3 /AKT signalings. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23720.
[3]. Guo Y, et al. An anticancer agent icaritin induces sustained activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway and inhibits growth of breast cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 May 11;658(2-3):114-22.
- Sagittatoside C
Catalog No.:BCN3059
CAS No.:118525-37-4
- Sagittatoside B
Catalog No.:BCN2357
CAS No.:118525-36-3
- Sagittatoside A
Catalog No.:BCN2285
CAS No.:118525-35-2
- DPPE fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC5669
CAS No.:1185241-83-1
- LP 12 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7517
CAS No.:1185136-22-4
- Myelin Basic Protein (87-99)
Catalog No.:BCC1028
CAS No.:118506-26-6
- TRIS hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7589
CAS No.:1185-53-1
- 5,7-Dichlorokynurenic acid sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7758
CAS No.:1184986-70-6
- Fmoc-D-Tyr(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3569
CAS No.:118488-18-9
- Cyclo(L-Phe-trans-4-hydroxy-L-Pro)
Catalog No.:BCN3989
CAS No.:118477-06-8
- Arcyriaflavin A
Catalog No.:BCC7370
CAS No.:118458-54-1
- Licoricesaponin G2
Catalog No.:BCN7897
CAS No.:118441-84-2
- Baohuoside V
Catalog No.:BCN2887
CAS No.:118544-18-6
- H-Orn(2-Cl-Z)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3002
CAS No.:118553-99-4
- Boc-Orn(2-Cl-Z)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3428
CAS No.:118554-00-0
- Phaseoloidin
Catalog No.:BCN8451
CAS No.:118555-82-1
- Floribundone 1
Catalog No.:BCN4726
CAS No.:118555-84-3
- Zileuton sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4216
CAS No.:118569-21-4
- NVP-BVU972
Catalog No.:BCC3828
CAS No.:1185763-69-2
- VD3-D6
Catalog No.:BCC4076
CAS No.:118584-54-6
- Vitexdoin A
Catalog No.:BCN4089
CAS No.:1186021-77-1
- BU 226 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6936
CAS No.:1186195-56-1
- Tocrifluor T1117
Catalog No.:BCC7401
CAS No.:1186195-59-4
- MTEP hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1780
CAS No.:1186195-60-7
Anticancer agent icaritin induces apoptosis through caspase-dependent pathways in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.[Pubmed:25434584]
Mol Med Rep. 2015 Apr;11(4):3094-100.
Icaritin is an active ingredient derived from the plant Herba epimedium, which exhibits various pharmacological and biological activities. However, the function, and the underlying mechanisms of Icaritin on the growth of SMMC7721 human hepatoma cells have yet to be elucidated. The present study aimed to investigate the function and underlying mechanisms of Icaritin in the growth of SMMC7721 cells. The cells were treated with varying concentrations of Icaritin for 12, 24 and 48 h, respectively, prior to cytotoxic analysis. Apoptosis of SMMC7721 cells following treatment with Icaritin was measured using flow cytometry. The gene expression of mitochondria and Fasmediated caspasedependent pathways was detected by reverse transcriptionquantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blotting. Statistical analysis was performed by Student's ttest and oneway analysis or variance. The present study demonstrated that treatment with Icaritin significantly inhibited growth, and induced apoptosis of SMMC7721 cells, in a time and dosedependent manner. In addition, Icaritin triggered the mitochondrial/caspase apoptotic pathway, by decreasing the Bcl2/Bax protein ratio and increasing activation of caspase3. Icaritin also activated the Fasmediated apoptosis pathway, as was evident by the increased expression levels of Fas and activation of caspase8. These data suggest that Icaritin may be a potent growth inhibitor and induce apoptosis of SMMC7721 cells through the mitochondria and Fasmediated caspasedependent pathways. The present study may provide experimental evidence for preclinical and clinical evaluations of Icaritin for HCC therapy.
Proliferation-stimulating effects of icaritin and desmethylicaritin in MCF-7 cells.[Pubmed:15541416]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2004 Nov 19;504(3):147-53.
Icariin, Icaritin and desmethylIcaritin are constituents of Epimedium with a similar structure to genistein and daidzein. Using the modified MCF-7 cell proliferation assay (E-SCREEN assessment system), these compounds were tested for their estrogen-like activities. Icaritin and desmethylIcaritin, but not icariin, strongly stimulated the proliferation of MCF-7/BUS cells. Cell cycle analysis revealed that the proliferation stimulatory effect was associated with a marked increase in the number of MCF-7/BUS cells in S phase and a significant increase in the G2/M population, with effects similar to those of estradiol. These actions were dose dependent (range from 1 nM to 10 microM) and could be significantly inhibited by the specific estrogen receptor antagonist ICI 182,780 [7 alpha-[9(4,4,5,5,5-pentafluoropentyl)sulfinyl]nonyl)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17b eta-diol)]. The estrogen receptor-regulated progesterone receptor and PS2 mRNA levels were increased by treatment with Icaritin or desmethylIcaritin within 24 h and the effects were also reversed by ICI 182,780. It was concluded that Icaritin and desmethylIcaritin are novel phytoestrogens and that the estrogenic effects of Icaritin and desmethylIcaritin are mediated by the estrogen receptor.
[A study on the effect of icaritin on rat chondrocytes].[Pubmed:26032072]
Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2015 May;40(5):517-21.
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the eff ect of Icaritin on proliferation and apoptosis in rat chondrocytes and to provide new theory for osteochondropathy treatment. METHODS: Icaritin (with a purity of 99%) at different concentrations (0, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 mumol/L) was incubated with rat chondrocytes for different time. The cell proliferation and apoptosis was assayed by MTT and fl ow cytometry, respectively. RESULTS: Compared with the control group, the cell proliferation was increased in the groups with Icaritin at 4 or 8 mumol/L (P<0.05), whereas the proliferation was decreased in the groups with Icaritin at 16, 32 or 64 mumol/L groups compared to the control group (P<0.05); the cell apoptosis ratio in the group with Icaritin at 4 mumol/L was obviously lower than that in the control group aft er incubation of Icaritin for 24 h and 48 h. Beyond 4 mumol/L, the higher concentration of Icaritin, the higher apoptosis ratio of cell. However, it did not show a time-dependent manner at a same concentration of Icaritin. CONCLUSION: The Icaritin at low concentration (4 or 8 mumol/L) can promote rat chondrocyte proliferation and inhibit cell apoptosis, while the effect of Icaritin on rat chondrocyte at high concentration was reversed.
Icaritin shows potent anti-leukemia activity on chronic myeloid leukemia in vitro and in vivo by regulating MAPK/ERK/JNK and JAK2/STAT3 /AKT signalings.[Pubmed:21887305]
PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23720.
PURPOSE: To explore the effects of Icaritin on chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cells and underlying mechanisms. METHOD: CML cells were incubated with various concentration of Icaritin for 48 hours, the cell proliferation was analyzed by MTT and the apoptosis was assessed with Annexin V and Hoechst 33258 staining. Cell hemoglobinization was determined. Western blotting was used to evaluate the expressions of MAPK/ERK/JNK signal pathway and Jak-2/Phorpho-Stat3/Phorsph-Akt network-related protein. NOD-SCID nude mice were applied to demonstrate the anti-leukemia effect of Icaritin in vivo. RESULTS: Icaritin potently inhibited proliferation of K562 cells (IC50 was 8 microM) and primary CML cells (IC50 was 13.4 microM for CML-CP and 18 microM for CML-BC), induced CML cells apoptosis and promoted the erythroid differentiation of K562 cells with time-dependent manner. Furthermore, Icaritin was able to suppress the growth of primary CD34+ leukemia cells (CML) and Imatinib-resistant cells, and to induce apoptosis. In mouse leukemia model, Icaritin could prolong lifespan of NOD-SCID nude mice inoculated with K562 cells as effective as Imatinib without suppression of bone marrow. Icaritin could up-regulate phospho-JNK or phospho-C-Jun and down-regulate phospho-ERK, phospho-P-38, Jak-2, phospho-Stat3 and phospho-Akt expression with dose- or time-dependent manner. Icaritin had no influence both on c-Abl and phospho-c-Abl protein expression and mRNA levels of Bcr/Abl. CONCLUSION: Icaritin from Chinese herb medicine may be a potential anti-CML agent with low adverse effect. The mechanism of anti-leukemia for Icaritin is involved in the regulation of Bcr/Abl downstream signaling. Icaritin may be useful for an alternative therapeutic choice of Imatinib-resistant forms of CML.
Neuroprotective effects of icaritin against beta amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in primary cultured rat neuronal cells via estrogen-dependent pathway.[Pubmed:17321691]
Neuroscience. 2007 Mar 30;145(3):911-22.
Beta-amyloid protein (Abeta) is the hallmark of pathogenic neurotoxins which contribute greatly to Alzheimer's disease (AD)-associated cascade including severe neuronal loss. In present study, Icaritin, an active natural ingredient from a Chinese plant, Epimedium sagittatum maxim, was investigated to assess its neuroprotective effect against the toxicity induced with Abeta(25-35) in primary cultured rat cortical neuronal cells as well as the underlying mechanisms. Abeta(25-35) induced neuronal toxicity, characterized by decreased cell viability, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release, and neuronal DNA condensation, which is associated with both the loss of membrane potential and the alteration of the expression of Bcl-2 family proteins. The phenotype alternation induced by Abeta(25-35) could be reversed by Icaritin. Furthermore, the neuroprotective effects of Icaritin mentioned above were estrogen receptor dependent due to the blocking action induced by estrogen receptor antagonist ICI 182,780 and well matched binding affinity with estrogen receptor by a receptor-ligand docking experiment. mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase inhibitor PD98059 weakened the protective effects, which implied mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway may also be involved in and partly contributed to the neuroprotective effects of Icaritin.
Synergistic inhibitory effect of Icariside II with Icaritin from Herba Epimedii on pre-osteoclastic RAW264.7 cell growth.[Pubmed:25442270]
Phytomedicine. 2014 Oct 15;21(12):1633-7.
Increasing evidence shows the therapeutic superiority of herbal extracts in comparison to isolated single constituents. One of the reasons may be attributed to the synergy effect of compound combinations. Flavonoids from Herba Epimedii have been shown to have therapeutic effect against bone loss. Our previous study showed that Icariside II inhibited pre-osteoclast RAW264.7 growth. The aim of this study was to investigate whether the activity of Icariside II is synergized by other components of Herba Epimedii. The inhibitory activity of Icariside II was significantly enhanced in the presence of the extract of Herba Epimedii (EHE) at the ratio of 1:1, 1:5 and 1:10. Icaritin, another flavonoid constituent, was shown here to inhibit RAW264.7 growth in a dose-dependent manner. Further, we found that Icariside II, together with Icaritin, synergistically inhibited RAW264.7 growth. The synergistic effect is significant when the ratio of Icariside II and Icaritin was 10:1, 5:1, 1:1, 1:2, and 1:5, respectively. In conclusion, Icaritin were an active component. The inhibitory activity of Icariside II on pre-osteoclast RAW264.7 growth was synergized by Icaritin, which maybe contribute to the efficiency of Herba Epimedii extract on curing bone-related diseases, such as osteoporosis.
Icaritin suppresses multiple myeloma, by inhibiting IL-6/JAK2/STAT3.[Pubmed:25865044]
Oncotarget. 2015 Apr 30;6(12):10460-72.
Icaritin is an active prenylflavonoid derived from Epimedium genus, a traditional Chinese medicine. Icaritin has a wide range of pharmacological and biological activities, including cardiovascular function improvement, hormone regulation and antitumor activity. Here, we investigated the effect of Icaritin on multiple myeloma (MM) in vitro and in vivo. Icaritin inhibited cell growth of MM cell line and primary MM cells. In contrast, Icaritin had low or no cytotoxic effect on normal hematopoiesis. We also demonstrated that in MM xenograft mouse models, Icaritin suppressed tumor growth and decreased serum IL-6 and IgE levels, but did not show adverse reactions such as body weight loss. The anti-MM activity of Icaritin was mainly mediated by inhibiting IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling. We suggest that Icaritin can be further tested in clinical trials in MM.


