Myelin Basic Protein (87-99)Encephalitogenic peptide CAS# 118506-26-6 |
- Amyloid β-Protein (1-15)
Catalog No.:BCC1003
CAS No.:183745-81-5
- Beta-Amyloid (1-11)
Catalog No.:BCC1002
CAS No.:190436-05-6
- Myelin Basic Protein (68-82), guinea pig
Catalog No.:BCC1020
CAS No.:98474-59-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 118506-26-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 71581453 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C74H114N20O17 | M.Wt | 1555.8 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 2 mg/ml in water | ||
| Sequence | VHFFKNIVTPRTP | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-1-[(2S,3R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-1-[(2S,3R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S,3S)-2-[[(2S)-4-amino-2-[[6-amino-2-[[(2S)-2-[[2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-amino-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]hexanoyl]amino]-4-oxobutanoyl]amino]-3-methylpentanoyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino]-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCC(C)C(C(=O)NC(C(C)C)C(=O)NC(C(C)O)C(=O)N1CCCC1C(=O)NC(CCCN=C(N)N)C(=O)NC(C(C)O)C(=O)N2CCCC2C(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CCCCN)NC(=O)C(CC3=CC=CC=C3)NC(=O)C(CC4=CC=CC=C4)NC(=O)C(CC5=CN=CN5)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XSSZRUKIAIQNAZ-UNBJHMBOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C74H114N20O17/c1-9-41(6)58(70(107)89-57(40(4)5)69(106)92-60(43(8)96)71(108)93-31-19-27-53(93)67(104)84-48(26-18-30-81-74(78)79)62(99)91-59(42(7)95)72(109)94-32-20-28-54(94)73(110)111)90-66(103)52(36-55(76)97)87-61(98)47(25-16-17-29-75)83-63(100)49(33-44-21-12-10-13-22-44)85-64(101)50(34-45-23-14-11-15-24-45)86-65(102)51(35-46-37-80-38-82-46)88-68(105)56(77)39(2)3/h10-15,21-24,37-43,47-54,56-60,95-96H,9,16-20,25-36,75,77H2,1-8H3,(H2,76,97)(H,80,82)(H,83,100)(H,84,104)(H,85,101)(H,86,102)(H,87,98)(H,88,105)(H,89,107)(H,90,103)(H,91,99)(H,92,106)(H,110,111)(H4,78,79,81)/t41-,42+,43+,47?,48-,49-,50?,51?,52-,53-,54-,56-,57-,58-,59-,60-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Encephalitogenic peptide that induces T cell proliferation with Th1 polarization in the CNS. Major antigenic component implicated in the pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis. |

Myelin Basic Protein (87-99) Dilution Calculator

Myelin Basic Protein (87-99) Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
The basic protein is a major structural protein of the central nervous system myelin in which it constitutes 30% of the total protein.(1)
T lymphocyte cell lines selected with whole MBP typically recognize only 1-3 immunodominant epitopes (Offner et al., 1987, 1988; Trotter et al., 1987: Bourdctte et al., 1988; McCarron and McFarlin, 1988) and these immunodominant MBP epitopes frequently are cncephalitogenic (Vandenbark et al., 1985b, 1989; Hashim et al., 1991). Thus, the identification of immunodominant MBP epitopes is likely to provide an in vitro method of identifying unrecognized enccphalitogenic epitopes of MBP. (2)
Although the cause of multiple sclerosis (MS) is not known, a T cell-mediated autoimmune process has been postulated. Myelin basic protein (MBP) is a potential target antigen because it induces experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) in susceptible animals. Encephalitogenic epitopes of MBP differ among susceptible strains and correlate with the MHC class II genotype. (3)
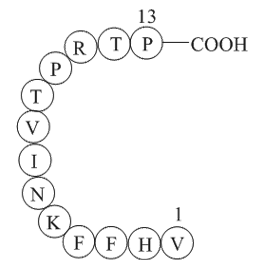
Figure1. Structure of Myelin Basic Protein
Figure2. Formula of Myelin Basic Protein (87-99)
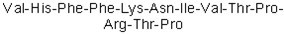
Ref:
1. EYLAR, E. H., in L.Rowland (Editor), Immunologic disorders of the nervous system, Academic Press, New York, 1971, Chapter 5.
2. Jones et al (1992) the synthetic 87-99 peptide of myelin basic protein is encelphalitogenic in Buffalo rats. J.Neuroimmunol. 37 203
3. Fritz, R., and D.E. McFarlin . 1989. Encephalitogenic epitopes 10. Richert, J., E.D. Robinson, G.E . Deibler, R.E. Martenson, of myelin basic protein. Chem. Immunol. 46:101.
- TRIS hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7589
CAS No.:1185-53-1
- 5,7-Dichlorokynurenic acid sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7758
CAS No.:1184986-70-6
- Fmoc-D-Tyr(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3569
CAS No.:118488-18-9
- Cyclo(L-Phe-trans-4-hydroxy-L-Pro)
Catalog No.:BCN3989
CAS No.:118477-06-8
- Arcyriaflavin A
Catalog No.:BCC7370
CAS No.:118458-54-1
- Licoricesaponin G2
Catalog No.:BCN7897
CAS No.:118441-84-2
- MK 886
Catalog No.:BCC7017
CAS No.:118414-82-7
- nTZDpa
Catalog No.:BCC7268
CAS No.:118414-59-8
- UNC 926 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2445
CAS No.:1184136-10-4
- AG-18
Catalog No.:BCC1051
CAS No.:118409-57-7
- Trimethylamine oxide
Catalog No.:BCN1819
CAS No.:1184-78-7
- Australine
Catalog No.:BCN2053
CAS No.:118396-02-4
- LP 12 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7517
CAS No.:1185136-22-4
- DPPE fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC5669
CAS No.:1185241-83-1
- Sagittatoside A
Catalog No.:BCN2285
CAS No.:118525-35-2
- Sagittatoside B
Catalog No.:BCN2357
CAS No.:118525-36-3
- Sagittatoside C
Catalog No.:BCN3059
CAS No.:118525-37-4
- Icaritin
Catalog No.:BCN5352
CAS No.:118525-40-9
- Baohuoside V
Catalog No.:BCN2887
CAS No.:118544-18-6
- H-Orn(2-Cl-Z)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3002
CAS No.:118553-99-4
- Boc-Orn(2-Cl-Z)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3428
CAS No.:118554-00-0
- Phaseoloidin
Catalog No.:BCN8451
CAS No.:118555-82-1
- Floribundone 1
Catalog No.:BCN4726
CAS No.:118555-84-3
- Zileuton sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4216
CAS No.:118569-21-4
Design and synthesis of a novel potent myelin basic protein epitope 87-99 cyclic analogue: enhanced stability and biological properties of mimics render them a potentially new class of immunomodulators.[Pubmed:15743189]
J Med Chem. 2005 Mar 10;48(5):1470-80.
A cyclic analogue, [cyclo(87-99)MBP(87)(-)(99)], of the human immunodominant MBP(87)(-)(99) epitope, was designed based on ROESY/NMR distance information and modeling data for linear epitope 87-99, taking into account T-cell (Phe(89), Lys(91), Pro(96)) and HLA (His(88), Phe(90), Ile(93)) contact side-chain information. The cyclic analogue was found to induce experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE), to bind HLA-DR4, and to increase CD4 T-cell line proliferation, like that of the conformationally related linear MBP(87)(-)(99) epitope peptide. The mutant cyclic peptides, the cyclo(91-99)[Ala(96)]MBP(87)(-)(99) and the cyclo(87-99)[Arg(91)Ala(96)]MBP(87)(-)(99), reported previously for suppressing, to a varying degree, autoimmune encephalomyelitis in a rat animal model, were found in this study to possess the following immunomodulatory properties: (i) they suppressed the proliferation of a CD4 T-cell line raised from a multiple sclerosis patient, (ii) they scored the best in vitro TH2/TH1 cytokine ratio in peripheral blood mononuclear cell cultures derived from 13 multiple sclerosis patients, inducing IL-10 selectively, and (iii) they bound to HLA-DR4, first to be reported for cyclic MBP peptides. In addition, cyclic peptides were found to be more stable to lysosomal enzymes and Cathepsin B, D, and H, compared to their linear counterparts. Taken together, these data render cyclic mimics as putative drugs for treating multiple sclerosis and potentially other Th1-mediated autoimmune diseases.
Molecular dynamics at the receptor level of immunodominant myelin basic protein epitope 87-99 implicated in multiple sclerosis and its antagonists altered peptide ligands: triggering of immune response.[Pubmed:17392002]
J Mol Graph Model. 2007 Sep;26(2):471-81.
This work reports molecular dynamics studies at the receptor level of the immunodominant myelin basic protein (MBP) epitope 87-99 implicated in multiple sclerosis, and its antagonists altered peptide ligands (APLs), namely [Arg91, Ala96] MBP87-99 and [Ala91,96] MBP87-99. The interaction of each peptide ligand with the receptor human leukocyte antigen HLA-DR2b was studied, starting from X-ray structure with pdb code: 1ymm. This is the first such study of APL-HLA-DR2b complexes, and hence the first attempt to gain a better understanding of the molecular recognition mechanisms that underlie TCR antagonism by these APLs. The amino acids His88 and Phe89 serve as T-cell receptor (TCR) anchors in the formation of the trimolecular complex TCR-peptide-HLA-DR2b, where the TCR binds in a diagonal, off-centered mode to the peptide-HLA complex. The present findings indicate that these two amino acids have a different orientation in the APLs [Arg91, Ala96] MBP87-99 and [Ala91,96] MBP87-99: His88 and Phe89 remain buried in HLA grooves and are not available for interaction with the TCR. We propose that this different topology could provide a possible mechanism of action for TCR antagonism.
Citrullination of linear and cyclic altered peptide ligands from myelin basic protein (MBP(87-99)) epitope elicits a Th1 polarized response by T cells isolated from multiple sclerosis patients: implications in triggering disease.[Pubmed:19053745]
J Med Chem. 2008 Dec 25;51(24):7834-42.
Derangement of cellular immunity is central in the pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis (MS) and is often manifested by abnormal cytokine production. We investigated cytokine secretion in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) of 18 MS patients and 15 controls and correlated cytokine polarization with the nature of antigenic stimulus. We synthesized two novel citrullinated peptides, linear [Cit(91), Ala(96), Cit(97)]MBP(87-99) and cyclo(87-99)[Cit(91), Ala(96), Cit(97)]MBP(87-99) that resulted from citrullination of 91,97 Arg residues in antagonists, linear [Arg(91), Ala(96)]MBP(87-99) and cyclo(87-99)[Arg(91), Ala(96)]MBP(87-99) peptides. PBMC from MS patients and controls were cultured with citrullinated peptides, and both peptides caused a Th1 polarization in all MS patients studied. In contrast, culture with noncitrullinated MBP peptides resulted in heterogeneous cytokine secretion that differed between individual patients. Thus, citrullination of self-antigens may potentially trigger disease in susceptible individuals. This finding may open new avenues in drug design of new substances that inhibit citrullination and arrest epitope spreading and worsening of MS.
Comparison of proposed putative active conformations of myelin basic protein epitope 87-99 linear altered peptide ligands by spectroscopic and modelling studies: the role of positions 91 and 96 in T-cell receptor activation.[Pubmed:17154499]
J Med Chem. 2006 Nov 16;49(23):6683-91.
This work proposes a structural motif for the inhibition of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) by the linear altered peptide ligands (APLs) [Ala91,96] MBP87-99 and [Arg91,Ala96] MBP87-99 of myelin basic protein. Molecular dynamics was applied to reveal distinct populations of EAE antagonist [Ala91,96] MBP87-99 in solution, in agreement with NOE data. The combination of the theoretical and experimental results led to the identification of a putative active conformation. This approach is of value as no crystallographic data is available for the APL-receptor complex. TCR contact residue Phe89 has an altered topology in the putative bioactive conformations of both APLs with respect to the native peptide, as found via crystallography; it is no longer prominent and solvent exposed. It is proposed that the antagonistic activity of the APLs is due to their binding to MHC, preventing the binding of self-myelin epitopes, with the absence of an immunologic response as the loss of some interactions with the TCR hinders activation of T-cells.
The synthetic 87-99 peptide of myelin basic protein is encephalitogenic in Buffalo rats.[Pubmed:1373154]
J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Apr;37(3):203-12.
A synthetic peptide corresponding to residues 87-99 (S87-99) of myelin basic protein (BP) induced the proliferation of an encephalitogenic, BP-specific T cell line selected in vitro from inbred Buffalo-strain rats (RT1b). Active immunization with guinea pig (GP)-BP or S87-99 in complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) and intravenous pertussigen induced acute experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) 10-12 days after immunization. Fifty percent of recovered rats developed a single relapse 17-21 days after immunization. T lymphocytes selected in vitro with S87-99 transferred acute, non-relapsing EAE into naive recipients. Histological examination during acute EAE revealed foci of inflammatory cells associated with demyelination in the spinal cords and peripheral nerve roots. Thus, as in several other rodent strains, the 87-99 region of BP is antigenic and encephalitogenic in the inbred Buffalo-strain rat. Additionally, the 87-99 sequence of GP-BP was predicted to be antigenic by two different methods. These results suggest that the 87-99 region of BP, which is highly conserved among mammalian species, may be widely encephalitogenic due to antigen-intrinsic properties.


