Trimethylamine oxideCAS# 1184-78-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1184-78-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 1145 | Appearance | Powder |
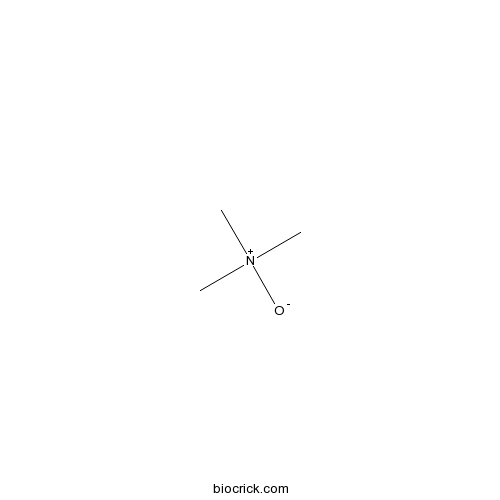
| Formula | C3H9NO | M.Wt | 75.11 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | N,N-dimethylmethanamine oxide | ||
| SMILES | C[N+](C)(C)[O-] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UYPYRKYUKCHHIB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C3H9NO/c1-4(2,3)5/h1-3H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Trimethylamine oxide has a thermo-protective role in these cells, thus eliminating the need for a heat shock response. 2. Trimethylamine oxide can stimulate both the anaerobic growth rate and the growth yield of Proteus NTHC 153 by serving as a terminal electron acceptor in an oxidative phosphorylation process. |
| Targets | HSP (e.g. HSP90) |

Trimethylamine oxide Dilution Calculator

Trimethylamine oxide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 13.3138 mL | 66.569 mL | 133.1381 mL | 266.2761 mL | 332.8452 mL |
| 5 mM | 2.6628 mL | 13.3138 mL | 26.6276 mL | 53.2552 mL | 66.569 mL |
| 10 mM | 1.3314 mL | 6.6569 mL | 13.3138 mL | 26.6276 mL | 33.2845 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.2663 mL | 1.3314 mL | 2.6628 mL | 5.3255 mL | 6.6569 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.1331 mL | 0.6657 mL | 1.3314 mL | 2.6628 mL | 3.3285 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Australine
Catalog No.:BCN2053
CAS No.:118396-02-4
- Licoricesaponin A3
Catalog No.:BCN7905
CAS No.:118325-22-7
- Tazarotene
Catalog No.:BCC2540
CAS No.:118292-40-3
- 6-O-Acetylscandoside
Catalog No.:BCN8320
CAS No.:118292-15-2
- AF-DX 384
Catalog No.:BCC7024
CAS No.:118290-26-9
- Lafutidine
Catalog No.:BCC4544
CAS No.:118288-08-7
- Isodorsmanin A
Catalog No.:BCN6460
CAS No.:118266-99-2
- 1,4-Dicaffeoylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5912
CAS No.:1182-34-9
- Soyasaponin Ab
Catalog No.:BCN2896
CAS No.:118194-13-1
- EMD638683
Catalog No.:BCC1551
CAS No.:1181770-72-8
- 2-Picenecarboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3063
CAS No.:118172-80-8
- 6-Oxo-23-norpristimerol
Catalog No.:BCN8054
CAS No.:118172-79-5
- AG-18
Catalog No.:BCC1051
CAS No.:118409-57-7
- UNC 926 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2445
CAS No.:1184136-10-4
- nTZDpa
Catalog No.:BCC7268
CAS No.:118414-59-8
- MK 886
Catalog No.:BCC7017
CAS No.:118414-82-7
- Licoricesaponin G2
Catalog No.:BCN7897
CAS No.:118441-84-2
- Arcyriaflavin A
Catalog No.:BCC7370
CAS No.:118458-54-1
- Cyclo(L-Phe-trans-4-hydroxy-L-Pro)
Catalog No.:BCN3989
CAS No.:118477-06-8
- Fmoc-D-Tyr(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3569
CAS No.:118488-18-9
- 5,7-Dichlorokynurenic acid sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7758
CAS No.:1184986-70-6
- TRIS hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7589
CAS No.:1185-53-1
- Myelin Basic Protein (87-99)
Catalog No.:BCC1028
CAS No.:118506-26-6
- LP 12 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7517
CAS No.:1185136-22-4
ESR studies on the thermal decomposition of trimethylamine oxide to formaldehyde and dimethylamine in jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) extract.[Pubmed:23993561]
Food Chem. 2013 Dec 15;141(4):3881-8.
The effects of ferrous iron, heating temperature and different additives on the decomposition of Trimethylamine oxide (TMAO) to formaldehyde (FA) and dimethylamine (DMA) and generation of free radicals in jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) extract during heating were evaluated by electron spin resonance (ESR). The thermal decomposition of TMAO to TMA, DMA and FA and free radical signals was observed in squid extract, whereas no DMA, FA and free radical signals were detected in cod extract or in aqueous TMAO solution in vitro at high temperatures. Significant increase in levels of DMA, FA and radicals intensity were observed in squid extract and TMAO solution in the presence of ferrous iron with increasing temperature. Hydrogen peroxide stimulated the production of DMA, FA and ESR signals in squid extract, while citric acid, trisodium citrate, calcium chloride, tea polyphenols and resveratrol had the opposite effect. Similar ESR spectra of six peaks regarded as amminium radical were detected in the squid extract and TMAO-iron(II) solution, suggesting that the amminium radical was involved in the decomposition of TMAO.
Coordination of chemical (trimethylamine oxide) and molecular (heat shock protein 70) chaperone responses to heat stress in elasmobranch red blood cells.[Pubmed:25244377]
Physiol Biochem Zool. 2014 Sep-Oct;87(5):652-62.
Chemical and molecular chaperones are organic compounds that protect and stabilize proteins from damage and aggregation as a result of cellular stress. Using the dogfish (Squalus acanthias) red blood cell (RBC) as a model, we examined whether elasmobranch cells with naturally high concentrations of the chemical chaperone Trimethylamine oxide (TMAO) would induce the molecular chaperone heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) when exposed to an acute thermal stress. Our hypothesis was that TMAO is itself capable of preventing damage and preserving cellular function during thermal stress and thus that the heat shock response would be inhibited/diminished. We incubated RBCs in vitro with and without physiologically relevant concentrations of TMAO at 13 degrees C and then exposed cells to a 1-h acute heat shock at 24 degrees C. HSP70 protein expression was elevated in dogfish RBCs after the acute heat stress, but this induction was inhibited by extracellular TMAO. Regardless of the presence of TMAO and/or HSP70, we did not observe any cell damage, as indicated by changes in caspase 3/7 activity, protein carbonyls, membrane viability, or levels of ubiquitin. We also saw no change in RBC cell function, as determined by hemoglobin oxygen affinity or carrying capacity, in cells lacking the heat shock response but protected by TMAO. This study demonstrates that there is cellular coordination between chemical and molecular chaperones in response to an acute thermal stress in dogfish RBCs and suggests that TMAO has a thermoprotective role in these cells, thus eliminating the need for a heat shock response.
Trimethylamine oxide: a terminal electron acceptor in anaerobic respiration of bacteria.[Pubmed:479836]
J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Jun;112(2):315-20.
Trimethylamine oxide (TMAO) stimulated both the anaerobic growth rate and the growth yield of Proteus NTHC 153. The molar growth yield from glucose and pyruvate in tryptone/yeast extract medium doubled in the presence of TMAO, and the organism grew anaerobically on the non-fermentable substrates L-lactate and formate when TMAO was added to the medium. We conclude that TMAO stimulated growth by serving as a terminal electron acceptor in an oxidative phosphorylation process.


