Soyasaponin AbCAS# 118194-13-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 118194-13-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 102004833 | Appearance | Powder |
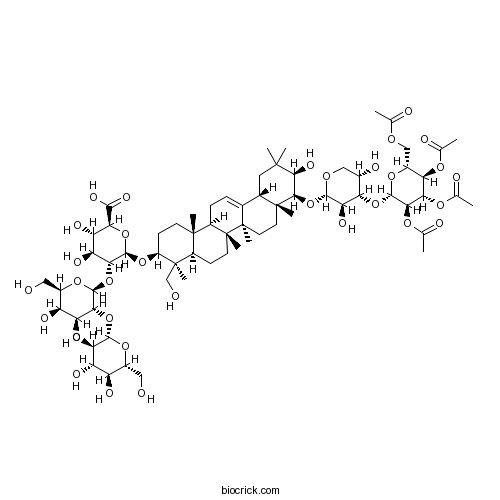
| Formula | C67H104O33 | M.Wt | 1437.6 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S,3S,4S,5R,6R)-6-[[(3S,4S,4aR,6aR,6bS,8aR,9S,10R,12aS,14aR,14bR)-9-[(2S,3R,4S,5S)-3,5-dihydroxy-4-[(2S,3R,4S,5R,6R)-3,4,5-triacetyloxy-6-(acetyloxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-10-hydroxy-4-(hydroxymethyl)-4,6a,6b,8a,11,11,14b-heptamethyl-1,2,3,4a,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,12a,14,14a-tetradecahydropicen-3-yl]oxy]-5-[(2S,3R,4S,5R,6R)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-3,4-dihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(=O)OCC1C(C(C(C(O1)OC2C(COC(C2O)OC3C(C(CC4C3(CCC5(C4=CCC6C5(CCC7C6(CCC(C7(C)CO)OC8C(C(C(C(O8)C(=O)O)O)O)OC9C(C(C(C(O9)CO)O)O)OC1C(C(C(C(O1)CO)O)O)O)C)C)C)C)(C)C)O)O)OC(=O)C)OC(=O)C)OC(=O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YZNCIXVBVQRGQN-YUTHWCJWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C67H104O33/c1-26(71)87-24-35-48(89-27(2)72)52(90-28(3)73)53(91-29(4)74)61(94-35)96-47-32(75)23-88-57(46(47)83)100-55-54(84)62(5,6)20-31-30-12-13-37-64(8)16-15-38(65(9,25-70)36(64)14-17-67(37,11)66(30,10)19-18-63(31,55)7)95-60-51(44(81)43(80)49(97-60)56(85)86)99-59-50(42(79)40(77)34(22-69)93-59)98-58-45(82)41(78)39(76)33(21-68)92-58/h12,31-55,57-61,68-70,75-84H,13-25H2,1-11H3,(H,85,86)/t31-,32-,33+,34+,35+,36+,37+,38-,39+,40-,41-,42-,43-,44-,45+,46+,47-,48+,49-,50+,51+,52-,53+,54-,55+,57-,58-,59-,60+,61-,63+,64-,65+,66+,67+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Soyasaponin Ab has anti-inflammatory effects, it can inhibit colon shortening, myeloperoxidase activity, the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB); soyasaponin Ab (1, 2, 5, and 10 μM) can inhibit the production of NO (IC50 = 1.6 ± 0.1 uM) and prosta. 2. Soyasaponin Aa and Ab can markedly inhibit adipocyte differentiation and expression of various adipogenic marker genes through the downregulation of the adipogenesis-related transcription factors PPARγ and C/EBPα in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. 3. Soyasaponins Ab and Bb can prevent scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice without the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase, exhibit memory-enhancing effects. 4. Soyasaponin Ab may represent a viable candidate for effective vaccine adjuvant, TLR4 receptor dependent pathway may be involved in immune stimulatory effects of soyasaponin Ab. |
| Targets | NOS | NF-kB | COX | NO | PPAR | TLR | TNF-α | JNK | ERK | p38MAPK | Fatty Acid Synthase | cAMP |

Soyasaponin Ab Dilution Calculator

Soyasaponin Ab Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.6956 mL | 3.478 mL | 6.956 mL | 13.9121 mL | 17.3901 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.1391 mL | 0.6956 mL | 1.3912 mL | 2.7824 mL | 3.478 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.0696 mL | 0.3478 mL | 0.6956 mL | 1.3912 mL | 1.739 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0139 mL | 0.0696 mL | 0.1391 mL | 0.2782 mL | 0.3478 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.007 mL | 0.0348 mL | 0.0696 mL | 0.1391 mL | 0.1739 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- EMD638683
Catalog No.:BCC1551
CAS No.:1181770-72-8
- 2-Picenecarboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3063
CAS No.:118172-80-8
- 6-Oxo-23-norpristimerol
Catalog No.:BCN8054
CAS No.:118172-79-5
- 6''-O-Acetylastragalin
Catalog No.:BCN6058
CAS No.:118169-27-0
- Volvaltrate B
Catalog No.:BCN6736
CAS No.:1181224-13-4
- [Phe8Ψ(CH-NH)-Arg9]-Bradykinin
Catalog No.:BCC5995
CAS No.:118122-39-7
- Schisanwilsonin I
Catalog No.:BCN5548
CAS No.:1181216-84-1
- Schisanwilsonin H
Catalog No.:BCN3315
CAS No.:1181216-83-0
- Karounidiol
Catalog No.:BCN2704
CAS No.:118117-31-0
- Cyprodime hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7425
CAS No.:118111-54-9
- Prehelminthosporolactone
Catalog No.:BCN7289
CAS No.:118101-72-7
- L-365,260
Catalog No.:BCC7477
CAS No.:118101-09-0
- 1,4-Dicaffeoylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5912
CAS No.:1182-34-9
- Isodorsmanin A
Catalog No.:BCN6460
CAS No.:118266-99-2
- Lafutidine
Catalog No.:BCC4544
CAS No.:118288-08-7
- AF-DX 384
Catalog No.:BCC7024
CAS No.:118290-26-9
- 6-O-Acetylscandoside
Catalog No.:BCN8320
CAS No.:118292-15-2
- Tazarotene
Catalog No.:BCC2540
CAS No.:118292-40-3
- Licoricesaponin A3
Catalog No.:BCN7905
CAS No.:118325-22-7
- Australine
Catalog No.:BCN2053
CAS No.:118396-02-4
- Trimethylamine oxide
Catalog No.:BCN1819
CAS No.:1184-78-7
- AG-18
Catalog No.:BCC1051
CAS No.:118409-57-7
- UNC 926 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2445
CAS No.:1184136-10-4
- nTZDpa
Catalog No.:BCC7268
CAS No.:118414-59-8
Soyasaponins Ab and Bb prevent scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice without the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase.[Pubmed:24450802]
J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Mar 5;62(9):2062-8.
Soy (Glycine max, family Leguminosae), which contains isoflavones and saponins as main constituents, is known to exhibit memory-enhancing effects. Therefore, to investigate the role of soyasaponins in memory impairments, we isolated soyasaponins Ab (SA) and Bb (SB) from soybean and measured their protective effects against scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. SA and SB significantly prevented scopolamine-induced memory impairment in passive avoidance and Y-maze tasks. Compared to SA, SB rescued memory impairment more potently. Treatment with SB (10 mg/kg, p.o.) protected memory impairment in passive avoidance and Y-maze tasks to 97% (F = 68.10, P < 0.05) and 78% (F = 35.57, P < 0.05) of untreated normal control level, respectively. SA and SB (10 mg/kg) also rescued scopolamine-induced memory impairment in Morris water maze task (F = 14.51, P < 0.05). In addition, soyasaponins preserved brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BNDF) expression (F = 33.69, P < 0.05) and cAMP response element-binding (CREB) protein phosphorylation (F = 91.62, P < 0.05) in the hippocampus of scopolamine-treated mice. However, SA and SB did not inhibit acetylcholinesterase in vitro and ex vivo. On the basis of these findings, we suggest that soybean, particularly soyasaponins, may protect memory impairment by increasing BDNF expression and CREB phosphorylation.
Soyasaponin Ab ameliorates colitis by inhibiting the binding of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to Toll-like receptor (TLR)4 on macrophages.[Pubmed:22060784]
J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Dec 28;59(24):13165-72.
Many clinical studies have shown that daily intake of soybean [ Glycine max (L.) Merr., Fabacease] or its foods may reduce the risk of osteoporosis, heart attack, hyperlipidemia, coronary heart disease, cardiovascular and chronic renal diseases, and cancers, including prostate, colon, and breast cancers. Of the soy constituents, soyasaponins exhibit anti-aging, antioxidant, apoptotic, and anti-inflammatory effects. However, the anti-inflammatory effect of Soyasaponin Ab has not been thoroughly studied. Therefore, we investigated its anti-inflammatory effects in 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitic mice and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated peritoneal macrophages. Soyasaponin Ab inhibited colon shortening, myeloperoxidase activity, the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB). Soyasaponin Ab (1, 2, 5, and 10 muM) inhibited the production of NO (IC(50) = 1.6 +/- 0.1 muM) and prostaglandin E(2) (IC(50) = 2.0 +/- 0.1 ng/mL), the expression of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha (IC(50) = 1.3 +/- 0.1 ng/mL), interleukin (IL)-1beta (IC(50) = 1.5 +/- 0.1 pg/mL), and toll-like receptor (TLR)4, and the phosphorylation of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK)-1 in LPS-stimulated peritoneal macrophages. Soyasaponin Ab weakly inhibited the phosphorylation of ERK, JNK, and p38. Soyasaponin Ab significantly reduced the binding of Alexa-Fluor-594-conjugated LPS to peritoneal macrophages. Soyasaponin Ab did not affect TLR4 expression or LPS-induced NF-kappaB activation in TLR4 siRNA-treated peritoneal macrophages (knockdown efficiency of TLR4 > 94%). On the basis of these findings, Soyasaponin Ab may ameliorate colitis by inhibiting the binding of LPS to TLR4 on macrophages.
Soyasaponins Aa and Ab exert an anti-obesity effect in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through downregulation of PPARgamma.[Pubmed:25366162]
Phytother Res. 2015 Feb;29(2):281-7.
Saponins are a diverse group of biologically functional products in plants. Soyasaponins are usually glycosylated, which give rise to a wide diversity of structures and functions. In this study, we investigated the effects and molecular mechanism of soyasaponins Aa and Ab in regulating adipocyte differentiation and expression of adipogenic marker genes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Soyasaponins Aa and Ab dose-dependently inhibited the accumulation of lipids and the expression of adiponectin, adipocyte determination and differentiation factor 1/sterol regulatory element binding protein 1c, adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein 2, fatty acid synthase, and resistin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. In addition, soyasaponins Aa and Ab suppressed the transcriptional activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) in HEK 293T cells. Furthermore, we confirmed that the expression of PPARgamma and of CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha) was suppressed at both the mRNA and protein levels in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by treatment with soyasaponins Aa and Ab. Taken together, these findings indicate that soyasaponin Aa and Ab markedly inhibit adipocyte differentiation and expression of various adipogenic marker genes through the downregulation of the adipogenesis-related transcription factors PPARgamma and C/EBPalpha in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.


