Neuroscience Peptides
Neurons communicate with each other, effector organs and sensory organs through the neurotransmitter – receptor pathway at synapses. Neurotransmitters can be divided into 4 major groups: 1. Amino acids (glumate, aspartate, serine, glycine and GABA); 2. Monoamines (norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine, histamine, and serotonin); 3. Peptides (opioid peptides, substance P, somatostatin); and 4. Others (acetylcholine, NO, nucleosides). Substance P is an undecapeptide in the tachykinin family responsible for transmitting pain from sensory neurons to the central nervous system. Short opioid peptides participate in pain pathways and modulate motivation, emotion, the response to stress and pain, and control food intake. Some opioid peptides have an analgesic effect. Opioid receptors are G protein coupled receptors, activated by endogenous opioid peptides like dynorphins, enkephalins, endorphins, endomorphins and nociceptin. Four subtypes of receptors (s, k, m and nociceptin) are responsible for different functions.
Products for Neuroscience Peptides
- Cat.No. Product Name Information
-
BCC1008
Endomorphin-1Potent and selective μ agonist

-
BCC1009
Beta-Lipotropin (1-10), porcineMorphine-like substance

-
BCC1010
alpha-EndorphinNeurotransmitters

-
BCC1011
Adrenorphin, Free Acidμ/κ opioid receptor agonist
-
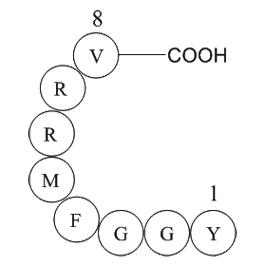
BCC1020
Myelin Basic Protein (68-82), guinea pigMyelin Basic Protein

-
BCC1028
Myelin Basic Protein (87-99)Major antigenic component implicated in the pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis
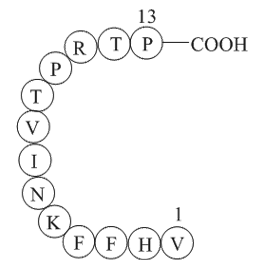
-
BCC1040
Parathyroid Hormone (1-34), bovineEnhancer of blood calcium level
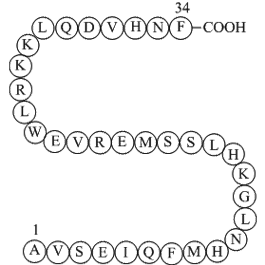
-
BCC1043
Melanocyte stimulating hormone release inhibiting factorAntagonizes opioid effects in vivo. Also inhibits α-MSH release

-
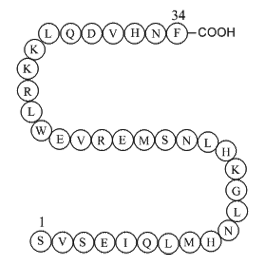
BCC1046
Parathyroid hormone (1-34) (human)Parathyroid hormone (PTH) receptor agonist
-
BCC5516
JNJ-31020028