alpha-EndorphinNeurotransmitters CAS# 59004-96-5 |

- Endomorphin-1
Catalog No.:BCC1008
CAS No.:189388-22-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 59004-96-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16133219 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C77H120N18O26S | M.Wt | 1745.95 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | alpha Endorphin;beta-Endorphin (1-16) | ||
| Solubility | >174.5mg/mL in DMSO | ||
| Sequence | H2N-Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Met-Thr-Ser-Glu-Lys-Ser-Gln-Thr-Pro-Leu-Val-Thr-OH | ||
| Chemical Name | 5-[[6-amino-1-[[1-[[5-amino-1-[[1-[2-[[1-[[1-[(1-carboxy-2-hydroxypropyl)amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]carbamoyl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-3-hydroxy-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-1,5-dioxopentan-2-yl]amino]-3-hydroxy-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxohexan-2-yl]amino]-4-[[2-[[2-[[2-[[2-[[2-[[2-[[2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]-4-methylsulfanylbutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-5-oxopentanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)CC(C(=O)NC(C(C)C)C(=O)NC(C(C)O)C(=O)O)NC(=O)C1CCCN1C(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(CCCCN)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)C(CCSC)NC(=O)C(CC2=CC=CC=C2)NC(=O)CNC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CC3=CC=C(C=C3)O)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NXSIJWJXMWBCBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C77H120N18O26S/c1-38(2)31-51(70(113)91-60(39(3)4)74(117)94-63(42(7)100)77(120)121)88-73(116)55-18-14-29-95(55)76(119)62(41(6)99)93-67(110)48(23-25-56(80)102)85-71(114)53(36-96)89-65(108)47(17-12-13-28-78)84-66(109)49(24-26-59(105)106)86-72(115)54(37-97)90-75(118)61(40(5)98)92-68(111)50(27-30-122-8)87-69(112)52(33-43-15-10-9-11-16-43)83-58(104)35-81-57(103)34-82-64(107)46(79)32-44-19-21-45(101)22-20-44/h9-11,15-16,19-22,38-42,46-55,60-63,96-101H,12-14,17-18,23-37,78-79H2,1-8H3,(H2,80,102)(H,81,103)(H,82,107)(H,83,104)(H,84,109)(H,85,114)(H,86,115)(H,87,112)(H,88,116)(H,89,108)(H,90,118)(H,91,113)(H,92,111)(H,93,110)(H,94,117)(H,105,106)(H,120,121) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

alpha-Endorphin Dilution Calculator

alpha-Endorphin Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Endorphins are endogenous opioid peptides that function as neurotransmitters(1). They are produced by the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus in vertebrates during exercise, excitement, pain, consumption of spicy food, love and orgasm, and they resemble the opiates in their abilities to produce analgesia and a feeling of well-being.The term implies a pharmacological activity (analogous to the activity of the corticosteroid category of biochemicals) as opposed to a specific chemical formulation. It consists of two parts: endo- and -orphin; these are short forms of the words endogenous and morphine(2), Beta-endorphin (β-Endorphin) is released into blood from the pituitary gland and into the spinal cord and brain from hypothalamic neurons. The β-endorphin that is released into the blood cannot enter the brain in large quantities because of the blood–brain barrier, so the physiological importance of the β-endorphin that can be measured in the blood is far from clear. β-Endorphin is a cleavage product of pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC), which is also the precursor hormone for adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH). The behavioural effects of β-endorphin are exerted by its actions in the brain and spinal cord, and it is presumed that the hypothalamic neurons are the major source of β-endorphin at these sites. In situations where the level of ACTH is increased (e.g., Cushing’s Syndrome), the level of endorphins also increases slightly(3).
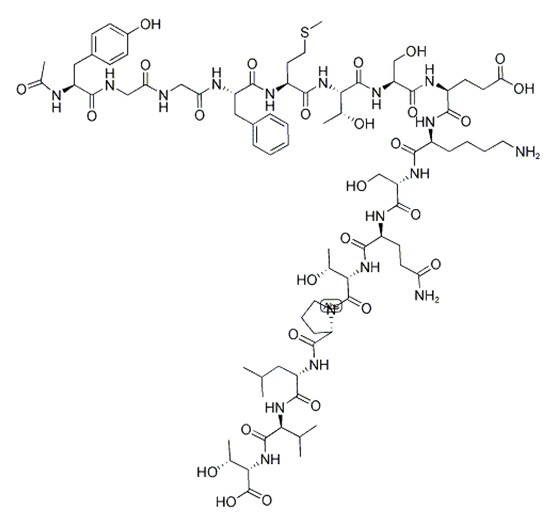
Figure1 Formula of a-Endorphin
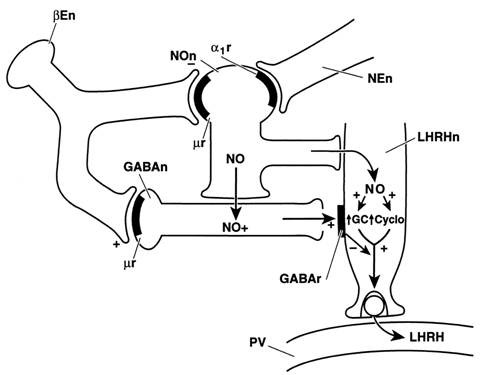
Figure 2 mechanism of endorphin to inhibit LHRH release
Ref:
1. Oswald Steward: Functional neuroscience (2000), page 116.
2. Goldstein A, Lowery PJ (September 1975). "Effect of the opiate antagonist naloxone on body temperature in rats". Life Sciences 17 (6): 927–31.
3. Simantov R, Snyder S (1976). "Morphine-like peptides in mammalian brain: isolation, structure elucidation, and interactions with the opiate receptor". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73 (7): 2515–9.
- Bethanechol chloride
Catalog No.:BCC4566
CAS No.:590-63-6
- Betaine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN6304
CAS No.:590-46-5
- Tolazoline HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4321
CAS No.:59-97-2
- Levodopa
Catalog No.:BCN1098
CAS No.:59-92-7
- Nitrofurazone
Catalog No.:BCC3825
CAS No.:59-87-0
- Nicotinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8328
CAS No.:59-67-6
- DL-Methionine
Catalog No.:BCC8318
CAS No.:59-51-8
- Oxindole
Catalog No.:BCN4050
CAS No.:59-48-3
- Procaine
Catalog No.:BCC5210
CAS No.:59-46-1
- Thiamine chloride
Catalog No.:BCN8344
CAS No.:59-43-8
- Sulfaquinoxaline
Catalog No.:BCC9158
CAS No.:59-40-5
- Mepyramine maleate
Catalog No.:BCC6740
CAS No.:59-33-6
- 8-Hydroxyhyperforin 8,1-hemiacetal
Catalog No.:BCN4091
CAS No.:59014-02-7
- Atropine sulfate monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC3728
CAS No.:5908-99-6
- Dehydrotoxicarol
Catalog No.:BCN3991
CAS No.:59086-93-0
- Albaspidin AP
Catalog No.:BCN2398
CAS No.:59092-91-0
- (+)-Rhododendrol
Catalog No.:BCN7091
CAS No.:59092-94-3
- Alpha-Angelica lactone
Catalog No.:BCN5001
CAS No.:591-12-8
- Misoprostol
Catalog No.:BCC5240
CAS No.:59122-46-2
- Neoisoliquiritin
Catalog No.:BCN2936
CAS No.:59122-93-9
- PSB 10 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7238
CAS No.:591771-91-4
- Sulforaphene
Catalog No.:BCN8179
CAS No.:592-95-0
- beta-Dihydroplumericinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4092
CAS No.:59204-61-4
- 8(14),15-Isopimaradiene-3,18-diol
Catalog No.:BCN4093
CAS No.:59219-64-6
High-efficiency synthesis of human alpha-endorphin and magainin in the erythrocytes of transgenic mice: a production system for therapeutic peptides.[Pubmed:7937766]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 27;91(20):9337-41.
Chemical synthesis of peptides, though feasible, is hindered by considerations of cost, purity, and efficiency of synthesizing longer chains. Here we describe a transgenic system for producing peptides of therapeutic interest as fusion proteins at low cost and high purity. Transgenic hemoglobin expression technology using the locus control region was employed to produce fusion hemoglobins in the erythrocytes of mice. The fusion hemoglobin contains the desired peptides as an extension at the C end of human alpha-globin. A protein cleavage site is inserted between the C end of the alpha-globin chain and the N-terminal residue of the desired peptide. The peptide is recovered after cleavage of the fusion protein with enzymes that recognize this cleavage signal as their substrate. Due to the selective compartmentalization of hemoglobin in the erythrocytes, purification of the fusion hemoglobin is easy and efficient. Because of its compact and highly ordered structure, the internal sites of hemoglobin are resistant to protease digestion and the desired peptide is efficiently released and recovered. The applicability of this approach was established by producing a 16-mer alpha-Endorphin peptide and a 26-mer magainin peptide in transgenic mice. Transgenic animals and their progeny expressing these fusion proteins remain health, even when the fusion protein is expressed at > 25% of the total hemoglobin in the erythrocytes. Additional applications and potential improvements of this methodology are discussed.
Construction of a quadroma to alpha-endorphin/horseradish peroxidase using an actinomycin D-resistant mouse myeloma cell line.[Pubmed:1358818]
Immunol Lett. 1992 Aug;33(3):217-22.
A hybrid hybridoma (quadroma), secreting antibodies with double specificity to alpha-Endorphin (alpha-EP) and horseradish peroxidase (HRP), has been produced. The bispecific antibodies constituted about 28-29% of all immunologically active IgG, produced by quadroma. The quadroma was isolated by fusion of two mouse hybridomas (anti-HRP and anti-alpha-EP) with distinct phenotypes: double mutant AMDR/HAT(S), and wild type (AMDS/HATR). A novel strategy for the construction of a double-mutant was applied, based on the use of an actinomycin D-resistant (AMDR) mouse myeloma for initiation of one of the parental hybridomas.
Isalpha-endorphin an uremic toxin?alpha-Endorphin isolated from filtrate of uremic patients with carbohydrate intolerance.[Pubmed:24190555]
Amino Acids. 1993 Feb;4(1-2):35-43.
A 16-residue peptide was isolated from filtrate of uremic patients with carbohydrate intolerance by ultrafiltration with an Amicon Centriflo DM-5 membrane, followed by gel-filtration on Sephadex G-50 and Sephadex G-25, droplet countercurrent chromatography and high performance liquid chromatography. The hexadecapeptide thus obtained was identical as the entire amino acid sequence ofalpha-Endorphin by amino acid analysis, application of the Edman degradation analysis and measurement of physical constants and analytical data of the synthetic hexadecapeptide. This result seems to suggest that an accumulation ofalpha-Endorphin in uremic patients might cause carbohydrate intolerance.
[The vagus-inhibiting action of alpha-endorphin].[Pubmed:1677295]
Biull Eksp Biol Med. 1991 Feb;111(2):174-5.
An intravenous bolus injection of 0.1 ml alpha-Endorphin (1 x 10(-8)-1 x 10(-4) g/ml) didn't change the heart rate in frogs. The parasympathetic bradycardia induced by the peripheral vagus stimulation was decreased by alpha-Endorphin. This vago-inhibitory action was dose-dependent (1 x 10(-5)-1 x 10(-4) g/ml). The maximal inhibitory action was watched in 4-8 and 9-15 minutes after bolus injection of alpha-Endorphin in concentration of 1 x 10(-5) and 1 x 10(-4) g/ml accordingly.


