SulforapheneCAS# 592-95-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 592-95-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6433206 | Appearance | Powder |
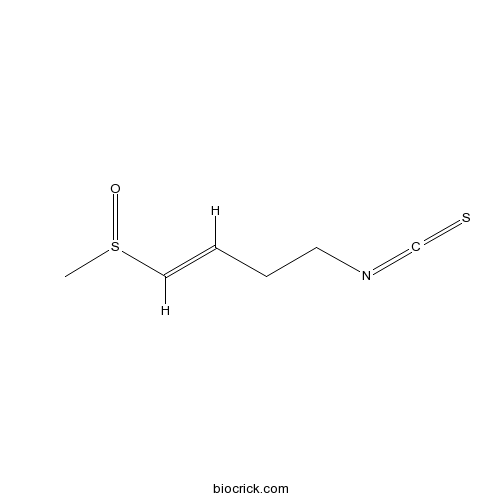
| Formula | C6H9NOS2 | M.Wt | 175.27 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (E)-4-isothiocyanato-1-methylsulfinylbut-1-ene | ||
| SMILES | CS(=O)C=CCCN=C=S | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QKGJFQMGPDVOQE-HWKANZROSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C6H9NOS2/c1-10(8)5-3-2-4-7-6-9/h3,5H,2,4H2,1H3/b5-3+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Sulforaphene has herbicidal activity, the ED50 of it against velvetleaf seedlings was approximately 2×10(-4) M. 2. Sulforaphene may be a potential anti- triple negative breast cancer natural compound and its antiproliferation effects may be mediated by tumor suppressor Egr1. 3. Sulforaphene has chemotherapeutic potential, it promotes Bax/Bcl2, MAPK-dependent human gastric cancer AGS cells apoptosis and inhibits migration via EGFR, p-ERK1/2 down-regulation. 4. Sulforaphene enhances radiosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma through suppression of the NF-κB pathway. 5. Sulforaphene has anti-proliferative and antibacterial properties. |
| Targets | ROS | Bcl-2/Bax | Caspase | PARP | JNK | ERK | EGFR | NF-kB | Antifection |

Sulforaphene Dilution Calculator

Sulforaphene Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.7055 mL | 28.5274 mL | 57.0548 mL | 114.1097 mL | 142.6371 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.1411 mL | 5.7055 mL | 11.411 mL | 22.8219 mL | 28.5274 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5705 mL | 2.8527 mL | 5.7055 mL | 11.411 mL | 14.2637 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1141 mL | 0.5705 mL | 1.1411 mL | 2.2822 mL | 2.8527 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0571 mL | 0.2853 mL | 0.5705 mL | 1.1411 mL | 1.4264 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- PSB 10 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7238
CAS No.:591771-91-4
- Neoisoliquiritin
Catalog No.:BCN2936
CAS No.:59122-93-9
- Misoprostol
Catalog No.:BCC5240
CAS No.:59122-46-2
- Alpha-Angelica lactone
Catalog No.:BCN5001
CAS No.:591-12-8
- (+)-Rhododendrol
Catalog No.:BCN7091
CAS No.:59092-94-3
- Albaspidin AP
Catalog No.:BCN2398
CAS No.:59092-91-0
- Dehydrotoxicarol
Catalog No.:BCN3991
CAS No.:59086-93-0
- Atropine sulfate monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC3728
CAS No.:5908-99-6
- 8-Hydroxyhyperforin 8,1-hemiacetal
Catalog No.:BCN4091
CAS No.:59014-02-7
- alpha-Endorphin
Catalog No.:BCC1010
CAS No.:59004-96-5
- Bethanechol chloride
Catalog No.:BCC4566
CAS No.:590-63-6
- Betaine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN6304
CAS No.:590-46-5
- beta-Dihydroplumericinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4092
CAS No.:59204-61-4
- 8(14),15-Isopimaradiene-3,18-diol
Catalog No.:BCN4093
CAS No.:59219-64-6
- Darutoside
Catalog No.:BCN4094
CAS No.:59219-65-7
- Erigeroside
Catalog No.:BCC8171
CAS No.:59219-76-0
- Laurocapram
Catalog No.:BCN8308
CAS No.:59227-89-3
- Chikusetsu Saponin Ib
Catalog No.:BCC8308
CAS No.:59252-87-8
- Rigosertib
Catalog No.:BCC4296
CAS No.:592542-59-1
- Rigosertib sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4067
CAS No.:592542-60-4
- Meptazinol HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4920
CAS No.:59263-76-2
- Acyclovir
Catalog No.:BCC3929
CAS No.:59277-89-3
- Decursin
Catalog No.:BCN5335
CAS No.:5928-25-6
- Sissotrin
Catalog No.:BCN4095
CAS No.:5928-26-7
Sulforaphene inhibits triple negative breast cancer through activating tumor suppressor Egr1.[Pubmed:27377973]
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Jul;158(2):277-86.
Sulforaphene (SFE, 4-methylsufinyl-3-butenyl isothiocyanate) is a member of isothiocyanates, which is derived from radish seeds. It has shown that multiple isothiocyanates, such as sulforaphane, can effectively inhibit cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. However, it is still largely unknown if SFE could impact breast cancer. In this study, we investigated the anticancer effects of SFE on triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) via a series of in vitro and in vivo assays. We found that SFE can significantly inhibit cell proliferation in multiple TNBC cell lines through inducing G2/M phase arrest as well as cell apoptosis. Nude mice xenograft assays support the anti-TNBC role of SFE in vivo. Interestingly, SFE can repress expression of cyclinB1, Cdc2, and phosphorylated Cdc2, and, then, induced G2/M phase arrest of TNBC cells. To identify SFE target genes, we detected genome-wide gene expression changes through gene expression profiling and observed 27 upregulated and 18 downregulated genes in MDA-MB-453 cells treated with SFE. Among these genes, Egr1 was successfully validated as a consistently activated gene after SFE treatment in TNBC MDA-MB-453 and MDA-MB-436 cells. Egr1 overexpression inhibited proliferation of TNBC cells. However, Egr1 knockdown using siRNAs significantly promoted TNBC cell growth, indicating the tumor suppressor nature of Egr1. In sum, we for the first time found that SFE might be a potential anti-TNBC natural compound and its antiproliferation effects might be mediated by tumor suppressor Egr1.
Sulforaphene enhances radiosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma through suppression of the NF-kappaB pathway.[Pubmed:28346727]
J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2017 Aug;31(8).
Sulforaphene (SFE), a naturally occurring isothiocyanate found in cruciferous vegetables, has attracted increasing attention for its anti-cancer effect in many cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the precise role of SFE in the radiosensitivity of HCC is still unclear. Here, cell proliferation and apoptosis were detected by MTT and flow cytometry assay, respectively. The activity of NF-kappaB was further evaluated by ELISA. We also observed the effect of SFE and/or radiation on tumor growth. The results showed that SFE inhibited cell proliferation and induced apoptosis in HCC cells. Radiation increased NF-kB activity, while PDTC, a NF-kB inhibitor, enhanced radiation-induced cell death. SFE inhibited NF-kB activity and the downstream gene expressions of the NF-kB pathway in HCC cells. Moreover, SFE enhanced the inhibitory effect of radiation on tumor growth both in vitro and in vivo. This study indicated that SFE sensitized the radiosensitivity of HCC by blocking the NF-kB pathway.
Herbicidal activity of sulforaphene from stock (Matthiola incana).[Pubmed:24248575]
J Chem Ecol. 1993 Oct;19(10):2279-84.
A herbicidal compound was isolated from extracts ofMatthiola incana and identified as Sulforaphene (4-methylsulfinyl-3-butenyl isothiocyanate). The ED50 of this compound against velvetleaf seedlings was approximately 2x10(-4) M. Glucoraphenin, the glucosinolate that is the natural precursor of Sulforaphene, was less phytotoxic, with an ED50 of near 6x10(-3)M.
Sulforaphene promotes Bax/Bcl2, MAPK-dependent human gastric cancer AGS cells apoptosis and inhibits migration via EGFR, p-ERK1/2 down-regulation.[Pubmed:26612919]
Gen Physiol Biophys. 2016 Jan;35(1):25-34.
Gastric cancer migration and invasion considered as main causes of this cancer-related death around the world. Sulforaphene (4-isothiocyanato-4R-(methylsulfinyl)-1-butene), a structural analog of sulforaphane, has been found to exhibit anticancer potential against different cancers. Our aim was to investigate whether dietary isothiocyanate Sulforaphene (SFE) can promote human gastric cancer (AGS) cells apoptosis and inhibit migration. Cells were treated with various concentrations of SFE and cell viability, morphology, intracellular ROS, migration and different signaling protein expressions were investigated. The results indicate that SFE decreases AGS cell viability and induces apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner. Intracellular ROS generation, dose- and time-dependent Bax/Bcl2 alteration and signaling proteins like cytochrome c, Casp-3, Casp-8 and PARP-1 higher expression demonstrated the SFE-induced apoptotic pathway in AGS cells. Again, SFE induced apoptosis also accompanied by the phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) like JNK and P-38. Moreover, dose-dependent EGFR, p-ERK1/2 down-regulation and cell migration inhibition at non-toxic concentration confirms SFE activity in AGS cell migration inhibition. Thus, this study demonstrated effective chemotherapeutic potential of SFE by inducing apoptisis as well as inhibiting migration and their preliminary mechanism for human gastric cancer management.


