Istaroxime hydrochlorideInhibitor of Na+/K+ ATPase CAS# 374559-48-5 |
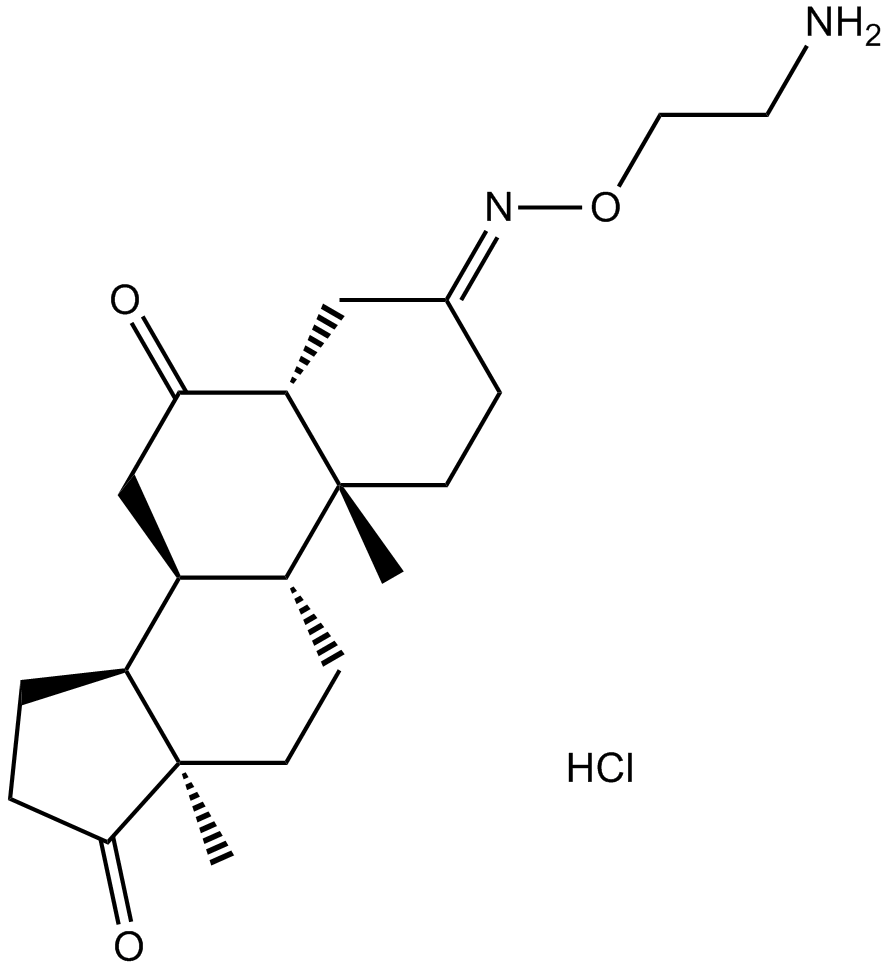
- Istaroxime
Catalog No.:BCC1660
CAS No.:203737-93-3
- Resibufogenin
Catalog No.:BCN5366
CAS No.:465-39-4
- Cinobufagin
Catalog No.:BCN5367
CAS No.:470-37-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 374559-48-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 72941813 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C21H33ClN2O3 | M.Wt | 396.95 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | PST2744 (hydrochloride) | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 45 mg/mL (113.36 mM); | ||
| Chemical Name | (5S,8R,9S,10R,13S,14S)-3-(2-aminoethoxyimino)-10,13-dimethyl-1,2,4,5,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-dodecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-6,17-dione;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CC12CCC(=NOCCN)CC1C(=O)CC3C2CCC4(C3CCC4=O)C.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AXHJYJDJXNOGNI-DESZRGPQSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H32N2O3.ClH/c1-20-7-5-13(23-26-10-9-22)11-17(20)18(24)12-14-15-3-4-19(25)21(15,2)8-6-16(14)20;/h14-17H,3-12,22H2,1-2H3;1H/t14-,15-,16-,17+,20+,21-;/m0./s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Istaroxime hydrochloride is an inhibitor of sodium/potassium adenosine triphosphatase (Na+/K+ ATPase) with IC50 value of 0.43 μM. | |||||
| Targets | Na+/K+ ATPase | |||||
| IC50 | 0.43 μM | |||||
| Cell experiment: [1] | |
| Cell lines | Guinea pig ventricular myocytes |
| Preparation method | The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
| Reacting condition | 4 μM, 0.5 s |
| Applications | Resting Ca2+ was similarly increased by istaroxime (from 61.3 to 92.4 nM). Istaroxime increased [Ca]SR-tot by 47%. Istaroxime increased the amount of Ca2+ extruded by the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (CaNCX) during caffeine-induced transients (+130). Istaroxime shortened the time elapsing between the start of the caffeine pulse and SR Ca2+ release. |
| Animal experiment: [2] | |
| Animal models | Bio TO.2 hamsters and Bio F1B hamsters |
| Dosage form | Oral administration, 30 mg/5 mL/kg/day |
| Application | Heart function of istaroxime-treated hamsters was comparable to that of healthy animals, and had a significantly higher LVSP and both positive and negative dP/dT when compared with that of vehicle-treated animals. Coronary flow rate in hearts isolated from istaroxime-treated hamsters was higher than that from vehicle-treated Bio TO.2 animals. Besides that, Bio TO.2 hamsters treated with istaroxime had both time and frequency domain indexes of HRV, i.e. standard deviation of R-R intervals, TP, LF and HF, augmented with respect to vehicle-treated animals. Moreover , the LF/HF ratio of istaroxime-treated animals was similar to that observed in Bio F1B hamsters. |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: [1] Rocchetti M, Besana A, Mostacciuolo G, et al. Modulation of sarcoplasmic reticulum function by Na+/K+ pump inhibitors with different toxicity: digoxin and PST2744 [(E, Z)-3-((2-aminoethoxy) imino) androstane-6, 17-dione hydrochloride]. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 2005, 313(1): 207-215. [2] Giudice P L, Mattera G G, Gagnol J P, et al. Chronic istaroxime improves cardiac function and heart rate variability in cardiomyopathic hamsters. Cardiovascular drugs and therapy, 2011, 25(2): 133-138. | |

Istaroxime hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

Istaroxime hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5192 mL | 12.596 mL | 25.1921 mL | 50.3842 mL | 62.9802 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5038 mL | 2.5192 mL | 5.0384 mL | 10.0768 mL | 12.596 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2519 mL | 1.2596 mL | 2.5192 mL | 5.0384 mL | 6.298 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0504 mL | 0.2519 mL | 0.5038 mL | 1.0077 mL | 1.2596 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0252 mL | 0.126 mL | 0.2519 mL | 0.5038 mL | 0.6298 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Istaroxime hydrochloride(PST2744) is a novel inhibitor of Na+/K+-ATPase with IC50 value of 0.43±0.15μM [1].
In vitro studies show that Istaroxime can inhibit the activity of Na+/K+-ATPase from dog kidney without significant interaction with other several receptors. It demonstrates the selectivity of Istaroxime. Ex vivo studies show the inotropic effect can be achieved up to 60% for Istaroxime. Istaroxime can also increase the force of contraction of guinea pig paced left atria in the range 0.3 to 30μM. In vivo assays prove Istaroxime is consistently safer than digoxin [1].
Istaroxime is a steroidal drug unrelated to cardiac glycosides that improves cellular calcium cycling. The inhibition of Na+/K+-ATPase induces cytosolic calcium accumulation during systole (inotropism). Clinical studies has been done with istaroxime in phase II. Istaroxime could be a promising alternative for patients with acute heart failure syndrome for whom the therapeutic options are currently limited [2].
References:
[1] R. Micheletti, G. G. Mattera, M. Rocchetti, A. Schiavone, M. F. Loi, A. Zaza, R. J. P. Gagnol, S. De Munari, P. Melloni, P. Carminati, G. Bianchi, and P. Ferrari. Pharmacological profile of the novel inotropic agent (e,z)-3-((2-aminoethoxy)imino)androstane-6,17-dione hydrochloride (PST2744). The journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics. 2002, 303 (2): 592-600.
[2] Suruchi Aditya, Aditya Rattan. Istaroxime: A rising star in acute heart failure. Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics. 2012, 3(4): 353-355.
- Boc-DL-Ala-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3050
CAS No.:3744-87-4
- DS2
Catalog No.:BCC7748
CAS No.:374084-31-8
- Cephaeline Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8307
CAS No.:3738-70-3
- Decloxizine
Catalog No.:BCC5529
CAS No.:3733-63-9
- 3-Quinuclidinone
Catalog No.:BCC8642
CAS No.:3731-38-2
- Flavokawain C
Catalog No.:BCN8456
CAS No.:37308-75-1
- H-D-Tyr-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3135
CAS No.:3728-20-9
- Sennoside D
Catalog No.:BCN1005
CAS No.:37271-17-3
- Sennoside C
Catalog No.:BCN1004
CAS No.:37271-16-2
- TCS OX2 29
Catalog No.:BCC7670
CAS No.:372523-75-6
- Wilfordine
Catalog No.:BCN3083
CAS No.:37239-51-3
- Wilfortrine
Catalog No.:BCN3085
CAS No.:37239-48-8
- Kisspeptin 10 (human)
Catalog No.:BCC7415
CAS No.:374675-21-5
- Metastin (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5761
CAS No.:374683-24-6
- DHP Linker
Catalog No.:BCC2830
CAS No.:3749-36-8
- Amikacin
Catalog No.:BCC5206
CAS No.:37517-28-5
- 2-Chlorocinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5036
CAS No.:3752-25-8
- LY451395
Catalog No.:BCC5377
CAS No.:375345-95-2
- H-D-Ala(4-pyridyl)-OH.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3325
CAS No.:37535-49-2
- 3-(2-Pyridyl)-Alanine
Catalog No.:BCC2656
CAS No.:37535-51-6
- H- Ala(2-pyridyl)-OH.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3318
CAS No.:37535-51-6 net
- 3-(2-Pyridyl)-D-Alanine
Catalog No.:BCC2655
CAS No.:37535-52-7
- 7'(Z)-(8''R,8'''R)-epi-salvianolic acid E
Catalog No.:BCC3319
CAS No.:
- Boc-Ala(4-pyridyl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3326
CAS No.:37535-57-2
Modulation of sarcoplasmic reticulum function by PST2744 [istaroxime; (E,Z)-3-((2-aminoethoxy)imino) androstane-6,17-dione hydrochloride)] in a pressure-overload heart failure model.[Pubmed:18539651]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008 Sep;326(3):957-65.
PST2744 [Istaroxime; (E,Z)-3-((2-aminoethoxy)imino) androstane-6,17-dione hydrochloride)] is a novel inotropic agent that enhances sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca(2+) ATPase (SERCA) 2 activity. We investigated the istaroxime effect on Ca(2+) handling abnormalities in myocardial hypertrophy/failure (HF). Guinea pig myocytes were studied 12 weeks after aortic banding (AoB) and compared with those of sham-operated animals (sham). The gain of calcium-induced Ca(2+) release (CICR), sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca(2+) content, Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger (NCX) function, and the rate of SR reloading after caffeine-induced depletion (SR Ca(2+) uptake, measured during NCX blockade) were evaluated by measurement of cytosolic Ca(2+) and membrane currents. HF characterization: AoB caused hypertrophy and failure in 100 and 25% of animals, respectively. Although CICR gain during constant pacing was preserved, SR Ca(2+) content and SR Ca(2+) uptake were strongly depressed. Resting Ca(2+) and the slope of the Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger current (I(NCX))/Ca(2+) relationship were unchanged by AoB. Istaroxime effects: CICR gain, SR Ca(2+) content, and SR Ca(2+) uptake rate were increased by istaroxime in sham myocytes and, to a significantly larger extent, in AoB myocytes; this led to almost complete recovery of SR Ca(2+) uptake in AoB myocytes. Istaroxime increased resting Ca(2+) and the slope of the I(NCX)/Ca(2+) relationship similarly in sham and AoB myocytes. Istaroxime failed to increase SERCA activity in skeletal muscle microsomes devoid of phospholamban. Thus, clear-cut abnormalities in Ca(2+) handling occurred in this model of hypertrophy, with mild decompensation. Istaroxime enhanced SR function more in HF myocytes than in normal ones; almost complete drug-induced recovery suggests a purely functional nature of SR dysfunction in this HF model.


