KH CB19inhibitor of CLK1 and CLK4, potent and selective CAS# 1354037-26-5 |
- PF-4981517
Catalog No.:BCC2270
CAS No.:1390637-82-7
- Abiraterone
Catalog No.:BCC2259
CAS No.:154229-19-3
- Avasimibe
Catalog No.:BCC2274
CAS No.:166518-60-1
- Alizarin
Catalog No.:BCN3479
CAS No.:72-48-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1354037-26-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 44237094 | Appearance | Powder |
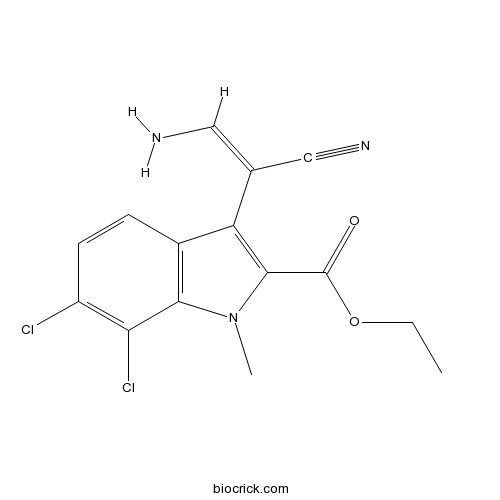
| Formula | C15H13Cl2N3O2 | M.Wt | 338.19 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL (147.85 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | ethyl 3-[(E)-2-amino-1-cyanoethenyl]-6,7-dichloro-1-methylindole-2-carboxylate | ||
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)C1=C(C2=C(N1C)C(=C(C=C2)Cl)Cl)C(=CN)C#N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CXJCGSPAPOTTSF-VURMDHGXSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H13Cl2N3O2/c1-3-22-15(21)14-11(8(6-18)7-19)9-4-5-10(16)12(17)13(9)20(14)2/h4-6H,3,18H2,1-2H3/b8-6- | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective, potent inhibitor of CDC2-like kinase (CLK) 1 and 4 (IC50 = 20 nM for CLK1). Suppresses serine/arginine-rich protein phosphorylation by CLKs under proinflammatory conditions. Displays selectivity over a panel of 71 protein kinases. ATP-competitive. |

KH CB19 Dilution Calculator

KH CB19 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9569 mL | 14.7846 mL | 29.5692 mL | 59.1384 mL | 73.9229 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5914 mL | 2.9569 mL | 5.9138 mL | 11.8277 mL | 14.7846 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2957 mL | 1.4785 mL | 2.9569 mL | 5.9138 mL | 7.3923 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0591 mL | 0.2957 mL | 0.5914 mL | 1.1828 mL | 1.4785 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0296 mL | 0.1478 mL | 0.2957 mL | 0.5914 mL | 0.7392 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
KH CB19 is a potent and selective inhibitor of CLK1 and CLK4 with IC50 values of 19.7 and 530 nM for CLK1 and CLK3, respectively [1] [2].
The cdc2-like kinases (CLKs) are dual specificity protein kinases that phosphorylate the serine- and arginine-rich (SR) proteins, which are involved in regulating the alternative pre-mRNA splicing process [1].
KH CB19 is a potent and selective inhibitor of CLK1 and CLK4. In endothelial cells, KH CB19 inhibited the phosphorylation of serine- and arginine-rich (SR) proteins stimulated by TNF-α and decreased the mRNA expression of tissue factor splice variants [1]. KH CB19 bound to the ATP binding site in CLK3 and CLK1. In enzyme kinetic assays, KH CB19 inhibited DYRK1A with IC50 value of 55.2 nM. In human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1), KH-CB19 (10 µM) reduced the phosphorylation of SRp75, SRp55 and SRp20. However, in TNF-α stimulated HMEC-1, KH-CB19 (10 µM) inhibited the phosphorylation of SRp75, SRp55, SRp40, SC35, SF2/ASF and SRp20. In HMEC-1, KH CB19 (10 µM) significantly reduced the expression of the membrane bound full-length tissue factor (flTF) as well as the soluble asHTF in TNF-α-induced and TNF-α-non-induced cells [2].
References:
[1]. Grant SK, Lunney EA. Kinase inhibition that hinges on halogen bonds. Chem Biol, 2011, 18(1): 3-4.
[2]. Fedorov O, Huber K, Eisenreich A, et al. Specific CLK inhibitors from a novel chemotype for regulation of alternative splicing. Chem Biol, 2011, 18(1): 67-76.
- Bullatine A
Catalog No.:BCN2374
CAS No.:1354-84-3
- CX-6258 hydrochloride hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1505
CAS No.:1353858-99-7
- 8-Prenyldaidzein
Catalog No.:BCN4711
CAS No.:135384-00-8
- 12alpha-Methoxygrandiflorenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7771
CAS No.:135383-94-7
- 4'-Hydroxyisojasminin
Catalog No.:BCN7383
CAS No.:135378-09-5
- Isojasminin
Catalog No.:BCN7492
CAS No.:135378-08-4
- 5,7,3',4'-Tetrahydroxy-3-methoxy-8,5'-diprenylflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6848
CAS No.:1353676-65-9
- 8,8'-Bibaicalein
Catalog No.:BCN6549
CAS No.:135309-02-3
- MEN 10376
Catalog No.:BCC7133
CAS No.:135306-85-3
- 2''-O-Rhamnosylicariside II
Catalog No.:BCN3464
CAS No.:135293-13-9
- EW-7197
Catalog No.:BCC6467
CAS No.:1352608-82-2
- Pulchinenoside B
Catalog No.:BCN6554
CAS No.:135247-95-9
- ACT 335827
Catalog No.:BCC6346
CAS No.:1354039-86-3
- trans-Ned 19
Catalog No.:BCC7825
CAS No.:1354235-96-3
- JW 480
Catalog No.:BCC6142
CAS No.:1354359-53-7
- 7-O-Prenylscopoletin
Catalog No.:BCN3547
CAS No.:13544-37-1
- Rehmapicrogenin
Catalog No.:BCN8507
CAS No.:135447-39-1
- Strontium Ranelate
Catalog No.:BCC3858
CAS No.:135459-87-9
- Araliadiol
Catalog No.:BCC8835
CAS No.:1354638-93-9
- Cabazitaxel intermediate
Catalog No.:BCN7432
CAS No.:1354900-65-4
- CYM 50260
Catalog No.:BCC6259
CAS No.:1355026-60-6
- ML 190
Catalog No.:BCC6308
CAS No.:1355244-02-8
- 2,3-Dihydro-12,13-dihydroxyeuparin
Catalog No.:BCN7189
CAS No.:135531-75-8
- Mutant IDH1-IN-1
Catalog No.:BCC6403
CAS No.:1355326-21-4
Spatial regulation of the KH domain RNA-binding protein Rnc1 mediated by a Crm1-independent nuclear export system in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.[Pubmed:28142187]
Mol Microbiol. 2017 May;104(3):428-448.
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) play important roles in the posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression, including mRNA stability, transport and translation. Fission yeast rnc1(+) encodes a K Homology (KH)-type RBP, which binds and stabilizes the Pmp1 MAPK phosphatase mRNA thereby suppressing the Cl(-) hypersensitivity of calcineurin deletion and MAPK signaling mutants. Here, we analyzed the spatial regulation of Rnc1 and discovered a putative nuclear export signal (NES)Rnc1 , which dictates the cytoplasmic localization of Rnc1 in a Crm1-independent manner. Notably, mutations in the NESRnc1 altered nucleocytoplasmic distribution of Rnc1 and abolished its function to suppress calcineurin deletion, although the Rnc1 NES mutant maintains the ability to bind Pmp1 mRNA. Intriguingly, the Rnc1 NES mutant destabilized Pmp1 mRNA, suggesting the functional importance of the Rnc1 cytoplasmic localization. Mutation in Rae1, but not Mex67 deletion or overproduction, induced Rnc1 accumulation in the nucleus, suggesting that Rnc1 is exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm via the mRNA export pathway involving Rae1. Importantly, mutations in the Rnc1 KH-domains abolished the mRNA-binding ability and induced nuclear localization, suggesting that Rnc1 may be exported from the nucleus together with its target mRNAs. Collectively, the functional Rae1-dependent mRNA export system may influence the cytoplasmic localization and function of Rnc1.
The interaction of a Trypanosoma brucei KH-domain protein with a ribonuclease is implicated in ribosome processing.[Pubmed:27965085]
Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2017 Jan;211:94-103.
Ribosomal RNA maturation is best understood in yeast. While substantial efforts have been made to explore parts of these essential pathways in animals, the similarities and uniquenesses of rRNA maturation factors in non-Opisthokonts remain largely unexplored. Eukaryotic ribosome synthesis requires the coordinated activities of hundreds of Assembly Factors (AFs) that transiently associate with pre-ribosomes, many of which are essential. Pno1 and Nob1 are two of six AFs that are required for the cytoplasmic maturation of the 20S pre-rRNA to 18S rRNA in yeast where it has been almost exclusively analyzed. Specifically, Nob1 ribonucleolytic activity generates the mature 3'-end of 18S rRNA. We identified putative Pno1 and Nob1 homologues in the protist Trypanosoma brucei, named TbPNO1 and TbNOB1, and set out to explore their rRNA maturation role further as they are both essential for normal growth. TbPNO1 is a nuclear protein with limited cytosolic localization relative to its yeast homologue. Like in yeast, it interacts directly with TbNOB1, with indications of associations with a larger AF-containing complex. Interestingly, in the absence of TbPNO1, TbNOB1 exhibits non-specific degradation activity on RNA substrates, and its cleavage activity becomes specific only in the presence of TbPNO1, suggesting that TbPNO1-TbNOB1 interaction is essential for regulation and site-specificity of TbNOB1 activity. These results highlight a conserved role of the TbPNO1-TbNOB1 complex in 18S rRNA maturation across eukaryotes; yet reveal a novel role of their interaction in regulation of TbNOB1 enzymatic activity.
FUBP/KH domain proteins in transcription: Back to the future.[Pubmed:28301294]
Transcription. 2017 May 27;8(3):185-192.
Drosophila genetic studies demonstrate that cell and tissue growth regulation is a primary developmental function of P-element somatic inhibitor (Psi), the sole ortholog of FUBP family RNA/DNA-binding proteins. Psi achieves growth control through interaction with Mediator, observations that should put to rest controversy surrounding Pol II transcriptional functions for these KH domain proteins.
The herbal formula KH-204 is protective against erectile dysfunction by minimizing oxidative stress and improving lipid profiles in a rat model of erectile dysfunction induced by hypercholesterolaemia.[Pubmed:28235412]
BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Feb 24;17(1):129.
BACKGROUND: Hypercholesterolaemia (HC) is a major risk factor for ischemic heart disease and is also known to be a risk factor for erectile dysfunction (ED). ED caused by HC is thought to be related to HC-induced oxidative stress damage in the vascular endothelium and erectile tissue. KH-204 is an herbal formula with a strong antioxidant effect. We evaluated the effects of KH-204 on erectile function in a rat model of HC-induced ED. METHODS: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (6 weeks old) were divided into normal control, high-fat and cholesterol diet (HFC), and HFC with KH-204 treatment (HFC + KH) groups (n = 12 each). Normal control group rats were fed normal chow diet. HFC and HFC + KH group rats were fed high-fat and cholesterol diets and treated with or without daily oral doses of KH-204 for 12 weeks. Subsequently, intracavernous pressure (ICP) and mean arterial pressure (MAP) were measured, and lipid profiles, expression of endothelial (eNOS) and neuronal (nNOS) nitric oxide synthase, oxidative stress (8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine), and ratio of smooth muscle cells and collagen fibres were evaluated in the serum and corpora tissue. RESULTS: Compared to the HFC group, the HFC + KH group showed statistically significant increases in peak ICP and ICP/MAP ratio, expression of eNOS and nNOS, and ratio of smooth muscle cells and collagen fibres (p < 0.05). The HFC + KH group also showed statistically significant decreases in oxidative stress (p < 0.05). Further the lipid profiles of this group were ameliorated compared to those of the HFC group (p < 0.05). CONCLUSIONS: The current study shows that the antioxidant and hypolipidemic effects of KH-204 are effective in ameliorating ED by restoring endothelial dysfunction and suggests that KH-204 may be a potential therapeutic agent for ED by correcting the fundamental cause of ED.


