trans-Ned 19CAS# 1354235-96-3 |
- PD 123319 ditrifluoroacetate
Catalog No.:BCC1841
CAS No.:136676-91-0
- Irbesartan
Catalog No.:BCC2560
CAS No.:138402-11-6
- Olmesartan
Catalog No.:BCC1819
CAS No.:144689-24-7
- AVE 0991
Catalog No.:BCC4032
CAS No.:304462-19-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1354235-96-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 1427628 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C30H31FN4O3 | M.Wt | 514.59 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
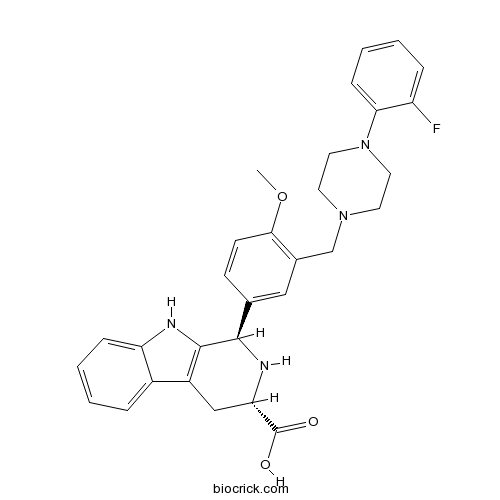
| Chemical Name | (1R,3S)-1-[3-[[4-(2-fluorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]methyl]-4-methoxyphenyl]-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C(C=C1)C2C3=C(CC(N2)C(=O)O)C4=CC=CC=C4N3)CN5CCN(CC5)C6=CC=CC=C6F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FUHCEERDBRGPQZ-LBNVMWSVSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C30H31FN4O3/c1-38-27-11-10-19(16-20(27)18-34-12-14-35(15-13-34)26-9-5-3-7-23(26)31)28-29-22(17-25(33-28)30(36)37)21-6-2-4-8-24(21)32-29/h2-11,16,25,28,32-33H,12-15,17-18H2,1H3,(H,36,37)/t25-,28+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) antagonist. Inhibits NAADP-mediated Ca2+ release (IC50 = 6 nM); also inhibits [32P]NAADP binding (IC50 = 0.4 nM). Fluorescently labels NAADP receptors in intact cells. Stereosiomer of cis-Ned 19. |

trans-Ned 19 Dilution Calculator

trans-Ned 19 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9433 mL | 9.7165 mL | 19.4329 mL | 38.8659 mL | 48.5824 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3887 mL | 1.9433 mL | 3.8866 mL | 7.7732 mL | 9.7165 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1943 mL | 0.9716 mL | 1.9433 mL | 3.8866 mL | 4.8582 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0389 mL | 0.1943 mL | 0.3887 mL | 0.7773 mL | 0.9716 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0194 mL | 0.0972 mL | 0.1943 mL | 0.3887 mL | 0.4858 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- ACT 335827
Catalog No.:BCC6346
CAS No.:1354039-86-3
- KH CB19
Catalog No.:BCC6135
CAS No.:1354037-26-5
- Bullatine A
Catalog No.:BCN2374
CAS No.:1354-84-3
- CX-6258 hydrochloride hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1505
CAS No.:1353858-99-7
- 8-Prenyldaidzein
Catalog No.:BCN4711
CAS No.:135384-00-8
- 12alpha-Methoxygrandiflorenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7771
CAS No.:135383-94-7
- 4'-Hydroxyisojasminin
Catalog No.:BCN7383
CAS No.:135378-09-5
- Isojasminin
Catalog No.:BCN7492
CAS No.:135378-08-4
- 5,7,3',4'-Tetrahydroxy-3-methoxy-8,5'-diprenylflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6848
CAS No.:1353676-65-9
- 8,8'-Bibaicalein
Catalog No.:BCN6549
CAS No.:135309-02-3
- MEN 10376
Catalog No.:BCC7133
CAS No.:135306-85-3
- 2''-O-Rhamnosylicariside II
Catalog No.:BCN3464
CAS No.:135293-13-9
- JW 480
Catalog No.:BCC6142
CAS No.:1354359-53-7
- 7-O-Prenylscopoletin
Catalog No.:BCN3547
CAS No.:13544-37-1
- Rehmapicrogenin
Catalog No.:BCN8507
CAS No.:135447-39-1
- Strontium Ranelate
Catalog No.:BCC3858
CAS No.:135459-87-9
- Araliadiol
Catalog No.:BCC8835
CAS No.:1354638-93-9
- Cabazitaxel intermediate
Catalog No.:BCN7432
CAS No.:1354900-65-4
- CYM 50260
Catalog No.:BCC6259
CAS No.:1355026-60-6
- ML 190
Catalog No.:BCC6308
CAS No.:1355244-02-8
- 2,3-Dihydro-12,13-dihydroxyeuparin
Catalog No.:BCN7189
CAS No.:135531-75-8
- Mutant IDH1-IN-1
Catalog No.:BCC6403
CAS No.:1355326-21-4
- AGI-5198
Catalog No.:BCC2293
CAS No.:1355326-35-0
- Cudraxanthone L
Catalog No.:BCN6187
CAS No.:135541-40-1
A case of ileus due to radiation enteritis 19 years after radiotherapy.[Pubmed:28381782]
Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2017;114(4):676-682.
A 73-year-old female visited our hospital complaining of nausea and epigastric pain because of ileus. She had a history of two laparotomy procedures in her youth, interferon treatment for chronic hepatitis C, and radiation therapy for uterine cervical cancer 19 years ago. Transanal double-balloon enteroscopy demonstrated annular stenosis with ulceration of the anal side of the dilated small intestine. Therefore, surgical resection was performed, and late radiation enteritis was diagnosed on histopathological examination. We report a case of ileus due to radiation enteritis 19 years after radiotherapy.
Correction: Evaluation of 19,460 Wheat Accessions Conserved in the Indian National Genebank to Identify New Sources of Resistance to Rust and Spot Blotch Diseases.[Pubmed:28384321]
PLoS One. 2017 Apr 6;12(4):e0175610.
[This corrects the article DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167702.].
Identification of a chemical probe for NAADP by virtual screening.[Pubmed:19234453]
Nat Chem Biol. 2009 Apr;5(4):220-6.
Research into the biological role of the Ca(2+)-releasing second messenger NAADP (nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate) has been hampered by a lack of chemical probes. To find new chemical probes for exploring NAADP signaling, we turned to virtual screening, which can evaluate millions of molecules rapidly and inexpensively. We used NAADP as the query ligand to screen the chemical library ZINC for compounds with similar three-dimensional shape and electrostatic properties. We tested the top-ranking hits in a sea urchin egg bioassay and found that one hit, Ned-19, blocks NAADP signaling at nanomolar concentrations. In intact cells, Ned-19 blocked NAADP signaling and fluorescently labeled NAADP receptors. Moreover, we show the utility of Ned-19 as a chemical probe by using it to demonstrate that NAADP is a key causal link between glucose sensing and Ca(2+) increases in mouse pancreatic beta cells.
Analogues of the nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) antagonist Ned-19 indicate two binding sites on the NAADP receptor.[Pubmed:19826006]
J Biol Chem. 2009 Dec 11;284(50):34930-4.
Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) is a Ca(2+)-releasing messenger. Biological data suggest that its receptor has two binding sites: one high-affinity locking site and one low-affinity opening site. To directly address the presence and function of these putative binding sites, we synthesized and tested analogues of the NAADP antagonist Ned-19. Ned-19 itself inhibits both NAADP-mediated Ca(2+) release and NAADP binding. A fluorometry bioassay was used to assess NAADP-mediated Ca(2+) release, whereas a radioreceptor assay was used to assess binding to the NAADP receptor (only at the high-affinity site). In Ned-20, the fluorine is para rather than ortho as in Ned-19. Ned-20 does not inhibit NAADP-mediated Ca(2+) release but inhibits NAADP binding. Conversely, Ned-19.4 (a methyl ester of Ned-19) inhibits NAADP-mediated Ca(2+) release but cannot inhibit NAADP binding. Furthermore, Ned-20 prevents the self-desensitization response characteristic of NAADP in sea urchin eggs, confirming that this response is mediated by a high-affinity allosteric site to which NAADP binds in the radioreceptor assay. Collectively, these data provide the first direct evidence for two binding sites (one high- and one low-affinity) on the NAADP receptor.
NAADP receptors mediate calcium signaling stimulated by endothelin-1 and norepinephrine in renal afferent arterioles.[Pubmed:19439521]
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009 Aug;297(2):F510-6.
The enzyme ADP-ribosyl (ADPR) cyclase plays a significant role in mediating increases in renal afferent arteriolar cytosolic calcium concentration ([Ca(2+)](i)) in vitro and renal vasoconstriction in vivo. ADPR cyclase produces cyclic ADP ribose, a second messenger that contributes importantly to ryanodine receptor-mediated Ca(2+) mobilization in renal vascular responses to several vasoconstrictors. Recent studies in nonrenal vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) have shown that nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP), another second messenger generated by ADPR cyclase, may contribute to Ca(2+) signaling. We tested the hypothesis that a Ca(2+) signaling pathway involving NAADP receptors participates in afferent arteriolar [Ca(2+)](i) responses to the G protein-coupled receptor agonists endothelin-1 (ET-1) and norepinephrine (NE). To test this, we isolated rat renal afferent arterioles and measured [Ca(2+)](I) using fura-2 fluorescence. We compared peak [Ca(2+)](i) increases stimulated by ET-1 and NE in the presence and absence of inhibitors of acidic organelle-dependent Ca(2+) signaling and NAADP receptors. Vacuolar H(+)-ATPase inhibitors bafilomycin A1 and concanamycin A, disruptors of pH and Ca(2+) stores of lysosomes and other acidic organelles, individually antagonized [Ca(2+)](i) responses to ET-1 and NE by 40-50% (P < 0.05). The recently discovered NAADP receptor inhibitor Ned-19 attenuated [Ca(2+)](i) responses to ET-1 or NE by 60-70% (P < 0.05). We conclude that NAADP receptors contribute to both ET-1- and NE-induced [Ca(2+)](i) responses in afferent arterioles, an effect likely dependent on acidic vesicle, possibly involving lysosome, signaling in VSMC in the renal microcirculation.


