L-xyloseCAS# 609-06-3 |
- D-Arabinose
Catalog No.:BCN3791
CAS No.:10323-20-3
- DL-Arabinose
Catalog No.:BCN8541
CAS No.:147-81-9
- D-(+)-Xylose
Catalog No.:BCN1010
CAS No.:58-86-6
- D-Ribose
Catalog No.:BCN9063
CAS No.:50-69-1
- D-Lyxose
Catalog No.:BCX0719
CAS No.:1114-34-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 609-06-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 95259.0 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C5H10O5 | M.Wt | 150.13 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
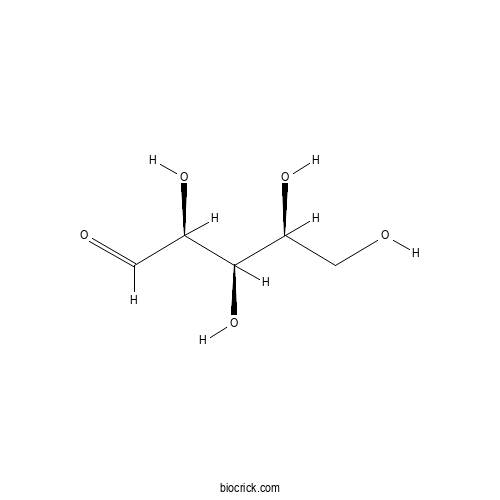
| Chemical Name | (2S,3R,4S)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentanal | ||
| SMILES | C(C(C(C(C=O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PYMYPHUHKUWMLA-WISUUJSJSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C5H10O5/c6-1-3(8)5(10)4(9)2-7/h1,3-5,7-10H,2H2/t3-,4+,5+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

L-xylose Dilution Calculator

L-xylose Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.6609 mL | 33.3045 mL | 66.6089 mL | 133.2179 mL | 166.5223 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.3322 mL | 6.6609 mL | 13.3218 mL | 26.6436 mL | 33.3045 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6661 mL | 3.3304 mL | 6.6609 mL | 13.3218 mL | 16.6522 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1332 mL | 0.6661 mL | 1.3322 mL | 2.6644 mL | 3.3304 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0666 mL | 0.333 mL | 0.6661 mL | 1.3322 mL | 1.6652 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 8-Epi-Loganic acid-6'-O-β-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0643
CAS No.:176226-39-4
- Isokadsuranin
Catalog No.:BCX0642
CAS No.:82467-52-5
- 2-O-β-D-Glucopyranosyl-L-ascorbic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0641
CAS No.:562043-82-7
- Gymnoside IX
Catalog No.:BCX0640
CAS No.:898827-00-4
- Palmitoleic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCX0639
CAS No.:1120-25-8
- Schiarisanrin A
Catalog No.:BCX0638
CAS No.:130252-41-4
- Lucidin Omega-Methyl Ether
Catalog No.:BCX0637
CAS No.:79560-36-4
- Crocetin methylester
Catalog No.:BCX0636
CAS No.:25368-09-6
- Manzamine A
Catalog No.:BCX0635
CAS No.:104196-68-1
- Ocimene
Catalog No.:BCX0634
CAS No.:13877-91-3
- N-Methyl-1-deoxynojirimycin
Catalog No.:BCX0633
CAS No.:69567-10-8
- Monoethyl fumaric acid
Catalog No.:BCX0632
CAS No.:2459-05-4
- Apigenin-6-C-β-D-xylopyranosyl-8-C-α-L-arabinopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX0645
CAS No.:85700-46-5
- Phytosphingosine
Catalog No.:BCX0646
CAS No.:554-62-1
- Genistein 8-C-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0647
CAS No.:66026-80-0
- Coniferylaldehydel
Catalog No.:BCX0648
CAS No.:458-36-6
- D-Tartaric acid
Catalog No.:BCX0649
CAS No.:147-71-7
- 4-Ethoxybenzyl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCX0650
CAS No.:6214-44-4
- Dehydrosulphurenic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0651
CAS No.:175615-56-2
- Coumalic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0652
CAS No.:500-05-0
- 3-Indoleacetamide
Catalog No.:BCX0653
CAS No.:879-37-8
- 8,9-epoxy-3-isobutyryloxy-10-(2-methylbutanoyl)thymol
Catalog No.:BCX0654
CAS No.:22518-07-6
- 4-O-galloylalbiflorin
Catalog No.:BCX0655
CAS No.:1201580-97-3
- Glycyroside
Catalog No.:BCX0656
CAS No.:125310-04-5
Lipopolysaccharides from Ralstonia solanacearum induce a broad metabolomic response in Solanum lycopersicum.[Pubmed:37635940]
Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Aug 10;10:1232233.
Ralstonia solanacearum, one of the most destructive crop pathogens worldwide, causes bacterial wilt disease in a wide range of host plants. The major component of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, lipopolysaccharides (LPS), has been shown to function as elicitors of plant defense leading to the activation of signaling and defense pathways in several plant species. LPS from a R. solanacearum strain virulent on tomato (LPS(R. sol.)), were purified, chemically characterized, and structurally elucidated. The lipid A moiety consisted of tetra- to hexa-acylated bis-phosphorylated disaccharide backbone, also decorated by aminoarabinose residues in minor species, while the O-polysaccharide chain consisted of either linear tetrasaccharide or branched pentasaccharide repeating units containing alpha-L-rhamnose, N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosamine, and beta-L-xylose. These properties might be associated with the evasion of host surveillance, aiding the establishment of the infection. Using untargeted metabolomics, the effect of LPS(R. sol.) elicitation on the metabolome of Solanum lycopersicum leaves was investigated across three incubation time intervals with the application of UHPLC-MS for metabolic profiling. The results revealed the production of oxylipins, e.g., trihydroxy octadecenoic acid and trihydroxy octadecadienoic acid, as well as several hydroxycinnamic acid amide derivatives, e.g., coumaroyl tyramine and feruloyl tyramine, as phytochemicals that exhibit a positive correlation to LPS(R. sol.) treatment. Although the chemical properties of these metabolite classes have been studied, the functional roles of these compounds have not been fully elucidated. Overall, the results suggest that the features of the LPS(R. sol.) chemotype aid in limiting or attenuating the full deployment of small molecular host defenses and contribute to the understanding of the perturbation and reprogramming of host metabolism during biotic immune responses.
Highly Stereoselective Synthesis of Bis-C-ferrocenyl Glycosides via Palladium-Catalyzed Directed C-H Glycosylation.[Pubmed:37231656]
Org Lett. 2023 Jun 9;25(22):4070-4074.
Conjugation of carbohydrates to ferrocene scaffolds is of great value in drug design, given the nontoxic and lipophilic nature of ferrocene. However, the efficient and stereoselective synthesis of C-ferrocenyl glycosides remains a challenge. Herein, we developed a Pd-catalyzed stereoselective C-H glycosylation to provide rapid access to sole bis-C-ferrocenyl glycosides in good to high yields (up to 98% yield) with exclusive stereoselectivity. A diverse range of glycosyl chlorides were well tolerated, including d-mannose, d-glucose, L-xylose, l-rhamnose, d-mannofuranose, and d-ribofuranose. Additionally, a mononuclear Pd(II) intermediate was characterized by X-ray single-crystal diffraction, and might participate in the C-H palladation step.


