LY2811376Non-peptidic BACE1 inhibitor CAS# 1194044-20-6 |
- INCB28060
Catalog No.:BCC3793
CAS No.:1029712-80-8
- c-Met inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC1488
CAS No.:1357072-61-7
- PHA-665752
Catalog No.:BCC1181
CAS No.:477575-56-7
- Cabozantinib (XL184, BMS-907351)
Catalog No.:BCC1264
CAS No.:849217-68-1
- Tivantinib (ARQ 197)
Catalog No.:BCC3688
CAS No.:905854-02-6
- PF-04217903 methanesulfonate
Catalog No.:BCC1849
CAS No.:956906-93-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1194044-20-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 44251605 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H14F2N4S | M.Wt | 320.4 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 31 mg/mL (96.77 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
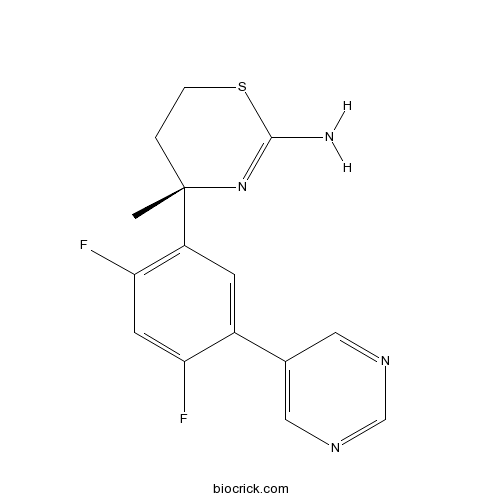
| Chemical Name | (4S)-4-(2,4-difluoro-5-pyrimidin-5-ylphenyl)-4-methyl-5,6-dihydro-1,3-thiazin-2-amine | ||
| SMILES | CC1(CCSC(=N1)N)C2=C(C=C(C(=C2)C3=CN=CN=C3)F)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MJQMRGWYPNIERM-HNNXBMFYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H14F2N4S/c1-15(2-3-22-14(18)21-15)11-4-10(12(16)5-13(11)17)9-6-19-8-20-7-9/h4-8H,2-3H2,1H3,(H2,18,21)/t15-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | IC50: 239-249 nM (BACE1) |

LY2811376 Dilution Calculator

LY2811376 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1211 mL | 15.6055 mL | 31.211 mL | 62.422 mL | 78.0275 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6242 mL | 3.1211 mL | 6.2422 mL | 12.4844 mL | 15.6055 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3121 mL | 1.5605 mL | 3.1211 mL | 6.2422 mL | 7.8027 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0624 mL | 0.3121 mL | 0.6242 mL | 1.2484 mL | 1.5605 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0312 mL | 0.1561 mL | 0.3121 mL | 0.6242 mL | 0.7803 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
LY2811376 is a non-peptidic inhibitor of BACE1.
Beta-secretase 1 (BACE1) is an aspartic-acid protease that cleaves the amyloid precursor protein (APP) into amyloid-βpeptide (Aβ), which plays a critical role in Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
In recombinant enzyme assays, LY2811376 inhibited hBACE1 with IC50 values of 249 nM and 239 nM against a larger chimeric protein substrate and a small synthetic peptide, respectively. In a human embryonic kidney cell line overexpressed APP, LY2811376 decreased Aβ secretion with EC50 value of 300 nM in a concentration-dependant way [1]. In SH-SY5Y cells, LY2811376 reduced Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 secreted to the cell medium while increased the level of Aβ5-40 [2].
In the APPV717F mouse, LY2811376 significantly reduced Aβ, as well as sAPP and C99, the cleavage products of APP by BACE1 [1]. In a healthy population (n =18), LY2811376 (30 mg, 90 mg) increased Aβ5-40 and Aβ5-X in a dose-dependant way, while Aβ1-34 reduced in a same way. These results suggested that LY2811376 inhibited N-terminally truncated Aβ peptides in a BACE1-independent pathway [2].
References:
[1]. May PC, Dean RA, Lowe SL, et al. Robust Central Reduction of Amyloid- in Humans with an
Orally Available, Non-Peptidic -Secretase Inhibitor. J Neurosci, 2011, 31(46): 16507-16516.
[2]. Portelius E, Dean RA, Andreasson U, et al. β-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) inhibitor treatment induces Aβ5-X peptides through alternative amyloid precursor protein cleavage. Alzheimers Res Ther, 2014, 6(5-8): 75.
- Przewalskin
Catalog No.:BCN6080
CAS No.:119400-87-2
- Salviolone
Catalog No.:BCN3141
CAS No.:119400-86-1
- 2,5-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN6081
CAS No.:1194-98-5
- mAChR-IN-1
Catalog No.:BCC5512
CAS No.:119391-56-9
- 2-Deacetoxytaxinine J
Catalog No.:BCN7291
CAS No.:119347-14-7
- CRANAD 2
Catalog No.:BCC6293
CAS No.:1193447-34-5
- 2-Hydroxydiplopterol
Catalog No.:BCN7290
CAS No.:1193250-54-2
- Olean-12-ene-3,24-diol
Catalog No.:BCN6079
CAS No.:119318-15-9
- 2-Benzyl-2-(dimethylamino)-4'-morpholinobutyrophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8563
CAS No.:119313-12-1
- Pinobanksin 5-methyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN7775
CAS No.:119309-36-3
- Atalantoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN4857
CAS No.:119309-02-3
- Rocuronium Bromide
Catalog No.:BCC1068
CAS No.:119302-91-9
- Topotecan hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN2604
CAS No.:119413-54-6
- Licoricesaponin E2
Catalog No.:BCN7894
CAS No.:119417-96-8
- Galanin (1-30) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC6961
CAS No.:119418-04-1
- Loureirin A
Catalog No.:BCN3671
CAS No.:119425-89-7
- Loureirin B
Catalog No.:BCN5021
CAS No.:119425-90-0
- Eliprodil
Catalog No.:BCC7280
CAS No.:119431-25-3
- Fruquintinib(HMPL-013)
Catalog No.:BCC6415
CAS No.:1194506-26-7
- Meropenem trihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4226
CAS No.:119478-56-7
- Ethyllucidone
Catalog No.:BCN6082
CAS No.:1195233-59-0
- Ceanothic acid acetate
Catalog No.:BCN6083
CAS No.:119533-63-0
- Othonnine
Catalog No.:BCN2061
CAS No.:119565-25-2
- N,N-Dimethylsphingosine
Catalog No.:BCC7959
CAS No.:119567-63-4
Robust central reduction of amyloid-beta in humans with an orally available, non-peptidic beta-secretase inhibitor.[Pubmed:22090477]
J Neurosci. 2011 Nov 16;31(46):16507-16.
According to the amyloid cascade hypothesis, cerebral deposition of amyloid-beta peptide (Abeta) is critical for Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathogenesis. Abeta generation is initiated when beta-secretase (BACE1) cleaves the amyloid precursor protein. For more than a decade, BACE1 has been a prime target for designing drugs to prevent or treat AD. However, development of such agents has turned out to be extremely challenging, with major hurdles in cell penetration, oral bioavailability/metabolic clearance, and brain access. Using a fragment-based chemistry strategy, we have generated LY2811376 [(S)-4-(2,4-difluoro-5-pyrimidin-5-yl-phenyl)-4-methyl-5,6-dihydro-4H-[1,3]thiazi n-2-ylamine], the first orally available non-peptidic BACE1 inhibitor that produces profound Abeta-lowering effects in animals. The biomarker changes obtained in preclinical animal models translate into man at doses of LY2811376 that were safe and well tolerated in healthy volunteers. Prominent and long-lasting Abeta reductions in lumbar CSF were measured after oral dosing of 30 or 90 mg of LY2811376. This represents the first translation of BACE1-driven biomarker changes in CNS from preclinical animal models to man. Because of toxicology findings identified in longer-term preclinical studies, this compound is no longer progressing in clinical development. However, BACE1 remains a viable target because the adverse effects reported here were recapitulated in LY2811376-treated BACE1 KO mice and thus are unrelated to BACE1 inhibition. The magnitude and duration of central Abeta reduction obtainable with BACE1 inhibition positions this protease as a tractable small-molecule target through which to test the amyloid hypothesis in man.
Near-infrared fluorescence molecular imaging of amyloid beta species and monitoring therapy in animal models of Alzheimer's disease.[Pubmed:26199414]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Aug 4;112(31):9734-9.
Near-infrared fluorescence (NIRF) molecular imaging has been widely applied to monitoring therapy of cancer and other diseases in preclinical studies; however, this technology has not been applied successfully to monitoring therapy for Alzheimer's disease (AD). Although several NIRF probes for detecting amyloid beta (Abeta) species of AD have been reported, none of these probes has been used to monitor changes of Abetas during therapy. In this article, we demonstrated that CRANAD-3, a curcumin analog, is capable of detecting both soluble and insoluble Abeta species. In vivo imaging showed that the NIRF signal of CRANAD-3 from 4-mo-old transgenic AD (APP/PS1) mice was 2.29-fold higher than that from age-matched wild-type mice, indicating that CRANAD-3 is capable of detecting early molecular pathology. To verify the feasibility of CRANAD-3 for monitoring therapy, we first used the fast Abeta-lowering drug LY2811376, a well-characterized beta-amyloid cleaving enzyme-1 inhibitor, to treat APP/PS1 mice. Imaging data suggested that CRANAD-3 could monitor the decrease in Abetas after drug treatment. To validate the imaging capacity of CRANAD-3 further, we used it to monitor the therapeutic effect of CRANAD-17, a curcumin analog for inhibition of Abeta cross-linking. The imaging data indicated that the fluorescence signal in the CRANAD-17-treated group was significantly lower than that in the control group, and the result correlated with ELISA analysis of brain extraction and Abeta plaque counting. It was the first time, to our knowledge, that NIRF was used to monitor AD therapy, and we believe that our imaging technology has the potential to have a high impact on AD drug development.


