LY2940680Hedgehog/SMO antagonist,inhibits Hh signaling CAS# 1258861-20-9 |
- Cyclopamine
Catalog No.:BCN2964
CAS No.:4449-51-8
- Purmorphamine
Catalog No.:BCC3641
CAS No.:483367-10-8
- GANT61
Catalog No.:BCC1090
CAS No.:500579-04-4
- GANT 58
Catalog No.:BCC1587
CAS No.:64048-12-0
- GDC-0449 (Vismodegib)
Catalog No.:BCC1285
CAS No.:879085-55-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1258861-20-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 49848070 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H24F4N6O | M.Wt | 512.5 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Taladegib | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 50 mg/mL (97.56 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
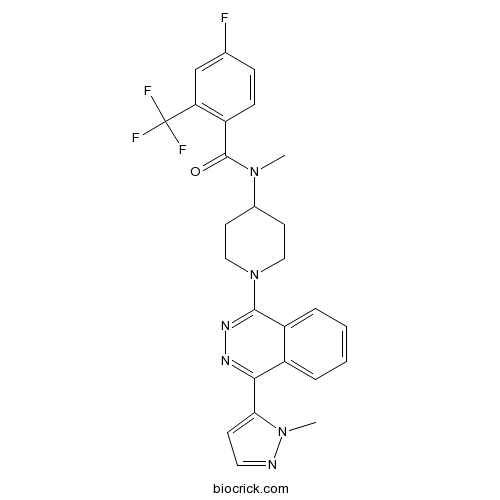
| Chemical Name | 4-fluoro-N-methyl-N-[1-[4-(2-methylpyrazol-3-yl)phthalazin-1-yl]piperidin-4-yl]-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide | ||
| SMILES | CN1C(=CC=N1)C2=NN=C(C3=CC=CC=C32)N4CCC(CC4)N(C)C(=O)C5=C(C=C(C=C5)F)C(F)(F)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SZBGQDXLNMELTB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H24F4N6O/c1-34(25(37)20-8-7-16(27)15-21(20)26(28,29)30)17-10-13-36(14-11-17)24-19-6-4-3-5-18(19)23(32-33-24)22-9-12-31-35(22)2/h3-9,12,15,17H,10-11,13-14H2,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | LY2940680 is a potent inhibitor of Smoothened (Smo) receptor and Hedgehog (Hh) signaling. | |||||
| Targets | Smoothened | |||||

LY2940680 Dilution Calculator

LY2940680 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9512 mL | 9.7561 mL | 19.5122 mL | 39.0244 mL | 48.7805 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3902 mL | 1.9512 mL | 3.9024 mL | 7.8049 mL | 9.7561 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1951 mL | 0.9756 mL | 1.9512 mL | 3.9024 mL | 4.878 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.039 mL | 0.1951 mL | 0.3902 mL | 0.7805 mL | 0.9756 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0195 mL | 0.0976 mL | 0.1951 mL | 0.3902 mL | 0.4878 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
LY2940680 is a selective inhibitor of Smo receptor and thus inhibits Hh signaling pathway [1].
Smoothened(Smo) receptor is a member of class F G protein-coupled receptors, which plays an important role in the main transducer of the Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway that implicated in a wide range of developmental and adult processes [2].
LY2940680 is a potent Smo receptor inhibitor that binds mostly to extracelluar loops and has a different functioning site with the reported Smo receptor inhibitor SANT-1 which binds to 7TM [2]. When tested with cell lines containing a mutation in the gene encoding Smoothened that researchers had previously observed in patient with cancer who developed resistance to vismodegib, LY2940680 inhibited cell proliferation [3].
Many studies have shown that Hh signaling pathway plays a pivotal role in CSCs and Hh inhibition caused many aspects of transformation attributed to CSCs. In patients with basal cell carcinoma and medulloblastoma, LY2940680 showed good efficacy as a monotherapy [1].
References:
[1]. Justilien, V. and A.P. Fields, Molecular pathways: novel approaches for improved therapeutic targeting of Hedgehog signaling in cancer stem cells. Clin Cancer Res, 2015. 21(3): p. 505-13.
[2]. Hoch, L., et al., MRT-92 inhibits Hedgehog signaling by blocking overlapping binding sites in the transmembrane domain of the Smoothened receptor. Faseb j, 2015. 29(5): p. 1817-29.
[3]. Redmond, E.M., et al., Investigational Notch and Hedgehog inhibitors--therapies for cardiovascular disease. Expert Opin Investig Drugs, 2011. 20(12): p. 1649-64.
- 9-O-Ethyldeacetylorientalide
Catalog No.:BCN7311
CAS No.:1258517-60-0
- Deacetylorientalide
Catalog No.:BCN7310
CAS No.:1258517-59-7
- Parathyroid Hormone (1-34), bovine
Catalog No.:BCC1040
CAS No.:12583-68-5
- Pristimerin
Catalog No.:BCN2315
CAS No.:1258-84-0
- CEP-33779
Catalog No.:BCC2199
CAS No.:1257704-57-6
- Amikacin hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4621
CAS No.:1257517-67-1
- TBA354
Catalog No.:BCC6459
CAS No.:1257426-19-9
- TC-E 5006
Catalog No.:BCC7981
CAS No.:1257395-14-4
- GSK 789472 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7818
CAS No.:1257326-24-1
- NPEC-caged-dopamine
Catalog No.:BCC7837
CAS No.:1257326-23-0
- NPEC-caged-serotonin
Catalog No.:BCC7836
CAS No.:1257326-22-9
- NPEC-caged-(S)-3,4-DCPG
Catalog No.:BCC7652
CAS No.:1257323-85-5
- (+)-Glaucarubinone
Catalog No.:BCN7956
CAS No.:1259-86-5
- 24-Methylenecycloartanol acetate
Catalog No.:BCN6137
CAS No.:1259-94-5
- SAMS Peptide
Catalog No.:BCC5745
CAS No.:125911-68-4
- JP 1302 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7449
CAS No.:1259314-65-2
- VU 0155041 sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7642
CAS No.:1259372-69-4
- SCH 23390 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6849
CAS No.:125941-87-9
- 10-O-Ethylcannabitriol
Catalog No.:BCN7312
CAS No.:1259515-25-7
- Griseofulvin
Catalog No.:BCC5327
CAS No.:126-07-8
- Solasodine
Catalog No.:BCN2346
CAS No.:126-17-0
- Sarsasapogenin
Catalog No.:BCN1269
CAS No.:126-19-2
- Oxethazaine
Catalog No.:BCC3832
CAS No.:126-27-2
- Polygalic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3172
CAS No.:1260-04-4
Molecular modeling study on the dynamical structural features of human smoothened receptor and binding mechanism of antagonist LY2940680 by metadynamics simulation and free energy calculation.[Pubmed:24637074]
Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jul;1840(7):2128-38.
BACKGROUND: The smoothened (SMO) receptor, one of the Class F G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), is an essential component of the canonical hedgehog signaling pathway which plays a key role in the regulation of embryonic development in animals. The function of the SMO receptor can be modulated by small-molecule agonists and antagonists, some of which are potential antitumour agents. Understanding the binding mode of an antagonist in the SMO receptor is crucial for the rational design of new antitumour agents. METHODS: Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation and dynamical network analysis are used to study the dynamical structural features of SMO receptor. Metadynamics simulation and free energy calculation are employed to explore the binding mechanism between the antagonist and SMO receptor. RESULTS: The MD simulation results and dynamical network analysis show that the conserved KTXXXW motif in helix VIII has strong interaction with helix I. The alpha-helical extension of transmembrane 6 (TM6) is detected as part of the ligand-binding pocket and dissociation pathway of the antagonist. The metadynamics simulation results illustrate the binding mechanism of the antagonist in the pocket of SMO receptor, and free energy calculation shows the antagonist needs to overcome about 38kcal/mol of energy barrier to leave the binding pocket of SMO receptor. CONCLUSIONS: The unusually long TM6 plays an important role on the binding behavior of the antagonist in the pocket of SMO receptor. GENERAL SIGNIFICANCE: The results can not only profile the binding mechanism between the antagonist and Class F GPCRs, but also supply the useful information for the rational design of a more potential small molecule antagonist bound to SMO receptor.


