Methyl brevifolincarboxylateCAS# 154702-76-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 154702-76-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5319518.0 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H10O8 | M.Wt | 306.23 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
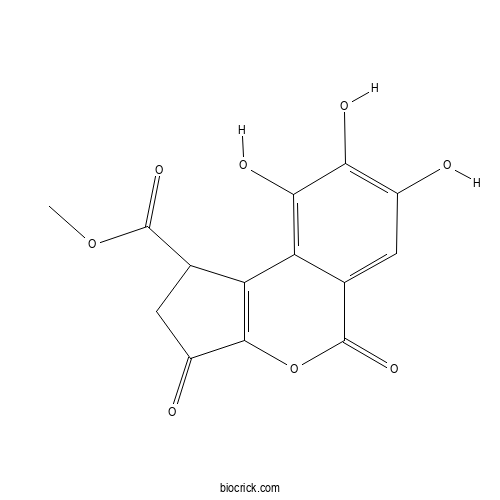
| Chemical Name | methyl 7,8,9-trihydroxy-3,5-dioxo-1,2-dihydrocyclopenta[c]isochromene-1-carboxylate | ||
| SMILES | COC(=O)C1CC(=O)C2=C1C3=C(C(=C(C=C3C(=O)O2)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JNWDNAASYHRXMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H10O8/c1-21-13(19)5-3-7(16)12-9(5)8-4(14(20)22-12)2-6(15)10(17)11(8)18/h2,5,15,17-18H,3H2,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Methyl brevifolincarboxylate Dilution Calculator

Methyl brevifolincarboxylate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2655 mL | 16.3276 mL | 32.6552 mL | 65.3104 mL | 81.638 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6531 mL | 3.2655 mL | 6.531 mL | 13.0621 mL | 16.3276 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3266 mL | 1.6328 mL | 3.2655 mL | 6.531 mL | 8.1638 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0653 mL | 0.3266 mL | 0.6531 mL | 1.3062 mL | 1.6328 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0327 mL | 0.1633 mL | 0.3266 mL | 0.6531 mL | 0.8164 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Rubropunctatin
Catalog No.:BCX1149
CAS No.:514-67-0
- Toralactone
Catalog No.:BCX1148
CAS No.:41743-74-2
- Eicosapentaenoic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1147
CAS No.:10417-94-4
- 24(28)-Dehydroergosterol
Catalog No.:BCX1146
CAS No.:29560-24-5
- Jaligonic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1145
CAS No.:51776-39-7
- Reptoside
Catalog No.:BCX1144
CAS No.:53839-03-5
- Euphornin
Catalog No.:BCX1143
CAS No.:80454-47-3
- Hydroxypropyl tetrahydropyrantriol
Catalog No.:BCX1142
CAS No.:439685-79-7
- Presenegenin
Catalog No.:BCX1141
CAS No.:2163-40-8
- Ligustrosidic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1140
CAS No.:96382-89-7
- 3α-Hydroxymogrol
Catalog No.:BCX1139
CAS No.:1343402-73-2
- N-methyltyramine
Catalog No.:BCX1138
CAS No.:370-98-9
- Butyl neochlorogenate
Catalog No.:BCX1151
CAS No.:409361-64-4
- Butyl chlorogenate
Catalog No.:BCX1152
CAS No.:132741-56-1
- Spicatine A
Catalog No.:BCX1153
CAS No.:124256-81-1
- Aljesaconitine B
Catalog No.:BCX1154
CAS No.:101247-24-9
- Pyroside
Catalog No.:BCX1155
CAS No.:10338-88-2
- Proprotogracillin
Catalog No.:BCX1156
CAS No.:78229-03-5
- Kadsurenone
Catalog No.:BCX1157
CAS No.:95851-37-9
- Neolinustatin
Catalog No.:BCX1158
CAS No.:72229-42-6
- Neotheaflavin
Catalog No.:BCX1159
CAS No.:36451-14-6
- Zingiberene
Catalog No.:BCX1160
CAS No.:495-60-3
- Soyasaponin Af
Catalog No.:BCX1161
CAS No.:117230-32-7
- Soyasaponin Ae
Catalog No.:BCX1162
CAS No.:117230-34-9
Methyl Brevifolincarboxylate Attenuates Free Fatty Acid-Induced Lipid Metabolism and Inflammation in Hepatocytes through AMPK/NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway.[Pubmed:34576229]
Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 17;22(18):10062.
The prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is one of the leading causes of chronic liver diseases worldwide. This study examined the potential protective effects of a naturally occurring polyphenolic compound, Methyl brevifolincarboxylate (MBC) on fatty liver injury in vitro. The results showed that MBC at its non-cytotoxic concentrations, reduced lipid droplet accumulation and triglyceride (TG) levels in the oleic acid (OA)-treated human hepatocarcinoma cell line, SK-HEP-1 and murine primary hepatocytes. In OA-treated SK-HEP-1 cells and primary murine hepatocytes, MBC attenuated the mRNA expression levels of the de novo lipogenesis molecules, acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase (Acc1), fatty acid synthase (Fasn) and sterol regulatory element binding protein 1c (Srebp1c). MBC promoted the lipid oxidation factor peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-alpha (Pparalpha), and its target genes, carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1 (Cpt1) and acyl-coenzyme A oxidase 1 (Acox1) in both the SK-HEP-1 cells and primary murine hepatocytes. The mRNA results were further supported by the attenuated protein expression of lipogenesis and lipid oxidation molecules in OA-treated SK-HEP-1 cells. The MBC increased the expression of AMP activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation. On the other hand, MBC treatment dampened the inflammatory mediator's, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-8, and IL-1beta secretion, and nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB expression (mRNA and protein) through reduced reactive oxygen species production in OA-treated SK-HEP-1 cells. Taken together, our results demonstrated that MBC possessed potential protective effects against NAFLD in vitro by amelioration of lipid metabolism and inflammatory markers through the AMPK/NF-kappaB signaling pathway.
Methyl brevifolincarboxylate, a novel influenza virus PB2 inhibitor from Canarium Album (Lour.) Raeusch.[Pubmed:32519462]
Chem Biol Drug Des. 2020 Nov;96(5):1280-1291.
Methyl brevifolincarboxylate (MBC) was isolated from ethyl acetate extract of Canarium album (Lour.) Raeusch. The structure was identified, and the effect on influenza A virus infection was evaluated. MBC exhibited inhibitory activity against influenza virus A/Puerto Rico/8/34 (H1N1) and A/Aichi/2/68 (H3N2) with IC(50) values of 27.16 +/- 1.39 muM and 33.41 +/- 2.34 muM. Mechanism studies indicated that MBC inhibited the replication of influenza A virus by targeting PB2 cap-binding domain. Our results demonstrated MBC was a potent PB2 cap-binding inhibitor and represented as a new type of promising lead compound for the development of anti-influenza virus drugs from natural products.
Chromatographic fingerprint and the simultaneous determination of five bioactive components of geranium carolinianum L. water extract by high performance liquid chromatography.[Pubmed:22272101]
Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(12):8740-9.
A simple and sensitive HPLC method has been developed in combination with fingerprint analysis and simultaneous determination of five markers, namely gallic acid, corilagin, Methyl brevifolincarboxylate, ellagic acid and rutin for evaluation and quality control of Geranium carolinianum L. water extract. Extraction methods were optimized by comparing the hydrolysis efficiency of geraniin, a major tannin of the herb, resulting in the method of extraction with water under reflux. Water extracts were analyzed by HPLC, with a mobile phase of 0.1% aqueous phosphoric acid (v/v) and acetonitrile in a gradient program within 65 min. Compounds were detected at 274 nm UV wavelength. For fingerprint analysis, 17 peaks were selected as the characteristic peaks to evaluate the similarities of different samples collected from the suburb of Nanjing. The correlation coefficients of similarity were greater than 0.993. In quantitative analysis, the five selected markers showed good regression (R > 0.9991) within test ranges, and the average recoveries were between 97.2-101.7% and their RSD values were less than 4.50%. The total contents of the five markers varied from 44.28 to 71.84 mg/g. The method can be very useful for further development of G. carolinianum L. extracts and preparations.
[Phenols from Euphorbia humifusa].[Pubmed:20506823]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2010 Mar;35(5):613-5.
The investigation on the herbal of Euphorbia humifusa Wild. was carried out to find its anti-HBV constituents. The isolation and purification were performed by chromatography such as macroporous resin, polyamide, Sephadex LH-20, MCI GEL CHP 20P and so on. Based on the spectral analysis, seven phenols were identified as brevifolin (1), brevifolin carboxylic acid (2), Methyl brevifolincarboxylate (3), phyllanthussin E methyl ester (4), sanguisorbic acid dilactone (5), 3,3'-2-di-O-methyl ellagic acid (6), ellagic acid (7). Among them, Compounds 2-6 were isolated from this plant for the first time.
Ellagitannins from Geranium potentillaefolium and G. bellum.[Pubmed:20433066]
Nat Prod Commun. 2010 Apr;5(4):531-4.
The aerial parts of Geranium potentillaefoium afforded geraniin (1), corilagin (2), gallic acid (4), methyl gallate (6), Methyl brevifolincarboxylate (7), quercetin, quercetin 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, quercetin 3-O-beta-D-[6"-O-galloyl)glucopyranoside, kaempferol, beta-sitosterol 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside and beta-sitosterol, while the aerial parts of G. bellum gave the same compounds in addition to kaempferol 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, isolated instead of kaempferol. The substances were identified by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy in comparison with published data. The water decoction preparations from air-dried plant materials (2.5 g) contain ca. 4.6 % of the ellagitannin 1, envisaging that when such decoction is ingested (250 mL), a therapeutic dose of ca. 36 mg of the antitumor ellagic acid (3) may be incorporated into the organism.
Determination of polyphenolics in extracts of Potentilla species by high-performance thin-layer chromatography photodensitometry method.[Pubmed:19845038]
Phytochem Anal. 2010 Mar-Apr;21(2):174-9.
INTRODUCTION: Separation of polyphenolics in different plant materials using high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) represents an effective method for their detection and quantification. OBJECTIVE: To develop a simple, specific, precise, sensitive and accurate method for the simultaneous quantification of tiliroside (TRS), Methyl brevifolincarboxylate (MBR) and ellagic acid (EA) in a plant extract using the HPTLC-photodensitometry method. METHODOLOGY: Aerial parts of the selected Potentilla species, P. anserina, P. erecta, P. grandiflora and P. nepalensis var. 'Miss Willmott', were extracted with methanol. After solvent evaporation, the methanolic extracts were diluted with water and successively partitioned between chloroform and then diethyl ether. The diethyl ether extracts from each sample were used for quantification. The analyses were performed on HPTLC precoated silica gel 60F(254) plates with toluene-ethyl formate-formic acid (6 : 4 : 1 v/v/v) as the mobile phase (distance of 7.5 cm). Densitometric detections of TRS, MBR and EA were performed at 320, 287 and 280 nm, respectively. The amounts of these compounds were calculated using the regression equations of the calibration curves, which were linear within a range of 0.05-0.5 microg/spot (R(2) = 0.9957) for TRS, 0.05-0.525 microg/spot (R(2) = 0.9965) for MBR and 0.0525-0.5 microg/spot (R(2) = 0.9998) for EA. RESULTS: The amounts of marker compounds measured by the method developed are expressed in mg/g of dry extracts. TRS ranged from 20.3 +/- 0.3 mg/g for P. erecta herbs to 197.7 +/- 2.9 mg/g for P. grandiflora herbs; MBR ranged from 5.0 +/- 0.6 mg/g for P. erecta herbs to 68.5 +/- 3.4 mg/g for P. nepalensis flowers; and EA ranged from 24.0 +/- 0.6 mg/g for P. erecta herbs to 216.2 +/- 3.2 mg/g for P. anserina leaves. CONCLUSION: The proposed method was found to be relatively simple, specific, precise, sensitive and accurate and may be used for the routine assay of simultaneous determination of TRS, MBR and EA in other extracts and phytomedicines containing Potentilla species.
Human DNA topoisomerase inhibitors from Potentilla argentea and their cytotoxic effect against MCF-7.[Pubmed:18557426]
Pharmazie. 2008 May;63(5):389-93.
Two polyphenolics, kaempferol 3-O-beta-D-(6"-E-p-coumaroyl)-glucopyranoside (tiliroside) (1) and Methyl brevifolincarboxylate (2) isolated from aerial parts of Potentilla argentea L. (Rosaceae) were evaluated for their cytotoxicities against human breast carcionoma cell line (MCF-7) and their DNA-binding ability. The DNA-binding ability of these compounds was studied by means of the human DNA topoisomerase I and II inhibition assay and ethidium displacement assay using calf thymus DNA, poly(dA-dT)2 and poly(dG-dC)2. Compound 2 was much more active and showed a higher level of cytotoxic potency than compound 1, with IC50 values of 1.11 +/- 2 microM and 21.60 +/- 2 microM, respectively. In DNA topoisomerase I and II inhibition in vitro assays both investigated compounds 1 and 2 were more effective against topoisomerase II than I. The results of DNA binding studies reveal that Methyl brevifolincarboxylate had a greater DNA binding affinity that tiliroside, which correlates with its greater potency as a topoisomerase I/II inhibitor.
Anti-oxidant and inflammatory mediator's growth inhibitory effects of compounds isolated from Phyllanthus urinaria.[Pubmed:18187278]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Mar 5;116(2):333-40.
Phyllanthus urinaria Linnea (Euphorbiaceae), is a traditional anti-hepatitis herb used in Taiwan. In continuation of our search for potent natural anti-inflammatory agents, from the ethanolic extract of this plant, nine compounds including phyllanthin (1), phyltetralin (2), trimethyl-3,4-dehydrochebulate (3), methylgallate (4), and rhamnocitrin (5), Methyl brevifolincarboxylate (6), beta-sitosterol-3-O-beta-d-glucopyranoside (7), quercitrin (8), and rutin (9) were isolated. The structures of compounds 3 and 6 were established based on NMR and mass spectral studies. The isolates 1-9 were investigated for their antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities in vitro. In the antioxidant assay, the isolates 3, 4 and 6 exhibited significant DPPH radical scavenging activity with an IC(50) value of 9.4, 9.8 and 8.9 microM, respectively. On the other hand, in the inflammatory mediators growth inhibitory assay from LPS/interferon (IFN)-gamma-activated peritoneal macrophages, all the isolates except 7, significantly and dose-dependently inhibited the enhanced production of NO radicals, and such modulation was closely associated with the inhibition of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and interleukin (IL)-6. In addition, 30 microM of isolates 3 and 6, and 50 microM of 4, significantly arrest the mitogen-stimulated spleen cells in G0/G1 stage. This is the first report on Phyllanthus urinaria isolates for their growth inhibitory activities against inflammatory mediators, in addition to spleen cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 stage. Therefore, these isolates from Phyllanthus urinaria may be useful for the treatment of cell-mediated immune diseases.
Inhibitory effects of methyl brevifolincarboxylate isolated from Phyllanthus niruri L. on platelet aggregation.[Pubmed:17268086]
Biol Pharm Bull. 2007 Feb;30(2):382-4.
A platelet-aggregatory inhibitor was isolated from the 50% MeOH extract of Phyllanthus niruri L. leaf. Its structure was determined to be Methyl brevifolincarboxylate on the basis of the 1H-, 13C-NMR, and high-resolution mass spectral data. We compared the antiplatelet aggregatory effects of the constituent with adenosine, a well-known inhibitor of platelet aggregation. Platelet aggregation was induced by collagen or adenosine 5'-diphosphate as an activating agent; the extent of inhibition was monitored with a platelet aggregometer employing a laser-scattering method. The inhibitory effects of Methyl brevifolincarboxylate were found to be as potent as adenosine that is known to act on an A2A subtype receptor.
[Studies on the chemical constituents in herb of Ludwigia octovalvis].[Pubmed:16494025]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2005 Dec;30(24):1923-6.
OBJECTIVE: To study the chemical constituents of the herb of Ludwigia octovalvis. METHOD: Chemical constituents were isolated by the repeated silica gel column chromatography, and their structures were elucidated by the physicochemical properties and spectral analysis. RESULT: Thirteen compounds were obtained and determined as follows: beta-sitosterol (1), oleanolic acid (2), 2alpha-hydroxy ursolic acid (3), tormentic acid (4), daucosterol (5), maltol (6), luteolin (7), quercetin (8), apigenin (9), Methyl brevifolincarboxylate (10), gallic acid (11), 3, 4, 8, 9, 10-pentahydroxydibenzo[b, d]pyran-6-one (12), and ellagic acid (13). CONCLUSION: Compounds 3, 4, 6-13 were isolated from the plant for the first time. And compounds 3, 4, 6, 10, 12 were obtained from the genus for the first time.
Vasorelaxant effects of methyl brevifolincarboxylate from the leaves of Phyllanthus niruri.[Pubmed:16394535]
Biol Pharm Bull. 2006 Jan;29(1):177-9.
Methyl brevifolincarboxylate (1) isolated from the leaves of Phyllanthus niruri L. showed a vasorelaxant effect on rat aortic rings. Compound 1 exhibited slow relaxation activity against norepinephrine (NE)-induced contractions of rat aorta with or without endothelium. The compound did not affect contractions induced by a high concentration (60 mM) of K+, whereas it inhibited NE-induced vasocontraction in the presence of nicardipine. These results suggest that the inhibition of NE-induced vasocontraction by compound 1 is in part attributable to a decrease in [Ca2+]i through receptor-operated Ca2+ channels.
[Chemical studies on the constituents of Phyllanthus urinaria L].[Pubmed:8009999]
Yao Xue Xue Bao. 1993;28(11):829-35.
Two new phenolic compounds (crystal VI and crystal IX) have been isolated from Phyllanthus urinaria L. (Euphorbiaceae). Their structures were determined by analysis of their UV, IR, 1H-NMR, 1H-1H COSY, 13C-1H COSY, long range 13C-1H COSY, DEPT, EIMS and HREIMS spectral data. Crystal VI was determined as Methyl brevifolincarboxylate. Crystal IX was elucidated as trimethyl ester dehydrochebulic acid. All of the signals of the 13C-NMR of these two new compounds have been assigned mainly according to DEPT, 13C-1H COSY and long range 13C-1H COSY. Accompanying these two new compounds, 8 known compounds have been isolated. By using chemical reactions, UV, IR, 1H-NMR, MS, their structures were elucidated as n-octadecane(I), beta-sitosterol(III), ellagic acid(IV), daucosterol(V), kaempferol(VII), quercetin(VIII), gallic acid(X) and rutin(XI). Crystal II is an aldehyde, its structure elucidation is in progress.


