NPE-caged-protonCAS# 1186195-63-0 |
- Mibefradil
Catalog No.:BCC1748
CAS No.:116644-53-2
- Mibefradil dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1749
CAS No.:116666-63-8
- Cilnidipine
Catalog No.:BCC1083
CAS No.:132203-70-4
- Pregabalin
Catalog No.:BCN2175
CAS No.:148553-50-8
- NNC 55-0396
Catalog No.:BCC1803
CAS No.:357400-13-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

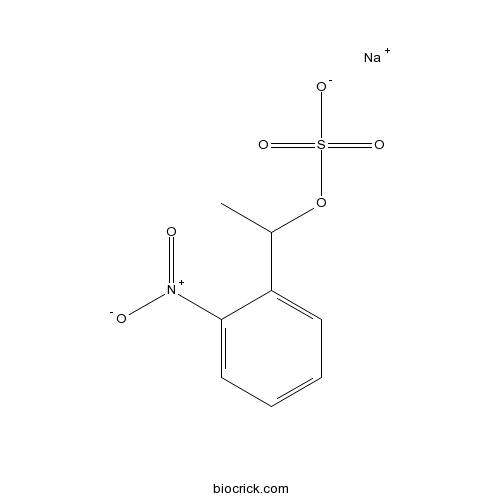
| Cas No. | 1186195-63-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 57369362 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C8H8NNaO6S | M.Wt | 269.21 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | NPE-caged-sulfate | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in water and to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | sodium;1-(2-nitrophenyl)ethyl sulfate | ||
| SMILES | CC(C1=CC=CC=C1[N+](=O)[O-])OS(=O)(=O)[O-].[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LCCXAXUWDTVOHF-UHFFFAOYSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C8H9NO6S.Na/c1-6(15-16(12,13)14)7-4-2-3-5-8(7)9(10)11;/h2-6H,1H3,(H,12,13,14);/q;+1/p-1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1-(2-nitrophenyl)ethyl caged proton that releases a proton and a sulfate ion upon photolysis. Generates rapid acidifications down to pH 2 (pH jumps). |

NPE-caged-proton Dilution Calculator

NPE-caged-proton Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.7146 mL | 18.5729 mL | 37.1457 mL | 74.2914 mL | 92.8643 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7429 mL | 3.7146 mL | 7.4291 mL | 14.8583 mL | 18.5729 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3715 mL | 1.8573 mL | 3.7146 mL | 7.4291 mL | 9.2864 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0743 mL | 0.3715 mL | 0.7429 mL | 1.4858 mL | 1.8573 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0371 mL | 0.1857 mL | 0.3715 mL | 0.7429 mL | 0.9286 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- MTEP hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1780
CAS No.:1186195-60-7
- Tocrifluor T1117
Catalog No.:BCC7401
CAS No.:1186195-59-4
- BU 226 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6936
CAS No.:1186195-56-1
- Vitexdoin A
Catalog No.:BCN4089
CAS No.:1186021-77-1
- VD3-D6
Catalog No.:BCC4076
CAS No.:118584-54-6
- NVP-BVU972
Catalog No.:BCC3828
CAS No.:1185763-69-2
- Zileuton sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4216
CAS No.:118569-21-4
- Floribundone 1
Catalog No.:BCN4726
CAS No.:118555-84-3
- Phaseoloidin
Catalog No.:BCN8451
CAS No.:118555-82-1
- Boc-Orn(2-Cl-Z)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3428
CAS No.:118554-00-0
- H-Orn(2-Cl-Z)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3002
CAS No.:118553-99-4
- Baohuoside V
Catalog No.:BCN2887
CAS No.:118544-18-6
- ALW-II-41-27
Catalog No.:BCC1350
CAS No.:1186206-79-0
- 4SC-202
Catalog No.:BCC5359
CAS No.:1186222-89-8
- Epivogeloside
Catalog No.:BCN6060
CAS No.:118627-52-4
- TMN 355
Catalog No.:BCC6121
CAS No.:1186372-20-2
- Evacetrapib (LY2484595)
Catalog No.:BCC2329
CAS No.:1186486-62-3
- 11-Hydroxycodaphniphylline
Catalog No.:BCN6061
CAS No.:1186496-68-3
- H-Cys(Me)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2908
CAS No.:1187-84-4
- Resminostat hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1888
CAS No.:1187075-34-8
- Cuniloside B
Catalog No.:BCN6062
CAS No.:1187303-40-7
- Trametinib DMSO solvate
Catalog No.:BCC2013
CAS No.:1187431-43-1
- PF 184
Catalog No.:BCC6130
CAS No.:1187460-81-6
- Baricitinib (LY3009104, INCB028050)
Catalog No.:BCC2195
CAS No.:1187594-09-7
Time-resolved infrared spectroscopy of pH-induced aggregation of the Alzheimer Abeta(1-28) peptide.[Pubmed:18462754]
J Mol Biol. 2008 Jun 6;379(3):589-96.
Aggregation of the Alzheimer's disease-related Abeta(1-28) peptide was induced by a rapid, sub-millisecond pH jump and monitored by time-resolved infrared spectroscopy on the millisecond to second time-scale. The release of protons was induced by the photolysis of a caged compound, 1-(2-nitrophenyl)ethyl sulfate (NPE-sulfate). The pH jump generated in our experimental setup is used to model the Abeta peptide structural conversions that may occur in the acidic endosomal/lysosomal cell compartment system. The aggregation of the Abeta(1-28) peptide induced by the pH jump from 8.5 to <6 yields an antiparallel beta-sheet structure. The kinetics of the structural transition is biphasic, showing an initial rapid phase with a transition from random coil to an oligomeric beta-sheet form with a time constant of 3.6 s. This phase is followed by a second slower transition, which yields larger aggregates during 48.0 s.
Kinetics of proton release after flash photolysis of 1-(2-nitrophenyl)ethyl sulfate (caged sulfate) in aqueous solution.[Pubmed:15998092]
J Am Chem Soc. 2005 Jul 13;127(27):9865-74.
The kinetics of proton release after laser photolysis of 1-(2-nitrophenyl)ethyl sulfate (caged sulfate) have been characterized by time-resolved absorbance and photoacoustic methods. The absorbance at approximately 400 nm is observed to rise with a biphasic behavior in which a prompt component (formation of the nitronic acid) is followed by a slower (tau approximately 63 +/- 6 ns) phase (deprotonation of the nitronic acid). The decay of this intermediate occurs with a lifetime which is affected by the pH of the solution and the laser pulse energy. In buffered aqueous solution at pH 7, 20 degrees C the aci-nitro decay rate is 18 +/- 4 s(-1). Protons are released to the solution with rate (1.58 +/- 0.09) x 10(7) s(-1) at neutral pH from the nitronic acid intermediate. From the numerical analysis of the protonation kinetics of suitable pH indicators, we could estimate the pK(a) of the nitronic acid as 3.69 +/- 0.05. At acidic pH, a substantial fraction of the aci-nitro intermediate is in the protonated form and this leads to a biphasic release of protons, with the slower phase being characterized by an apparent rate constant strongly dependent on the pH. The strongly acidic character of the final photoproduct (sulfate ion) means that there is negligible buffering of photoreleased protons.
Characterization of a new caged proton capable of inducing large pH jumps.[Pubmed:12414718]
Biophys J. 2002 Nov;83(5):2864-71.
A new caged proton, 1-(2-nitrophenyl)ethyl sulfate (caged sulfate), is characterized by infrared spectroscopy and compared with a known caged, proton 2-hydroxyphenyl 1-(2-nitrophenyl)ethyl phosphate (caged HPP). In contrast to caged HPP, caged sulfate can induce large pH jumps and protonate groups that have pK values as low as 2.2. The photolysis mechanism of caged sulfate is analogous to that of P(3)-[1-(2-nitrophenyl)ethyl] ATP (caged ATP), and the photolysis efficiency is similar. The utility of this new caged compound for biological studies was demonstrated by its ability to drive the acid-induced conformational change of metmyoglobin. This transition from the native conformation to a partially unfolded form takes place near pH 4 and was monitored by near-UV absorption spectroscopy.


