Baricitinib (LY3009104, INCB028050)JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor,selective orally bioavailable CAS# 1187594-09-7 |
- CYT387
Catalog No.:BCC2196
CAS No.:1056634-68-4
- CYT387 sulfate salt
Catalog No.:BCC1506
CAS No.:1056636-06-6
- WHI-P154
Catalog No.:BCC2202
CAS No.:211555-04-3
- WHI-P97
Catalog No.:BCC2056
CAS No.:211555-05-4
- Tofacitinib (CP-690550) Citrate
Catalog No.:BCC2189
CAS No.:540737-29-9
- TG101209
Catalog No.:BCC2198
CAS No.:936091-14-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1187594-09-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 44205240 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H17N7O2S | M.Wt | 371.42 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | INCB028050; LY3009104 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 74 mg/mL (199.23 mM) in DMSO | ||
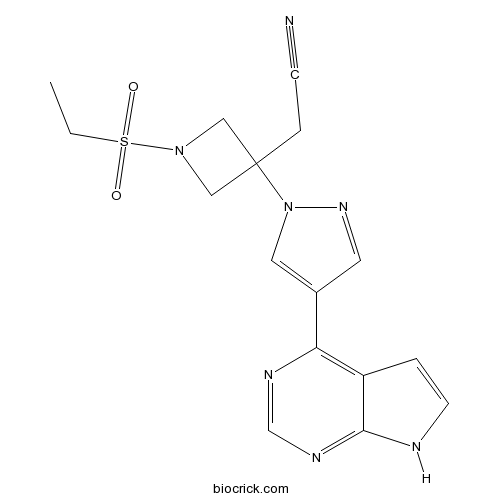
| Chemical Name | 2-[1-ethylsulfonyl-3-[4-(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)pyrazol-1-yl]azetidin-3-yl]acetonitrile | ||
| SMILES | CCS(=O)(=O)N1CC(C1)(CC#N)N2C=C(C=N2)C3=C4C=CNC4=NC=N3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XUZMWHLSFXCVMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H17N7O2S/c1-2-26(24,25)22-9-16(10-22,4-5-17)23-8-12(7-21-23)14-13-3-6-18-15(13)20-11-19-14/h3,6-8,11H,2,4,9-10H2,1H3,(H,18,19,20) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Baricitinib (LY3009104, INCB028050) is a selective inhibitor of JAK1 and JAK2 with IC50 values of 5.9 nM and 5.7 nM, | |||||
| Targets | JAK2 | JAK1 | TYK2 | JAK3 | Chk2 | c-Met |
| IC50 | 5.7 nM | 5.9 nM | 53 nM | >400 nM | >1 μM | >10 μM |
| Kinase experiment [1]: | |
| Inhibitory activities | Enzyme assays were performed using a homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence assay with recombinant epitope tagged kinase domains (JAK1, 837-1142; JAK2, 828-1132; JAK3, 718-1124; Tyk2, 873-1187) or fulllength enzyme (cMET and Chk2) and peptide substrate. Each enzyme reaction was performed with or without Baricitinib (LY3009104, INCB028050) (11-point dilution), JAK, cMET, or Chk2 enzyme, 500 nM (100 nM for Chk2) peptide, ATP (at the Km specific for each kinase or 1 mM), and 2.0% DMSO in assay buffer. The calculated IC50 value is the Baricitinib (LY3009104, INCB028050) concentration required for inhibition of 50% of the fluorescent signal. Additional kinase assays were performed at Cerep using standard conditions at 200 nM. Enzymes tested included: Abl, Akt1, AurA, AurB, CDC2, CDK2, CDK4, CHK2, c-kit, EGFR, EphB4, ERK1, ERK2, FLT-1, HER2, IGF1R, IKKa, IKKb, JNK1, Lck, MEK1, p38a, p70S6K, PKA, PKCa, Src, and ZAP70. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
| Cell lines | Human PBMCs; PHA-stimulated T cells. |
| Preparation method | Soluble in DMSO > 10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
| Reacting condition | 10, 100, 1000, 10000 nM; 48 h. |
| Applications | In PBMCs, INCB028050 inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation stimulated by IL-6 and the production of chemokine MCP-1 with IC50 values of 44 and 40 nM, respectively. In isolated naive T-cells, INCB028050 inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation with IC50 value of 20 nM and inhibits the production of IL-17 and IL-22 with IC50 value of 50 nM. |
| Animal experiment [1]: | |
| Animal models | Female rats; adjuvant-induced arthritis rats; DBA/1j arthritis mice induced by bovine type II collagen. |
| Dosage form | Female rats: 10 mg/kg; 24 h; oral gavage.Adjuvant-induced arthritis rats: 1, 3, or 10 mg/kg; once daily for 2 wk; administrated orally.Collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model: 1, 3, or 10 mg/kg; twice daily for 15 d; administrated orally. |
| Preparation method | Suspended in 0.5% methylcellulose and given by oral gavage at 10 ml/kg.. |
| Application | In female rats, INCB028050 (10 mg/kg) inhibits JAK1/2 signaling by ≥50% for 8 h. In rat adjuvant-induced arthritis, INCB028050 (1, 3, or 10 mg/kg) reduces disease scores by 24%, 57% and 81% respectively and inhibits the increase of hind paw volumes by 50%, >95% and >95%, respectively. Also, INCB028050 reduced bone resorption. In CIA mice model, INCB028050 (1, 3, or 10 mg/kg) reduces clinical scores by 19%, 67% and 61% respectively and inhibits IL-6 and IL-23 signaling and function. |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: [1]. Fridman JS, Scherle PA, Collins R, et al. Selective inhibition of JAK1 and JAK2 is efficacious in rodent models of arthritis: preclinical characterization of INCB028050. J Immunol, 2010, 184(9): 5298-5307. | |

Baricitinib (LY3009104, INCB028050) Dilution Calculator

Baricitinib (LY3009104, INCB028050) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6924 mL | 13.4618 mL | 26.9237 mL | 53.8474 mL | 67.3092 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5385 mL | 2.6924 mL | 5.3847 mL | 10.7695 mL | 13.4618 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2692 mL | 1.3462 mL | 2.6924 mL | 5.3847 mL | 6.7309 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0538 mL | 0.2692 mL | 0.5385 mL | 1.0769 mL | 1.3462 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0269 mL | 0.1346 mL | 0.2692 mL | 0.5385 mL | 0.6731 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Baricitinib, formerly named LY3009104 or INCB028050, is a new selective orally bioavailable inhibitor of tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 or JAK2. Also, it is an ATP competitive kinase inhibitor. In vitro, it is able to inhibit JAK1 and JAK2 in a low nanomolar range with IC50 values of 5.9 and 5.7 nM, respectively, while it demonstrates low inhibitory activity for JAK3 and moderate activity for TYK2. Baricitinib inhibits intracellular signaling of multiple proinflammatory cytokines including IL-6 and IL-23 at concentrations <50 nM. It should also be recognized that JAK signaling is central to a number of fundamental processes, including the generation of RBCs
Reference
Gras, J. Baricitinib. Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor, treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Drugs of the future. 2013, 38(9): 611.
Jordan S. Fridman, Peggy A. Scherle, Robert Collins, Timothy C. Burn, Yanlong Li, Jun Li, Maryanne B. Covington, Beth Thomas, Paul Collier, Margaret F. Favata, Xiaoming Wen, Jack Shi, Ryan McGee, Patrick J. Haley, Stacey Shepard, James D. Rodgers, Swamy Yeleswaram, Greg Hollis, Robert C. Newton, Brian Metcalf, Steven M. Friedman and Kris Vaddi. Selective Inhibition of JAK1 and JAK2 Is Efficacious in Rodent Models of Arthritis: Preclinical Characterization of INCB028050. The Journal of Immunology May 1, 2010 vol. 184 no. 9 5298-5307.
- PF 184
Catalog No.:BCC6130
CAS No.:1187460-81-6
- Trametinib DMSO solvate
Catalog No.:BCC2013
CAS No.:1187431-43-1
- Cuniloside B
Catalog No.:BCN6062
CAS No.:1187303-40-7
- Resminostat hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1888
CAS No.:1187075-34-8
- H-Cys(Me)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2908
CAS No.:1187-84-4
- 11-Hydroxycodaphniphylline
Catalog No.:BCN6061
CAS No.:1186496-68-3
- Evacetrapib (LY2484595)
Catalog No.:BCC2329
CAS No.:1186486-62-3
- TMN 355
Catalog No.:BCC6121
CAS No.:1186372-20-2
- Epivogeloside
Catalog No.:BCN6060
CAS No.:118627-52-4
- 4SC-202
Catalog No.:BCC5359
CAS No.:1186222-89-8
- ALW-II-41-27
Catalog No.:BCC1350
CAS No.:1186206-79-0
- NPE-caged-proton
Catalog No.:BCC7698
CAS No.:1186195-63-0
- Baricitinib phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC1401
CAS No.:1187595-84-1
- Carabrolactone A
Catalog No.:BCN6063
CAS No.:1187925-30-9
- Carabrolactone B
Catalog No.:BCN6064
CAS No.:1187925-31-0
- Diosbulbin I
Catalog No.:BCN6065
CAS No.:1187951-05-8
- Diosbulbin J
Catalog No.:BCN6066
CAS No.:1187951-06-9
- Ac-Leu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2967
CAS No.:1188-21-2
- ent-14,16-Epoxy-8-pimarene-3,15-diol
Catalog No.:BCN6067
CAS No.:1188281-98-2
- 7-Hydroxydarutigenol
Catalog No.:BCN6068
CAS No.:1188281-99-3
- 9-Hydroxydarutigenol
Catalog No.:BCN6069
CAS No.:1188282-00-9
- 16-O-Acetyldarutigenol
Catalog No.:BCN6070
CAS No.:1188282-01-0
- 15,16-Di-O-acetyldarutoside
Catalog No.:BCN6071
CAS No.:1188282-02-1
- Ustusol C
Catalog No.:BCN6757
CAS No.:1188398-13-1
Patient-reported outcomes of baricitinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and no or limited prior disease-modifying antirheumatic drug treatment.[Pubmed:28923098]
Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 Sep 18;19(1):208.
BACKGROUND: This study evaluates patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in a double-blind, phase III study of baricitinib as monotherapy or combined with methotrexate (MTX) in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with no or minimal prior conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and naive to biological DMARDs. METHODS: Patients were randomized 4:3:4 to MTX administered once weekly (N = 210), baricitinib monotherapy (4 mg once daily (QD), N = 159), or combination of baricitinib (4 mg QD) and MTX (baricitinib + MTX, N = 215). PROs included the Patient's Global Assessment of Disease Activity (PtGA), patient's assessment of pain, Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI), Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT-F), duration of morning joint stiffness (MJS), worst joint pain, worst tiredness, Work Productivity and Activity Impairment-Rheumatoid Arthritis (WPAI-RA), Short Form 36 version 2, Acute (SF-36); and EuroQol 5-Dimensions (EQ-5D) Health State Profile. Comparisons were assessed with analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) and logistic regression models. RESULTS: Compared to MTX, patients in both baricitinib groups reported greater improvement (p
Small molecule therapy for managing moderate to severe psoriatic arthritis.[Pubmed:28891341]
Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2017 Oct;18(15):1557-1567.
INTRODUCTION: The majority of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) patients experience a good clinical response to conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) and biologic therapies (bDMARDs). However, treatment failure with these drugs can represent a relevant clinical problem. Moreover, in daily clinical practice, the appropriate identification of patients eligible for these agents can be conditioned by numerous aspects, mainly represented by comorbidities, such as history of malignancies, chronic and recurrent infectious diseases. Areas covered: We searched in the PUBMED database and review published data on the efficacy and safety profile of the small molecules, inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 4, apremilast, and of JAK/STAT pathways, tofacitinib, in PsA. Moreover, we report data on the other JAK inhibitor, baricitinib, and the A(3) adenosine receptors agonist, CF101, emerging by studies conducted in psoriasis patients. Expert opinion: In Psoriatic Arthritis, apremilast appears promising for PsA and recent studies have shown a good efficacy and an acceptable safety profile. Data on tofacitinib in PsA are limited. Studies on the small molecules, baricitinib and CF101 are still incomplete and limited to trials conducted in Rheumatoid Arthritis and in psoriasis. Further studies on small molecules and on their underlining mechanisms are advocated in PsA.
Dose/Exposure-Response Modeling to Support Dosing Recommendation for Phase III Development of Baricitinib in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.[Pubmed:28891251]
CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2017 Dec;6(12):804-813.
Baricitinib is an oral inhibitor of Janus kinases (JAKs), selective for JAK1 and 2. It demonstrated dose-dependent efficacy in patients with moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in a phase IIb study up to 24 weeks. Population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PopPK/PD) models were developed to characterize concentration-time profiles and dose/exposure-response (D/E-R) relationships for the key efficacy (proportion of patients achieving American College of Rheumatology 20%, 50%, or 70% response rate) and safety endpoints (incidence of anemia) for the phase IIb study. The modeling suggested that 4 mg q.d. was likely to offer the optimum risk/benefit balance, whereas 2 mg q.d. had the potential for adequate efficacy. In addition, at the same total daily dose, a twice-daily regimen is not expected to provide an advantage over q.d. dosing for the efficacy or safety endpoints. The model-based simulations formed the rationale for key aspects of dosing, such as dose levels and dosing frequency for phase III development.
Two new drugs for rheumatoid arthritis.[Pubmed:28882850]
Drug Ther Bull. 2017 Sep;55(9):102-105.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, progressive autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and destruction of the joints.(1-3) It can also affect the eyes, the heart and the lungs and is associated with significant disability and increased mortality. RA is estimated to affect just under 1% of the population aged over 16 years, equating to more than 400,000 people in the UK.(4) Baricitinib (Olumiant) and tofacitinib (Xeljanz) were launched in the UK in April 2017 and represent a new therapeutic class of medicines known as targeted synthetic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs.(5,6) Here, we review the evidence for the safety and effectiveness of these new oral agents.


