WHI-P154JAK3 inhibitor CAS# 211555-04-3 |
- PP 1
Catalog No.:BCC3630
CAS No.:172889-26-8
- PP 2 (AG 1879)
Catalog No.:BCC3631
CAS No.:172889-27-9
- Dasatinib (BMS-354825)
Catalog No.:BCC1281
CAS No.:302962-49-8
- Saracatinib (AZD0530)
Catalog No.:BCC1166
CAS No.:379231-04-6
- KX2-391
Catalog No.:BCC5080
CAS No.:897016-82-9
- Lck inhibitor 2
Catalog No.:BCC1690
CAS No.:944795-06-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 211555-04-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3795 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H14BrN3O3 | M.Wt | 376.2 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 47 mg/mL (124.93 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
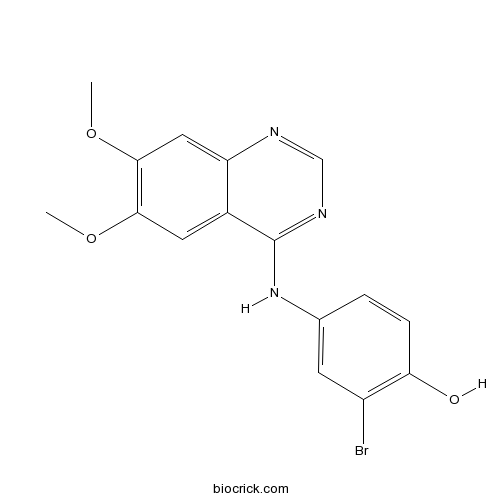
| Chemical Name | 2-bromo-4-[(6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-yl)amino]phenol | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C2C(=C1)C(=NC=N2)NC3=CC(=C(C=C3)O)Br)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CBIAKDAYHRWZCU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H14BrN3O3/c1-22-14-6-10-12(7-15(14)23-2)18-8-19-16(10)20-9-3-4-13(21)11(17)5-9/h3-8,21H,1-2H3,(H,18,19,20) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | JAK3 inhibitor (IC50 = 1.8 μM) that displays no activity at JAK1 or JAK2. Inhibits STAT1 activation, iNOS expression and NO production in macrophages in vitro. Also inhibits other common kinases including EGFR (IC50 = 4 nM), Src, Abl, VEGFR, MAPK and PI 3-K and induces apoptosis in human glioblastoma cell lines (IC50 = 158 μM). Induces differentiation of neural progenitor cells. |

WHI-P154 Dilution Calculator

WHI-P154 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6582 mL | 13.2908 mL | 26.5816 mL | 53.1632 mL | 66.454 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5316 mL | 2.6582 mL | 5.3163 mL | 10.6326 mL | 13.2908 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2658 mL | 1.3291 mL | 2.6582 mL | 5.3163 mL | 6.6454 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0532 mL | 0.2658 mL | 0.5316 mL | 1.0633 mL | 1.3291 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0266 mL | 0.1329 mL | 0.2658 mL | 0.5316 mL | 0.6645 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
WHI-P154 is an inhibitor of JAK3 with IC50 value of 1.8μM [1].
In vitro kinase assays show that WHI-P154 is not a specific inhibitor. Besides JAK3, it also inhibits many other kinases, including EGFR, ABL, LCK, SRC and VEGFR. WHI-P154 inhibits EGFR with IC50 value of 4nM. The specificity of WHI-P154 has not been shown in cell-based assays either [1].
WHI-P154 shows cytotoxicity against the U373 human glioblastoma cell line in vitro. This antitumor activity can be enhanced by conjugation to EGF. WHI-P154 also shows antitumor activity in a SCID mouse xenograft model of human glioblastoma [2].
References:
[1] Changelian PS, Moshinsky D, Kuhn CF, Flanagan ME, Munchhof MJ, Harris TM, Whipple DA, Doty JL, Sun J, Kent CR, Magnuson KS, Perregaux DG, Sawyer PS, Kudlacz EM. The specificity of JAK3 kinase inhibitors. Blood. 2008 Feb 15;111(4):2155-7.
[2] Narla RK, Liu XP, Myers DE, Uckun FM. 4-(3'-Bromo-4'hydroxylphenyl)-amino-6,7-dimethoxyquinazoline: a novel quinazoline derivative with potent cytotoxic activity against human glioblastoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 1998 Jun;4(6):1405-14.
- Dalcetrapib (JTT-705, RO4607381)
Catalog No.:BCC2328
CAS No.:211513-37-0
- Dendrobine
Catalog No.:BCN5923
CAS No.:2115-91-5
- Astrocasine
Catalog No.:BCN2150
CAS No.:2114-92-3
- R18
Catalog No.:BCC2383
CAS No.:211364-78-2
- m-Chlorophenylbiguanide hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6650
CAS No.:2113-05-5
- 9,17-Octadecadiene-12,14-diyne-1,11,16-triol
Catalog No.:BCN1497
CAS No.:211238-60-7
- Rubranol
Catalog No.:BCN4917
CAS No.:211126-61-3
- Sobetirome
Catalog No.:BCC1957
CAS No.:211110-63-3
- Marsformoxide B
Catalog No.:BCN6687
CAS No.:2111-46-8
- SB 265610
Catalog No.:BCC5936
CAS No.:211096-49-0
- Mahanimbine
Catalog No.:BCN3174
CAS No.:21104-28-9
- BMY 7378
Catalog No.:BCC5063
CAS No.:21102-95-4
- WHI-P97
Catalog No.:BCC2056
CAS No.:211555-05-4
- WHI-P180
Catalog No.:BCC3928
CAS No.:211555-08-7
- Nudicaucin B
Catalog No.:BCN7843
CAS No.:211557-36-7
- Picroside IV
Catalog No.:BCN6533
CAS No.:211567-04-3
- 2',4',5'-Trimethoxy-2'',2''-dimethylpyrano[5'',6'':6,7]isoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN1496
CAS No.:211799-56-3
- Nudicaucin A
Catalog No.:BCN7842
CAS No.:211815-97-3
- Flumorph
Catalog No.:BCC5467
CAS No.:211867-47-9
- Gliclazide
Catalog No.:BCC5002
CAS No.:21187-98-4
- BIBR 953 (Dabigatran, Pradaxa)
Catalog No.:BCC2139
CAS No.:211914-51-1
- BIBR-1048
Catalog No.:BCC3738
CAS No.:211915-06-9
- 1,3,7-Trihydroxy-2-methoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN7549
CAS No.:211948-69-5
- Vatalanib (PTK787) 2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1111
CAS No.:212141-51-0
The JAK3 inhibitor WHI-P154 prevents PDGF-evoked process outgrowth in human neural precursor cells.[Pubmed:16515549]
J Neurochem. 2006 Apr;97(1):201-10.
The prospect of manipulating endogenous neural stem cells to replace damaged tissue and correct functional deficits offers a novel mechanism for treating a variety of CNS disorders. The aim of this study was to investigate pathways controlling neurite outgrowth in human neural precursor cells, in particular in response to platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF). PDGF-AA, -AB and -BB were found to initiate calcium signalling and produce robust increases in neurite outgrowth. PDGF-induced outgrowth of Tuj1-positive precursors was abolished by the addition of EGTA, suggesting that calcium entry is a critical part of the signalling pathway. Wortmannin and PD098059 failed to inhibit PDGF-induced outgrowth. Clostridium Toxin B increased the amount of PDGF-induced neurite branching but had no effect on basal levels. In contrast, WHI-P154, an inhibitor of Janus protein tyrosine kinase (JAK3), Hck and Syk, prevented PDGF-induced neurite outgrowth. PDGF activates multiple signalling pathways with considerable potential for cross-talk. This study has highlighted the complexity of the pathways leading to neurite outgrowth in human neural precursors, and provided initial evidence to suggest that calcium entry is critical in producing the morphological changes observed.
Janus kinase 3 inhibitor WHI-P154 in macrophages activated by bacterial endotoxin: differential effects on the expression of iNOS, COX-2 and TNF-alpha.[Pubmed:18068105]
Int Immunopharmacol. 2008 Jan;8(1):100-8.
Bacterial endotoxin is a potent inducer of inflammatory response, including the induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression and nitric oxide (NO) production, and the expression of cyclo-oxygenase (COX)-2 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha in inflammatory cells. In the present study, we investigated the effects of pharmacological inhibition of Janus kinase (JAK) 3 on the production of these proinflammatory molecules in macrophages exposed to bacterial endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide; LPS). JAK3 inhibitors WHI-P154 (4-(3'-bromo-4'-hydroxylphenyl)-amino-6,7-dimethoxyquinazoline) and its derivative WHI-P131 inhibited LPS-induced iNOS expression and NO production in a dose-dependent manner. WHI-P154 inhibited the activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 1 and the expression of iNOS mRNA but it had no effect on iNOS mRNA decay when determined by actinomycin D assay. The JAK3 inhibitor had no effect on COX-2 expression, and TNF-alpha production was slightly inhibited only at higher drug concentrations (30 microM). In addition, WHI-P154 inhibited iNOS expression and NO production also in human epithelial cells. Our results suggest that JAK3 inhibition modulates human and murine iNOS expression and NO production in response to inflammatory stimuli.
WHI-P154 enhances the chemotherapeutic effect of anticancer agents in ABCG2-overexpressing cells.[Pubmed:24903205]
Cancer Sci. 2014 Aug;105(8):1071-8.
ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transmembrane proteins evidently decrease the intracellular accumulation of substrate chemotherapeutic drugs by extruding them against a concentration gradient, thereby inducing drug resistance. Here we reported the effect of WHI-P154, an irreversible inhibitor of Janus kinase 3 and epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases, on reversing ABC transporters-mediated drug resistance. We found that WHI-P154 significantly enhanced the sensitivity of ABCG2-overexpressing cells to its substrates. WHI-P154 moderately sensitized ABCB1-overexpressing KB-C2 cells to its substrates whereas showed no sensitizing effect on ABCC1-, ABCC2 or ABCC10-mediated drug resistance. Moreover, WHI-P154 produced a significant increase in the intracellular accumulation of [(3)H]-mitoxantrone in ABCG2-overexpressing cells. The expression levels nor the localization of the ABCG2 protein was altered after treatment of ABCG2-overexpressing cells with WHI-P154. Further studies indicated that WHI-P154 enhanced the ATPase activity of ABCG2 at low concentrations (<10 muM). Additionally, a docking model predicted the binding conformation of WHI-P154 within the transmembrane region of homology-modeled human ABCG2 transporter. Collectively, these findings highlighted WHI-P154 could significantly reverse ABCG2-mediated multidrug drug resistance by directly blocking the efflux function.
JAK inhibitors AG-490 and WHI-P154 decrease IFN-gamma-induced iNOS expression and NO production in macrophages.[Pubmed:16883061]
Mediators Inflamm. 2006;2006(2):16161.
In inflammation, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) produces nitric oxide (NO), which modulates inflammatory processes. We investigated the effects of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, AG-490 and WHI-P154, on iNOS expression and NO production in J774 murine macrophages stimulated with interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). JAK inhibitors AG-490 and WHI-P154 decreased IFN-gamma-induced nuclear levels of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1alpha (STAT1alpha). JAK inhibitors AG-490 and WHI-P154 decreased also iNOS protein and mRNA expression and NO production in a concentration-dependent manner. Neither of the JAK inhibitors affected the decay of iNOS mRNA when determined by actinomycin D assay. Our results suggest that the inhibition of JAK-STAT1-pathway by AG-490 or WHI-P154 leads to the attenuation of iNOS expression and NO production in IFN-gamma-stimulated macrophages.
Differential regulation of proliferation and differentiation in neural precursor cells by the Jak pathway.[Pubmed:20979137]
Stem Cells. 2010 Oct;28(10):1816-28.
Neuronal precursor cells (NPCs) are temporally regulated and have the ability to proliferate and differentiate into mature neurons, oligodendrocytes, and astrocytes in the presence of growth factors (GFs). In the present study, the role of the Jak pathway in brain development was investigated in NPCs derived from neurosphere cultures using Jak2 and Jak3 small interfering RNAs and specific inhibitors. Jak2 inhibition profoundly decreased NPC proliferation, preventing further differentiation into neurons and glial cells. However, Jak3 inhibition induced neuronal differentiation accompanied by neurite growth. This phenomenon was due to the Jak3 inhibition-mediated induction of neurogenin (Ngn)2 and NeuroD in NPCs. Jak3 inhibition induced NPCs to differentiate into scattered neurons and increased the expression of Tuj1, microtubule associated protein 2 (MAP2), Olig2, and neuroglial protein (NG)2, but decreased glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) expression, with predominant neurogenesis/polydendrogenesis compared with astrogliogenesis. Therefore, Jak2 may be important for NPC proliferation and maintenance, whereas knocking-down of Jak3 signaling is essential for NPC differentiation into neurons and oligodendrocytes but does not lead to astrocyte differentiation. These results suggest that NPC proliferation and differentiation are differentially regulated by the Jak pathway.
The specificity of JAK3 kinase inhibitors.[Pubmed:18094329]
Blood. 2008 Feb 15;111(4):2155-7.
PF-956980 is a selective inhibitor of JAK3, related in structure to CP-690550, a compound being evaluated in clinical trials for rheumatoid arthritis and prevention of allograft rejection. PF-956980 has been evaluated against a panel of 30 kinases, and found to have nanomolar potency against only JAK3. Cellular and whole blood activity of this compound parallels its potency and selectivity in enzyme assays. It was effective in vivo at inhibiting the delayed type hypersensivity reaction in mice. We compared 2 commercially available JAK3 inhibitors (WHI-P131 and WHI-P154) in the same panel of biochemical and cellular assays and found them to be neither potent nor selective for JAK3. Both were found to be nanomolar inhibitors of the EGF receptor family of kinases. As these compounds have been used in numerous publications in the transplant and autoimmune disease literature, their specificity should be considered when interpreting these results.
4-(3'-Bromo-4'hydroxylphenyl)-amino-6,7-dimethoxyquinazoline: a novel quinazoline derivative with potent cytotoxic activity against human glioblastoma cells.[Pubmed:9626456]
Clin Cancer Res. 1998 Jun;4(6):1405-14.
The novel quinazoline derivative 4-(3'-bromo-4'-hydroxylphenyl)-amino-6,7-dimethoxyquinazoline (WHI-P154) exhibited significant cytotoxicity against U373 and U87 human glioblastoma cell lines, causing apoptotic cell death at micromolar concentrations. The in vitro antiglioblastoma activity of WHI-P154 was amplified > 200-fold and rendered selective by conjugation to recombinant human epidermal growth factor (EGF). The EGF-P154 conjugate was able to bind to and enter target glioblastoma cells within 10-30 min via receptor (R)-mediated endocytosis by inducing internalization of the EGF-R molecules. In vitro treatment with EGF-P154 resulted in killing of glioblastoma cells at nanomolar concentrations with an IC50 of 813 +/- 139 nM, whereas no cytotoxicity against EGF-R-negative leukemia cells was observed, even at concentrations as high as 100 microM. The in vivo administration of EGF-P154 resulted in delayed tumor progression and improved tumor-free survival in a severe combined immunodeficient mouse glioblastoma xenograft model. Whereas none of the control mice remained alive tumor-free beyond 33 days (median tumor-free survival, 19 days) and all control mice had tumors that rapidly progressed to reach an average size of > 500 mm3 by 58 days, 40% of mice treated for 10 consecutive days with 1 mg/kg/day EGF-P154 remained alive and free of detectable tumors for more than 58 days with a median tumor-free survival of 40 days. The tumors developing in the remaining 60% of the mice never reached a size > 50 mm3. Thus, targeting WHI-P154 to the EGF-R may be useful in the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme.


