Nagilactone BCAS# 19891-51-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 19891-51-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3084329 | Appearance | Powder |
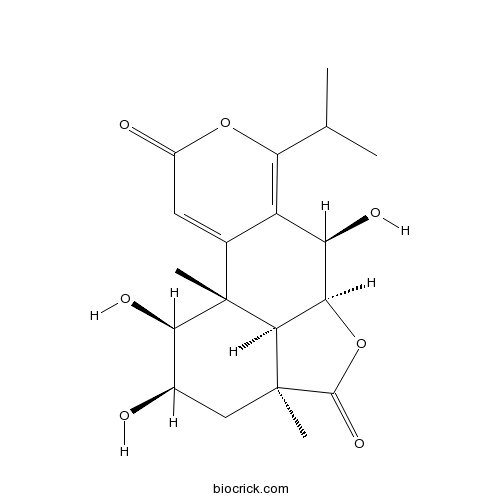
| Formula | C19H24O7 | M.Wt | 364.4 |
| Type of Compound | Diterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)C1=C2C(C3C4C(CC(C(C4(C2=CC(=O)O1)C)O)O)(C(=O)O3)C)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AEGWYWSJGKOLGB-ZLNDBNLZSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H24O7/c1-7(2)13-11-8(5-10(21)25-13)19(4)15-14(12(11)22)26-17(24)18(15,3)6-9(20)16(19)23/h5,7,9,12,14-16,20,22-23H,6H2,1-4H3/t9-,12-,14-,15+,16-,18+,19-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Selective LXR activation in macrophages with nagilactone B induces ABCA1- and ABCG1-mediated cholesterol efflux while exerting minimal effects on lipogenesis and lipid accumulation in liver, resulting in regression of atherosclerosis, and therefore might be a promising strategy for therapeutics. |
| Targets | Liver X receptor |

Nagilactone B Dilution Calculator

Nagilactone B Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7442 mL | 13.7212 mL | 27.4424 mL | 54.8847 mL | 68.6059 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5488 mL | 2.7442 mL | 5.4885 mL | 10.9769 mL | 13.7212 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2744 mL | 1.3721 mL | 2.7442 mL | 5.4885 mL | 6.8606 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0549 mL | 0.2744 mL | 0.5488 mL | 1.0977 mL | 1.3721 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0274 mL | 0.1372 mL | 0.2744 mL | 0.5488 mL | 0.6861 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Atazanavir
Catalog No.:BCC3622
CAS No.:198904-31-3
- Continentalic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6526
CAS No.:19889-23-7
- Humulene epoxide II
Catalog No.:BCN4873
CAS No.:19888-34-7
- Alisol A
Catalog No.:BCN3455
CAS No.:19885-10-0
- H-Phe(2-F)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3222
CAS No.:19883-78-4
- H-D-Phg-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3314
CAS No.:19883-41-1
- Z-D-Tyr(tBu)-OH.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC2744
CAS No.:198828-72-7
- (7R)-Methoxy-8-epi-matairesinol
Catalog No.:BCN7582
CAS No.:198827-23-5
- Merimepodib
Catalog No.:BCC4128
CAS No.:198821-22-6
- Windorphen
Catalog No.:BCC6486
CAS No.:19881-70-0
- Bavachin
Catalog No.:BCN4872
CAS No.:19879-32-4
- Bavachinin
Catalog No.:BCN4871
CAS No.:19879-30-2
- Jaborosalactone D
Catalog No.:BCN7946
CAS No.:19891-82-8
- 29-Nor-20-oxolupeol
Catalog No.:BCN6678
CAS No.:19891-85-1
- Kaempferol 3-O-beta-sophoroside
Catalog No.:BCN3336
CAS No.:19895-95-5
- Syringaresinol diacetate
Catalog No.:BCN4874
CAS No.:1990-77-8
- Dihydromethysticin
Catalog No.:BCN2476
CAS No.:19902-91-1
- Bakkenolide A
Catalog No.:BCN5402
CAS No.:19906-72-0
- Maackiain
Catalog No.:BCN1236
CAS No.:19908-48-6
- H-Phe(4-Me)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3270
CAS No.:1991-87-3
- Balaglitazone
Catalog No.:BCC1395
CAS No.:199113-98-9
- T 98475
Catalog No.:BCC7395
CAS No.:199119-18-1
- Furanodiene
Catalog No.:BCN6454
CAS No.:19912-61-9
- Chamigrenal
Catalog No.:BCN7847
CAS No.:19912-84-6
A novel small molecule liver X receptor transcriptional regulator, nagilactone B, suppresses atherosclerosis in apoE-deficient mice.[Pubmed:27460841]
Cardiovasc Res. 2016 Oct;112(1):502-14.
AIMS: Atherosclerosis is the most common cause of cardiovascular diseases, such as myocardial infarction and stroke. We hypothesized that Nagilactone B (NLB), a small molecule extracted from the root bark of Podocarpus nagi (Podocarpaceae), suppresses atherosclerosis in an atherosclerotic mouse model. METHODS AND RESULTS: Male apoE-deficient mice on C57BL/6J background received NLB (10 and 30 mg/kg) for 12 weeks. Compared with the model group, NLB treatment (10 and 30 mg/kg) significantly reduced en face lesions of total aorta areas. In RAW264.7 cells, NLB significantly ameliorated cholesterol accumulation in macrophages via enhancing apolipoprotein A-I and HDL-mediated cholesterol efflux. Mechanistically, NLB induced messenger RNA and protein expression of the ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) and G1 (ABCG1) in RAW264.7 and THP-1 cells. Liver X receptor (LXR) site mutations in the mouse ABCA1 promoter abrogated NLB-mediated luciferase reporter activity. LXRalpha and LXRbeta small interfering RNA suppressed NLB-mediated induction of ABCA1 expression. Consistent with in vitro results, NLB induced ABCA1 expression and suppressed macrophage areas in the aortic sinus. Moreover, NLB treatment did not induce the protein expression of LXR in liver. Hepatic and intestinal cholesterol accumulation was significantly alleviated on NLB treatment. Besides, NLB significantly improved plasma lipid profiles in apoE-deficient mice. CONCLUSION: Selective LXR activation in macrophages with NLB induces ABCA1- and ABCG1-mediated cholesterol efflux while exerting minimal effects on lipogenesis and lipid accumulation in liver, resulting in regression of atherosclerosis, and therefore might be a promising strategy for therapeutics.


