Notoginsenoside R4CAS# 87741-77-3 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 87741-77-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 131752824 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C59H100O27 | M.Wt | 1241.4 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
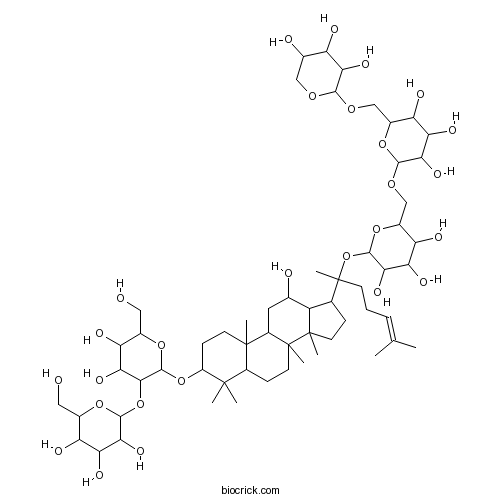
| Chemical Name | 2-[4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-2-[[12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-[6-methyl-2-[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[(3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl)oxymethyl]oxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]oxan-2-yl]oxyhept-5-en-2-yl]-2,3,5,6,7,9,11,12,13,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl]oxy]oxan-3-yl]oxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol | ||
| SMILES | CC(=CCCC(C)(C1CCC2(C1C(CC3C2(CCC4C3(CCC(C4(C)C)OC5C(C(C(C(O5)CO)O)O)OC6C(C(C(C(O6)CO)O)O)O)C)C)O)C)OC7C(C(C(C(O7)COC8C(C(C(C(O8)COC9C(C(C(CO9)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IWDYQBDCEDNTDP-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C59H100O27/c1-24(2)10-9-14-59(8,86-53-48(76)43(71)40(68)31(83-53)23-79-51-46(74)42(70)39(67)30(82-51)22-78-50-45(73)36(64)27(63)21-77-50)25-11-16-58(7)35(25)26(62)18-33-56(5)15-13-34(55(3,4)32(56)12-17-57(33,58)6)84-54-49(44(72)38(66)29(20-61)81-54)85-52-47(75)41(69)37(65)28(19-60)80-52/h10,25-54,60-76H,9,11-23H2,1-8H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| In vitro | Effects of ginsenosides from Panax ginseng on cell-to-cell communication function mediated by gap junctions.[Pubmed: 11488454 ]Planta Med. 2001 Jul;67(5):417-22.Gap junctions have been shown or are believed to be involved in the pathogenesis of many inherited and acquired human diseases. Agents that regulate the gap junction-mediated intercellular communication (GJIC) function may facilitate prevention and treatment of GJIC-involved diseases.
|
| Structure Identification | Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013 Sep;38(17):2807-17.Chemical constituents from roots and rhizomes of Panax ginseng cultivated in Jilin province.[Pubmed: 24380303]
|

Notoginsenoside R4 Dilution Calculator

Notoginsenoside R4 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.8055 mL | 4.0277 mL | 8.0554 mL | 16.1108 mL | 20.1386 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.1611 mL | 0.8055 mL | 1.6111 mL | 3.2222 mL | 4.0277 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.0806 mL | 0.4028 mL | 0.8055 mL | 1.6111 mL | 2.0139 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0161 mL | 0.0806 mL | 0.1611 mL | 0.3222 mL | 0.4028 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0081 mL | 0.0403 mL | 0.0806 mL | 0.1611 mL | 0.2014 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Hythiemoside B
Catalog No.:BCN8833
CAS No.:853267-90-0
- Randialic acid B
Catalog No.:BCN8832
CAS No.:14021-14-8
- Harmidol hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN8831
CAS No.:6028-07-5
- Cassiaside B2
Catalog No.:BCN8830
CAS No.:218155-40-9
- Anemarrhenasaponin III
Catalog No.:BCN8829
CAS No.:163047-23-2
- Isorhamnetin 3,7-O-diglucoside
Catalog No.:BCN8828
CAS No.:6758-51-6
- 5'''-O-Feruloyl complanatoside B
Catalog No.:BCN8827
CAS No.:142473-98-1
- 11-Oxomogroside IV
Catalog No.:BCN8826
CAS No.:2096516-32-2
- Chrysophanol 1-O-beta-tetraglucoside
Catalog No.:BCN8825
CAS No.:120181-08-0
- Ardisicrenoside A
Catalog No.:BCN8824
CAS No.:160824-52-2
- Ardisiacrispin B
Catalog No.:BCN8823
CAS No.:112766-96-8
- Combretol
Catalog No.:BCN8822
CAS No.:5084-19-5
- 4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one,2,3-dihydro-5-hydroxy-3-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-7-methoxy-
Catalog No.:BCN8835
CAS No.:108001-32-7
- 6-Hydroxykaempferol 3-O-beta-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN8836
CAS No.:145134-61-8
- Quercetin 3-O-neohesperidoside
Catalog No.:BCN8837
CAS No.:32453-36-4
- Arjunetin
Catalog No.:BCN8838
CAS No.:31297-79-7
- Celosin J
Catalog No.:BCN8839
CAS No.:1623405-29-7
- Iso-sagittatoside A
Catalog No.:BCN8840
CAS No.:503456-08-4
- Hydroxy-beta-sanshool
Catalog No.:BCN8841
CAS No.:97465-69-5
- Mulberrofuran Q
Catalog No.:BCN8844
CAS No.:101383-35-1
- 4'-Methoxyagarotetrol
Catalog No.:BCN8845
CAS No.:123278-01-3
- Sterebin E
Catalog No.:BCN8846
CAS No.:114343-74-7
- Bacopaside N2
Catalog No.:BCN8847
CAS No.:871706-75-1
- Hyperforin
Catalog No.:BCN8848
CAS No.:11079-53-1
[Chemical constituents from processed rhizomes of Panax notoginseng].[Pubmed:24558875]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013 Nov;38(22):3910-7.
To investigate the chemical constituents of the processed rhizomes of Panax notoginseng, their 70% ethanol extract was chromatographed on macroporous resin (SP825), silica gel, RP-C18 and semi-preparative HPLC to afford compounds 1-23. On the basis of physicochemical properties and spectral data analysis, their structures were identified to be 6'-O-Acetylginsenoside Rh1 (1), ginsenoside RK3 (2), ginsenoside Rh4 (3), 20S-ginsenoside Rg3 (4), ginsenoside Rk1 (5), 20R-ginsenoside Rg3 (6), ginsenoside Rg5 (7), ginsenoside F2 (8), 20S-ginsenoside Rh1 (9), 20R-ginsenoside Rh1 (10), gypenoside X VII (11), notoginsenoside Fa, (12), ginsenoside Ra3 (13), ginsenoside Rg1 (14), ginsenoside Re (15), notoginsenoside R2 (16), ginsenoside Rg2 (17), notoginsenoside R1 (18), ginsenoside Rd (19), ginsenoside Rb1 (20), notoginsenoside D (21), Notoginsenoside R4 (22) and ginsenoside Rb2 (23), respectively. Among them, compound 1 was isolated from P. notoginseng for the first time, and compounds 4, 6, 8 and 11 were isolated from the processed P. notoginseng for the first time. According to the fingerprint profiles of raw and processed P. notoginseng, the putative chemical conversion pathways of panoxatriol and panoxadiol compounds in the processing procedure was deduced, and the results revealed the main reactions to be dehydration and glycosyl hydrolysis.
[Chemical constituents from roots and rhizomes of Panax ginseng cultivated in Jilin province].[Pubmed:24380303]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013 Sep;38(17):2807-17.
The chemical constituents of the roots and rhizomes of Panax ginseng were systematically investigated by various column chromatographic methods including Amberlite XAD-4 macroporous adsorptive resins and silica gel as well as high-performance liquid chromatography, and their chemical structures were identified by physico-chemical properties and spectral analyses. Twenty-eight compounds were isolated from the 70% ethanolic-aqueous extract and identified as koryoginsenoside R1 (1), ginsenoside Rg1 (2), ginsenoside Rf (3), notoginsenoside R2 (4), ginsenoside Rg2 (5), notoginsenoside Fe (6), ginsenjilinol (7), ginsenoside Re5 (8), noto-ginsenoside N (9), notoginsenoside R1 (10), ginsenoside Re2 (11), ginsenoside Re1 (12), ginsenoside Re (13), ginsenoside Rs2 (14), ginsenoside Ro methyl ester (15), ginsenoside Rd (16), ginsenoside Re3 (17), ginsenoside Re4 (18), 20-gluco-ginsenoside Rf (19), ginsenoside Ro (20), ginsenoside Rc (21), quinquenoside-R1 (22), ginsenoside Ra2 (23), ginsenoside Rb1 (24), ginsenoside Ra1 (25), ginsenoside Ra3 (26), ginsenoside Rb2 (27), and Notoginsenoside R4 (28). All isolated compounds are 20 (S) -protopanaxadiol or protopanaxatriol type triterpenoid saponins. Compound 1 was isolated from the roots and rhizomes of P. ginseng cultivated in Jilin province for the first time and compound 6 was isolated from the roots and rhizomes of P. ginseng for the first time. The 1H-NMR data of compounds 6, 14 and 19 were assigned for the first time.
Simultaneous determination of nucleobases, nucleosides and saponins in Panax notoginseng using multiple columns high performance liquid chromatography.[Pubmed:18995982]
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2008 Dec 15;48(5):1361-7.
A new multiple columns HPLC method for simultaneous determination of 16 characteristic components, 5 nucleobases and nucleosides (uracil, cytidine, uridine, guanosine and adenosine), and 11 saponins (notoginsenoside R1, ginsenoside Rg1, ginsenoside Re, Notoginsenoside R4, notoginsenoside Fa, ginsenoside Rb1, notoginsenoside R2, ginsenoside Rg2, ginsenoside Rh1, ginsenoside Rd and notoginsenoside K), in the root of Panax notoginseng, a valued traditional Chinese medicinal herb, were developed. Notoginsenoside R4, Fa and K were first quantitatively determined in P. notoginseng. The 5 nucleobases and nucleosides compounds were separated on a Zorbax SB-Aq column (150 x 4.6 mm, 5.0 microm) and 11 saponins were analyzed using a Zorbax Bonus-RP column (150 x 4.6 mm, 5.0 microm) with column switching. The column temperature was set at 30 degrees C. Mobile phase was composed of 5mM ammonium acetate aqueous (A), water (B) and acetonitrile (C) using a gradient elution. The flow rate was 1.5 mL/min and detection wavelengths were set at 260 nm for nucleobases and nucleosides, and 203 nm for saponins. The developed method had good repeatability and sensitivity for quantification of 16 analytes with overall precision (including intra- and inter-day) less than 3% (RSD), and LOD and LOQ were less than 1.33 microg/mL and 5.12 microg/mL, respectively. The method was successfully applied to the simultaneous determination of 16 analytes in 15 samples of P. notoginseng collected from different places of China, which indicated that multiple columns HPLC can be used for comprehensive quality control of P. notoginseng.


