OF-1BRPF1B and BRPF2 bromodomain inhibitor CAS# 919973-83-4 |
- Calpain Inhibitor I, ALLN
Catalog No.:BCC1233
CAS No.:110044-82-1
- CA 074
Catalog No.:BCC1141
CAS No.:134448-10-5
- Cathepsin Inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC4896
CAS No.:225120-65-0
- L 006235
Catalog No.:BCC2361
CAS No.:294623-49-7
- Balicatib
Catalog No.:BCC5139
CAS No.:354813-19-7
- MDL 28170
Catalog No.:BCC2352
CAS No.:88191-84-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 919973-83-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 35397514 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H18BrN3O4S | M.Wt | 440.31 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 13 mg/mL (29.52 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) | ||
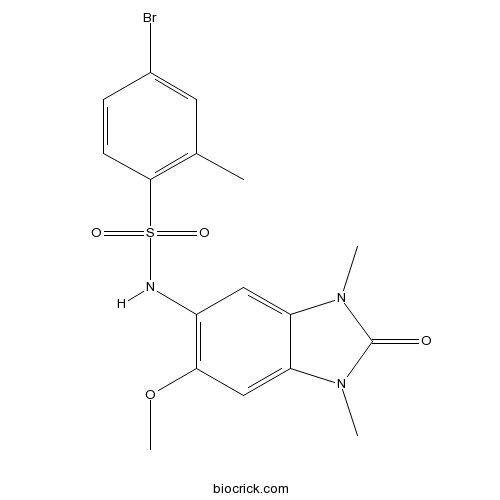
| Chemical Name | 4-bromo-N-(6-methoxy-1,3-dimethyl-2-oxobenzimidazol-5-yl)-2-methylbenzenesulfonamide | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C=CC(=C1)Br)S(=O)(=O)NC2=C(C=C3C(=C2)N(C(=O)N3C)C)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YUNQZQREIHWDQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H18BrN3O4S/c1-10-7-11(18)5-6-16(10)26(23,24)19-12-8-13-14(9-15(12)25-4)21(3)17(22)20(13)2/h5-9,19H,1-4H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective BRPF1B and BRPF2 bromodomain inhibitor (Kd values are 100 and 500 nM respectively). Exhibits 39-fold selectivity for BRPF1B and BRPF2 over BRD4. Accelerates FRAP recovery at 5 μM in a BRPF2 FRAP assay. |

OF-1 Dilution Calculator

OF-1 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2711 mL | 11.3556 mL | 22.7113 mL | 45.4225 mL | 56.7782 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4542 mL | 2.2711 mL | 4.5423 mL | 9.0845 mL | 11.3556 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2271 mL | 1.1356 mL | 2.2711 mL | 4.5423 mL | 5.6778 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0454 mL | 0.2271 mL | 0.4542 mL | 0.9085 mL | 1.1356 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0227 mL | 0.1136 mL | 0.2271 mL | 0.4542 mL | 0.5678 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
OF-1 is a selective BRPF1B and BRPF2 bromodomain inhibitor (Kd value = 100nM and 500 nM, respectively; >100-fold selectivity over majority of other bromodomains).
BRPF (BRomodomain and PHD Finger containing) protein family are scaffolding proteins that assembles MYST histone acetyltransferase complexes. MYST complexes play important role in DNA repair, recombination, replication and transcription activation.
In cellular thermal shift assay (CETSA) of full length BRPF1B, OF-1 enhanced thermal stability at 1 µM. In BRPF2 FRAP assay, OF-1 showed accelerated FRAP recovery at 5µM. OF-1 exhibited modest general cytotoxicity.
References:
[1]. OF-1 - A chemical probe for BRPF bromodomains. (2010, October 13). SGC. Retrieved from http://www.thesgc.org/chemical-probes/OF-1
- Saikosaponin H
Catalog No.:BCN7808
CAS No.:91990-63-5
- Buergerinin B
Catalog No.:BCN4555
CAS No.:919769-83-8
- Zatebradine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7286
CAS No.:91940-87-3
- AZD1283
Catalog No.:BCC5370
CAS No.:919351-41-0
- Rubrisandrin A
Catalog No.:BCN3248
CAS No.:919289-30-8
- Ro 15-4513
Catalog No.:BCC7230
CAS No.:91917-65-6
- Atrial natriuretic factor (1-28) (human, porcine)
Catalog No.:BCC5839
CAS No.:91917-63-4
- 1-Methoxyindole-3-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3946
CAS No.:91913-76-7
- 19-[(beta-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy]-19-oxo-ent-labda-8(17),13-dien-16,15-olide
Catalog No.:BCN1308
CAS No.:919120-78-8
- GPi 688
Catalog No.:BCC6091
CAS No.:918902-32-6
- TH-302
Catalog No.:BCC1998
CAS No.:918633-87-1
- PLX-4720
Catalog No.:BCC1280
CAS No.:918505-84-7
- o-Acetoacetaniside
Catalog No.:BCC9107
CAS No.:92-15-9
- 6-Methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN6906
CAS No.:92-48-8
- Scopoletin
Catalog No.:BCN4470
CAS No.:92-61-5
- Phenothiazine
Catalog No.:BCC4701
CAS No.:92-84-2
- 4,4'-Biphenol
Catalog No.:BCC8654
CAS No.:92-88-6
- 4-Acetylbiphenyl
Catalog No.:BCC8673
CAS No.:92-91-1
- 4-Biphenylcarboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8701
CAS No.:92-92-2
- Influenza Hemagglutinin (HA) Peptide
Catalog No.:BCC2563
CAS No.:92000-76-5
- P276-00
Catalog No.:BCC4415
CAS No.:920113-03-7
- Tenacigenoside A
Catalog No.:BCN4458
CAS No.:920502-42-7
- Schisanlactone D
Catalog No.:BCN3247
CAS No.:92051-26-8
- Schisanlactone C
Catalog No.:BCN3314
CAS No.:92051-27-9
A formal intermolecular [4 + 2] cycloaddition reaction of 1,3-disubstituted indoles and alkylquinones.[Pubmed:28379272]
Org Biomol Chem. 2017 Apr 18;15(16):3472-3478.
A formal [4 + 2] cycloaddition reaction of 1,3-disubstituted indoles and alkylquinones was realized to furnish polycyclic indolines in good yields. This protocol proceeded smoothly under basic conditions, with high atom-economy and broad substrate scope.
Donor Promiscuity of a Thermostable Transketolase by Directed Evolution: Efficient Complementation of 1-Deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate Synthase Activity.[Pubmed:28378514]
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017 May 2;56(19):5358-5362.
Enzymes catalyzing asymmetric carboligation reactions typically show very high substrate specificity for their nucleophilic donor substrate components. Structure-guided engineering of the thermostable transketolase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus by directed in vitro evolution yielded new enzyme variants that are able to utilize pyruvate and higher aliphatic homologues as nucleophilic components for acyl transfer instead of the natural polyhydroxylated ketose phosphates or hydroxypyruvate. The single mutant H102T proved the best hit toward 3-methyl-2-oxobutyrate as donor, while the double variant H102L/H474S showed highest catalytic efficiency toward pyruvate as donor. The latter variant was able to complement the auxotrophic deficiency of Escherichia coli cells arising from a deletion of the dxs gene, which encodes for activity of the first committed step into the terpenoid biosynthesis, offering the chance to employ a growth selection test for further enzyme optimization.
Culture Clash? Investigating constructions of sexual and reproductive health from the perspective of 1.5 generation migrants in Australia using Q methodology.[Pubmed:28376911]
Reprod Health. 2017 Apr 4;14(1):50.
BACKGROUND: In Australia, those who migrate as children or adolescents (1.5 generation migrants) may have entered a new cultural environment at a crucial time in their psychosexual development. These migrants may have to contend with constructions of sexual and reproductive health from at least two cultures which may be at conflict on the matter. This study was designed to investigate the role of culture in constructions of sexual and reproductive health and health care seeking behaviour from the perspective of 1.5 generation migrants. METHODS: Forty-two adults from various ethno-cultural backgrounds took part in this Q methodological study. Online, participants rank-ordered forty-two statements about constructions of sexual and reproductive health and health seeking behaviours based on the level to which they agreed or disagreed with them. Participants then answered a series of questions about the extent to which their ethnic/cultural affiliations influenced their identity. A by-person factor analysis was then conducted, with factors extracted using the centroid technique and a varimax rotation. RESULTS: A seven-factor solution provided the best conceptual fit for constructions of sexual and reproductive health and help-seeking. Factor A compared progressive and traditional sexual and reproductive health values. Factor B highlighted migrants' experiences through two cultural lenses. Factor C explored migrant understandings of sexual and reproductive health in the context of culture. Factor D explained the role of culture in migrants' intimate relationships, beliefs about migrant sexual and reproductive health and engagement of health care services. Factor E described the impact of culture on sexual and reproductive health related behaviour. Factor F presented the messages migrant youth are given about sexual and reproductive health. Lastly, Factor G compared constructions of sexual and reproductive health across cultures. CONCLUSIONS: This study has demonstrated that when the cultural norms of migrants' country of origin are maintained it has a significant influence on how 1.5 generation migrants construct, experience and understand various aspects of sexual and reproductive health. Policy makers, health care professionals and resettlement service providers are advised to engage with migrant parents and youth in exploring, discussing, reframing and reconstructing SRH in an Australian context.
Usefulness of 1,3 Beta-D-Glucan Detection in non-HIV Immunocompromised Mechanical Ventilated Critically Ill Patients with ARDS and Suspected Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia.[Pubmed:28378239]
Mycopathologia. 2017 Aug;182(7-8):701-708.
INTRODUCTION: Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) is a major cause of disease in immunocompromised individuals. Diagnosis is typically obtained by microscopy and/or PCR. For ambiguous PCR results, we evaluated the new biomarker 1,3-Beta-D-Glucan (BDG). METHODS: BDG serum levels were assessed and correlated to PCR results in immunosuppressed patients with ARDS. RESULTS: 11 (22%) out of 50 patients had suspected PCP. APACHE II (26 vs. 24; p < 0.002), SOFA score (16 vs. 14; p < 0.010) and mortality rate (34 vs. 69% p < 0.004; 34 vs. 80% p < 0.003) were significantly altered in patients with positive (pPCR) and slightly positive (spPCR) PCJ PCR as compared to patients with no-PCP (nPCP). BDG levels were significantly lower in patients with nPCP (86; 30-315 pg/ml) than in patients with pPCR (589; 356-1000 pg/ml; p < 0.001) and spPCP (398; 297-516 pg/ml; p < 0.004) referring to the cutoff in this study for PCP of 275 pg/ml. An overall sensitivity (S) of 92% (95% CI 86-96%) and specificity (SP) of 84% (95% CI 79-85%) for PCP were found for the BDG Fungitell assay. In detail, S of 98% (95% CI 94-100%) and SP of 86% (95% CI 82-92%) for pPCP and S of 98% (95% CI 96-100%) and SP of 88% (95% CI 86-96%) for spPCO were found. CONCLUSION: Serum BDG levels were strongly elevated in PCP, and the negative predictive value is high. BDG could be used as a preliminary test for patients with suspected PCP, especially in patients with slightly positive PCR results.


