PD 135158CAS# 130285-87-9 |
- Irbesartan
Catalog No.:BCC2560
CAS No.:138402-11-6
- Olmesartan
Catalog No.:BCC1819
CAS No.:144689-24-7
- AVE 0991
Catalog No.:BCC4032
CAS No.:304462-19-9
- Tranilast
Catalog No.:BCC2514
CAS No.:53902-12-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 130285-87-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 44385784 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C35H44N4O6 | M.Wt | 616.76 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | CAM 1028 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
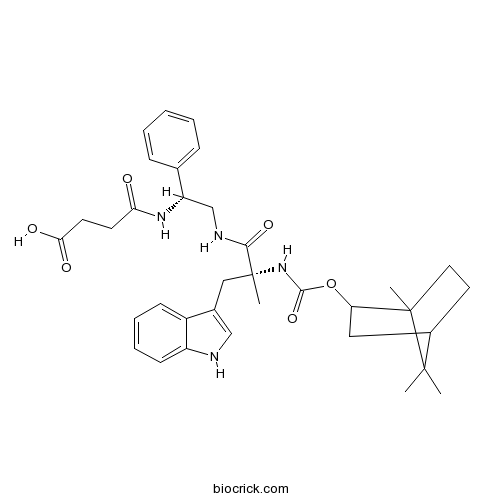
| Chemical Name | 4-[[(1R)-2-[[(2R)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-2-methyl-2-[(1,7,7-trimethyl-2-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptanyl)oxycarbonylamino]propanoyl]amino]-1-phenylethyl]amino]-4-oxobutanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC1(C2CCC1(C(C2)OC(=O)NC(C)(CC3=CNC4=CC=CC=C43)C(=O)NCC(C5=CC=CC=C5)NC(=O)CCC(=O)O)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NNTPEWZUKRSTMM-CFHPNWNBSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C35H44N4O6/c1-33(2)24-16-17-34(33,3)28(18-24)45-32(44)39-35(4,19-23-20-36-26-13-9-8-12-25(23)26)31(43)37-21-27(22-10-6-5-7-11-22)38-29(40)14-15-30(41)42/h5-13,20,24,27-28,36H,14-19,21H2,1-4H3,(H,37,43)(H,38,40)(H,39,44)(H,41,42)/t24?,27-,28?,34?,35+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent and selective, nonpeptide CCK2 receptor antagonist (IC50 values are 2.8 and 1232 nM for CCK2 and CCK1 respectively) that displays negligible affinity at GABAA, benzodiazepine, substance P, neurotensin, opioid, bradykinin and 5-HT3 receptors (IC50 > 10 μM). Exhibits anxiolytic activity in elevated plus maze and social interaction tests and increases food intake in rats. |

PD 135158 Dilution Calculator

PD 135158 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6214 mL | 8.1069 mL | 16.2138 mL | 32.4275 mL | 40.5344 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3243 mL | 1.6214 mL | 3.2428 mL | 6.4855 mL | 8.1069 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1621 mL | 0.8107 mL | 1.6214 mL | 3.2428 mL | 4.0534 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0324 mL | 0.1621 mL | 0.3243 mL | 0.6486 mL | 0.8107 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0162 mL | 0.0811 mL | 0.1621 mL | 0.3243 mL | 0.4053 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 3'-Demethoxypiplartine
Catalog No.:BCN4021
CAS No.:130263-10-4
- Acerogenin G
Catalog No.:BCN7328
CAS No.:130233-83-9
- N-(4-Hydroxyphenylacetyl)spermine
Catalog No.:BCC6594
CAS No.:130210-32-1
- Cirsimarin
Catalog No.:BCN6821
CAS No.:13020-19-4
- Torilin
Catalog No.:BCN6611
CAS No.:13018-10-5
- Torilolone
Catalog No.:BCN6659
CAS No.:13018-09-2
- Ergosterol glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN7327
CAS No.:130155-33-8
- (+)-Igmesine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5902
CAS No.:130152-35-1
- Lomustine
Catalog No.:BCC4794
CAS No.:13010-47-4
- Mafenide Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC5236
CAS No.:13009-99-9
- Dehydrocorydaline nitrate
Catalog No.:BCN2745
CAS No.:13005-09-9
- GSK1324726A
Catalog No.:BCC4038
CAS No.:1300031-52-0
- Rubiarbonol B
Catalog No.:BCN6159
CAS No.:130288-60-7
- Fmoc-Asp(OcHex)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3468
CAS No.:130304-80-2
- HOE 140
Catalog No.:BCC5964
CAS No.:130308-48-4
- Fmoc-D-Tic-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3342
CAS No.:130309-33-0
- Fmoc-Oic-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3305
CAS No.:130309-37-4
- H-D-Phe-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3013
CAS No.:13033-84-6
- CI 988
Catalog No.:BCC7430
CAS No.:130332-27-3
- Cathayanon H
Catalog No.:BCN3570
CAS No.:1303438-51-8
- Cathayanon I
Catalog No.:BCN3678
CAS No.:1303438-52-9
- MI-773
Catalog No.:BCC5155
CAS No.:1303607-07-9
- MI-773 (SAR405838)
Catalog No.:BCC5648
CAS No.:1303607-60-4
- AC 45594
Catalog No.:BCC7544
CAS No.:13037-86-0
PD-135158, a CCKB receptor antagonist, microinjected into the nucleus accumbens and the expression of conditioned rewarded behavior.[Pubmed:8761988]
Neurosci Lett. 1996 May 10;209(2):85-8.
Cholecystokinin (CCK) has been localized in the nucleus accumbens (NAC) where it may interact with dopamine neurotransmission. NAC dopamine is involved in the control over behavior produced by conditioned rewards. The present experiment examines whether the blockade of CCKB receptors in the NAC with microinjection of PD-135158 (10 micrograms in 0.5 microliter) potentiates bar-pressing for stimuli previously associated with food reward. Intra-NAC microinjections of amphetamine (10 micrograms in 0.5 microliter) increased the number of bar presses for conditioned reward presentation. Furthermore, similar administration of PD-135158 produced no significant effect on responding when administered alone but potentiated the level of amphetamine responding. These findings suggest that endogenous CCKB mechanisms in the NAC may normally inhibit dopamine function in reward-related behaviors.
PD 135158, a CCKB/gastrin receptor antagonist, stimulates rat pancreatic enzyme secretion as a CCKA receptor agonist.[Pubmed:7901038]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep 21;242(1):105-8.
The CCKB/gastrin receptor antagonist, PD 135158 (CAM 1028), surprisingly stimulates lipase release from isolated rat pancreatic acini dose dependently in a biphasic manner, with identical efficacy but lower potency compared to cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK-8). Half-maximal stimulation occurred at 0.6 microM and maximal secretion was induced at 50 microM. Supramaximal concentrations decreased lipase release. Acinar lipase secretion in response to 25 pM CCK-8 or 1 microM CAM-1028 was abolished by 5 microM of the specific CCKA receptor antagonist loxiglumide (CR 1505), half-maximal inhibition was observed at 0.6 microM for CCK-8 and 0.4 microM for PD 135158. These data demonstrate that the CCKB/gastrin receptor antagonist, PD 135158, acts as a full agonist at the rat pancreatic CCKA receptor.
PD-135,158, a cholecystokinin(B) antagonist, enhances latent inhibition in the rat.[Pubmed:10683486]
Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2000 Mar;65(3):459-63.
The antipsychotic potential of cholecystokinin (CCK)-related compounds stems from CCK's colocalization with dopamine (DA). CCK demonstrates excitatory and inhibitory effects on DA in the mesolimbic pathway. Such diverse actions might be mediated by different receptor subtypes (CCK(A) or CCK(B)). Multiple hypotheses have emerged regarding the clinical application of CCK-based drugs. Administering selective nonpeptide antagonists within animal models relevant to schizophrenia would help delineate CCK receptor involvement. One animal model simulating a cognitive dysfunction of schizophrenia is latent inhibition (LI). An animal repeatedly exposed to a stimulus that is devoid of consequence is subsequently inhibited in making new associations with that stimulus. This reflects a process of learning to ignore irrelevant stimuli. The present study examined the effects of the selective CCK(B) antagonist PD-135,158 (0.001, 0. 01, and 0.1 mg/kg) using a conditioned suppression of drinking procedure in rats. For purposes of comparison the effects of haloperidol (0.1 mg/kg) were also investigated. PD-135,158 (0.1 mg/kg), similar to haloperidol (0.1 mg/kg), elicited a clear LI effect under conditions that did not lead to LI in control rats (low number of preexposures). These findings highlight the antipsychotic potential of CCK(B) antagonists, and further illustrate the LI paradigm's capacity to detect novel, antipsychotic-like, drug activity.
Suppression of conditioned fear by administration of CCKB receptor antagonist PD135158.[Pubmed:10657528]
Neuropeptides. 1999 Dec;33(6):483-6.
In order to examine the involvement of CCK in the formation of anxiety, we have investigated whether CCKB receptor antagonist PD135158 suppressed conditioned fear stress. Rats were individually subjected to 30 min of inescapable electric footshock in a chamber with a grid floor. First, the rats were individually subjected to 30 min of footshock. Twenty-four h after the footshock, the rats were again placed in the chamber and observed for 5 min without shocks. PD135158 was administered 30 min before placing the rats in the chamber again. Secondly, PD135158 was administered 30 min before footshock. Thirdly, PD135158 was administered 5 min after footshock. Administration of PD135158 30 min before conditioned fear stress significantly reduced freezing behavior. Administration of PD135158 30 min before footshock also significantly reduced freezing behavior. But, administration of PD135158 5 min after footshock did not significantly reduce freezing behavior. PD135158 blocked not only the acquisition but also the expression of conditioned fear. These results suggest that the CCKB receptor might play an important role in conditioned fear stress and that it might be related to anxiety.
CholecystokininB receptor antagonist increases food intake in rats.[Pubmed:9811359]
Physiol Behav. 1998 Aug;65(1):11-4.
To investigate the role of cholecystokininB (CCKB) receptors in the brain in the control of food intake, we administered PD-135158, a specific and potent CCKB antagonist, into the lateral ventricle of male, Sprague-Dawley rats 30 min before a 60-min intake test. PD-135158 (0.001-0.5 mg) increased intake significantly; the mean peak increase was 39% more than the intake after vehicle treatment. The increased intake was due to a larger first meal and more intake during the last 30 min of the test. Because intake during the first 3 min, a measure of palatability or orosensory stimulation did not change significantly, we suggest that antagonism of brain CCK at central CCKB receptors decreased the satiating potency of the ingested food during the meal and decreased the potency of the mechanisms that prevent the reinitiation of eating during the postprandial intermeal interval.


