CirsimarinCAS# 13020-19-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 13020-19-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 159460 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
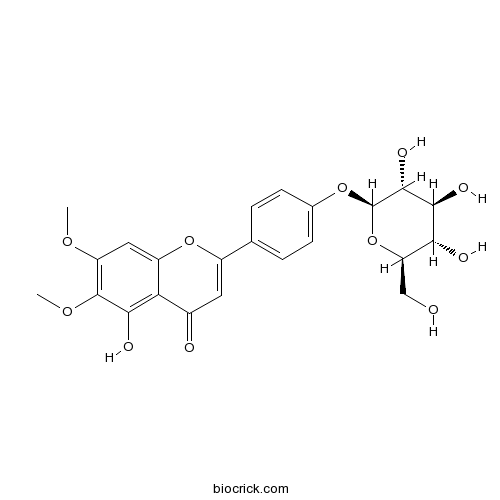
| Formula | C23H24O11 | M.Wt | 476.43 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Cirsimaretin; Cirsimaritin 4'-glucoside; Cirsitakaoside; 4',5-Dihydroxy 6,7-dimethoxyflavone 4'-glucoside | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO and methan | ||
| Chemical Name | 5-hydroxy-6,7-dimethoxy-2-[4-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxyphenyl]chromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C(=C2C(=C1)OC(=CC2=O)C3=CC=C(C=C3)OC4C(C(C(C(O4)CO)O)O)O)O)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RETJLKUBHXTIGH-FZFRBNDOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H24O11/c1-30-15-8-14-17(19(27)22(15)31-2)12(25)7-13(33-14)10-3-5-11(6-4-10)32-23-21(29)20(28)18(26)16(9-24)34-23/h3-8,16,18,20-21,23-24,26-29H,9H2,1-2H3/t16-,18-,20+,21-,23-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Cirsimarin exerts potent antilipogenic effect and decreases adipose tissue deposition in mice, it could therefore be a potential candidate for the treatment of obesity. 2. Cirsimarin shows antioxidant activity. |
| Targets | Immunology & Inflammation related |

Cirsimarin Dilution Calculator

Cirsimarin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0989 mL | 10.4947 mL | 20.9894 mL | 41.9789 mL | 52.4736 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4198 mL | 2.0989 mL | 4.1979 mL | 8.3958 mL | 10.4947 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2099 mL | 1.0495 mL | 2.0989 mL | 4.1979 mL | 5.2474 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.042 mL | 0.2099 mL | 0.4198 mL | 0.8396 mL | 1.0495 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.021 mL | 0.1049 mL | 0.2099 mL | 0.4198 mL | 0.5247 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Torilin
Catalog No.:BCN6611
CAS No.:13018-10-5
- Torilolone
Catalog No.:BCN6659
CAS No.:13018-09-2
- Ergosterol glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN7327
CAS No.:130155-33-8
- (+)-Igmesine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5902
CAS No.:130152-35-1
- Lomustine
Catalog No.:BCC4794
CAS No.:13010-47-4
- Mafenide Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC5236
CAS No.:13009-99-9
- Dehydrocorydaline nitrate
Catalog No.:BCN2745
CAS No.:13005-09-9
- GSK1324726A
Catalog No.:BCC4038
CAS No.:1300031-52-0
- I-BET151 (GSK1210151A)
Catalog No.:BCC4476
CAS No.:1300031-49-5
- Quinine
Catalog No.:BCN2341
CAS No.:130-95-0
- Quinine HCl
Catalog No.:BCN2262
CAS No.:130-89-2
- Protopine
Catalog No.:BCN6165
CAS No.:130-86-9
- N-(4-Hydroxyphenylacetyl)spermine
Catalog No.:BCC6594
CAS No.:130210-32-1
- Acerogenin G
Catalog No.:BCN7328
CAS No.:130233-83-9
- 3'-Demethoxypiplartine
Catalog No.:BCN4021
CAS No.:130263-10-4
- PD 135158
Catalog No.:BCC7431
CAS No.:130285-87-9
- Rubiarbonol B
Catalog No.:BCN6159
CAS No.:130288-60-7
- Fmoc-Asp(OcHex)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3468
CAS No.:130304-80-2
- HOE 140
Catalog No.:BCC5964
CAS No.:130308-48-4
- Fmoc-D-Tic-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3342
CAS No.:130309-33-0
- Fmoc-Oic-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3305
CAS No.:130309-37-4
- H-D-Phe-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3013
CAS No.:13033-84-6
- CI 988
Catalog No.:BCC7430
CAS No.:130332-27-3
- Cathayanon H
Catalog No.:BCN3570
CAS No.:1303438-51-8
Cirsimarin, a potent antilipogenic flavonoid, decreases fat deposition in mice intra-abdominal adipose tissue.[Pubmed:20458325]
Int J Obes (Lond). 2010 Nov;34(11):1566-75.
OBJECTIVE: We previously reported that the flavonoid Cirsimarin exerts in vitro a strong lipolytic activity on isolated adipocytes. This study was therefore designed to evaluate in vivo the effects of Cirsimarin on white adipose tissue (WAT) accretion in mice. METHODS: Male CD1 mice were injected daily with either vehicle (intraperitoneal (i.p.)) or Cirsimarin (25 or 50 mg kg(-1) per day, i.p.) for 18 days. Mice were killed and fat pads weighted. Epididymal fat pads were used for cellularity measurement. Effects of Cirsimarin treatment on lipolysis and lipogenesis in WAT were assessed. RESULTS: Mice treated with 25 or 50 mg kg(-1) per day Cirsimarin showed a decrease in retroperitoneal (-29 and -37% respectively, P<0.005) and epididymal (-25 and -28% respectively, P<0.005) fat pad weights compared with controls. This effect was restricted to intra-abdominal WAT as no difference was noticed for subcutaneous inguinal WAT. The decrease in intra-abdominal WAT accretion was due to a decrease in adipose cell diameter (-5 and -8% for 25 and 50 mg kg(-1) per day Cirsimarin, respectively) resulting in a 14 and 35% decrease in adipose cell volume while no change was noticed in total adipocyte number. Direct injection of Cirsimarin (50 mg kg(-1)) to rats did not trigger lipolysis. In contrast, Cirsimarin showed in vivo as well as in vitro a strong antilipogenic activity, which may be the critical aspect of its effects on fat accretion in mice. The inhibitory concentration 50% of Cirsimarin on lipogenic activity in isolated adipocytes was found to be 1.28+/-0.04 muM. Cirsimarin given orally reduced intra-abdominal fat accretion in mice. CONCLUSION: Cirsimarin exerts potent antilipogenic effect and decreases adipose tissue deposition in mice. Cirsimarin could therefore be a potential candidate for the treatment of obesity.
Flavonoid glycosides from Microtea debilis and their cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory effects.[Pubmed:20804824]
Fitoterapia. 2011 Mar;82(2):168-72.
Two new 5-O-glucosylflavones, 5-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl cirsimaritin (1) and 5, 4'-O-beta-D-diglucopyranosyl cirsimaritin (2), four known flavonoids, Cirsimarin (3), cirsimaritin (4), salvigenin (5), 4', 5-dihydroxy-7-methoxyflavone (6), and a norisoprenoid, vomifoliol (7), have been isolated from the aerial parts of Microtea debilis. All isolates were tested for cytotoxicity in human cancer cell lines (Hep G2, COLO 205, and HL-60) and anti-inflammatory activities in LPS-treated RAW264.7 macrophages. Compound 6 was found to be a potent inhibitor to nitrite production in macrophages. Compounds 2, 4, 6, and 7 showed moderate anti-proliferative activity against COLO-205 cells with IC(50) values of 7.1, 13.1, 6.1, and 6.8 muM, respectively.
Comparative antioxidant activity and HPLC profiles of some selected Korean thistles.[Pubmed:18277604]
Arch Pharm Res. 2008 Jan;31(1):28-33.
As yet, no comparative analyses have been conducted regarding the comparative antioxidant activities and HPLC profiles of thistles distributed in Korea. Thus, this study was performed in order to evaluate the antioxidant potentials of seven Korean thistles: Cirsium lineare, Cirsium chanroenicum, Cirsium setidens, Cirsium japonicum var. ussuriense, Cirsium nipponicum, Cirslum pendulum and Carduus crispus, via peroxynitrite and DPPH free radical assays. Among seven Korean thistles, Carduus crispus exhibited the most significant antioxidant activity in both DPPH assay and peroxynitrite. In order to characterize the compounds contained in Korean thistles, we conducted HPLC analyses on the following ten flavonoids: luteolin-5-glucoside (1), luteolin-7-glucoside (2), apigenin-7-glucoside (3), hispidulin-7-neohesperidoside (4), apigenin-7-glucuronide (5), Cirsimarin (6), pectolinarin (7), luteolin (8), apigenin (9) and acacetin (10). The results of our HPLC analyses indicated the presence of pectolinarin in the whole plants of C. setidens, C. lineare, C. nipponicum, C. pendulum, the aerial and underground parts of C. japonicum var. ussuriense, and the aerial parts of C. chanroenicum. Moreover, we were able to identify hispidulin-7-neohesperidoside and luteolin-7-glucoside in the whole plants of Carduus crispus, acacetin in the aerial parts of C. chanroenicum, Cirsimarin in C. lineare.


