PF-04217903C-Met inhibitor,selective and ATP-competitive CAS# 956905-27-4 |
- AMG-208
Catalog No.:BCC1054
CAS No.:1002304-34-8
- SGX-523
Catalog No.:BCC1055
CAS No.:1022150-57-7
- PHA-665752
Catalog No.:BCC1181
CAS No.:477575-56-7
- SU11274
Catalog No.:BCC1243
CAS No.:658084-23-2
- Cabozantinib (XL184, BMS-907351)
Catalog No.:BCC1264
CAS No.:849217-68-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 956905-27-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 17754438 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H16N8O | M.Wt | 372.38 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Ethanol : < 1 mg/mL (insoluble) DMSO : 20 mg/mL (53.71 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
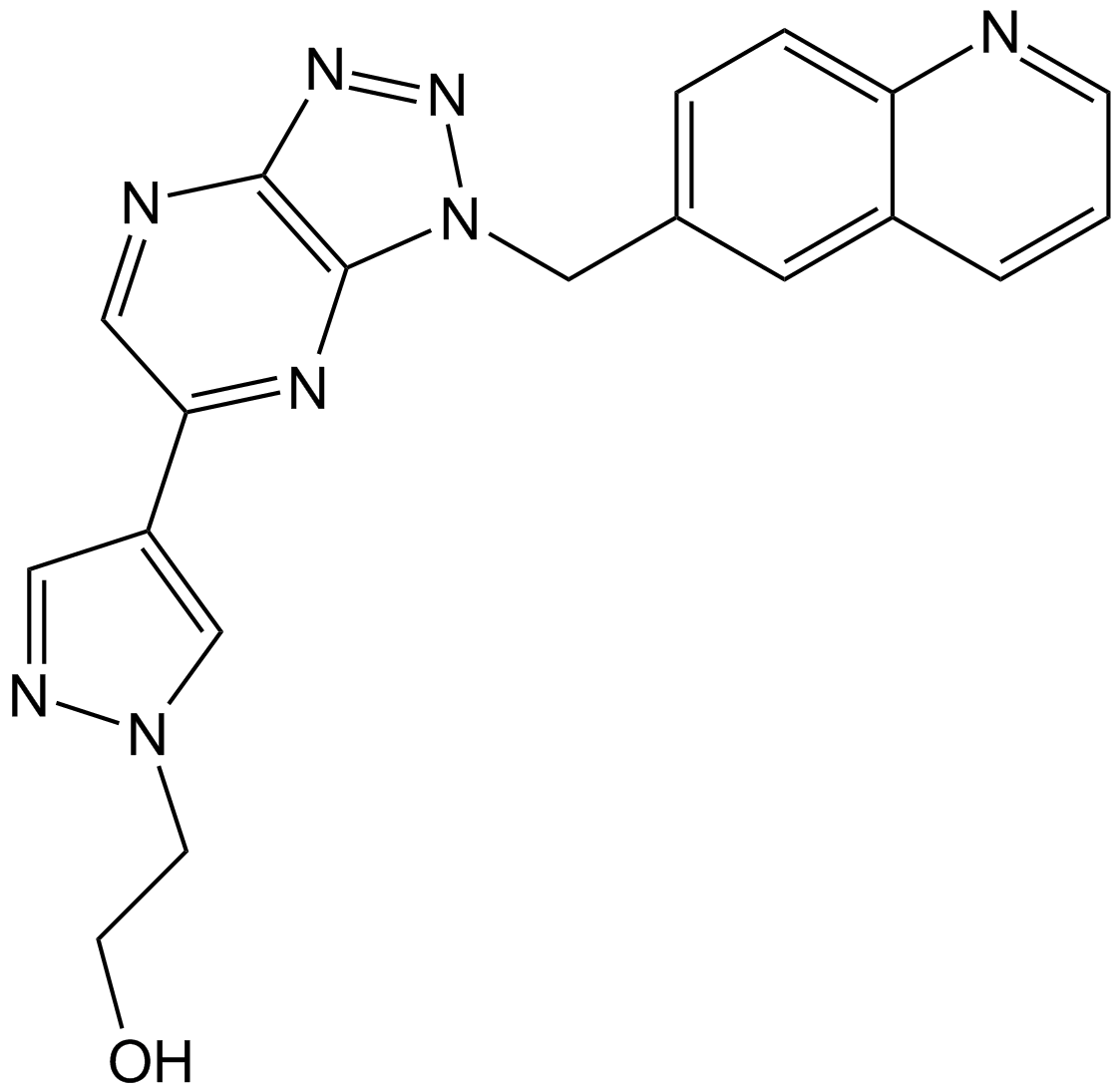
| Chemical Name | 2-[4-[3-(quinolin-6-ylmethyl)triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-5-yl]pyrazol-1-yl]ethanol | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC2=C(C=CC(=C2)CN3C4=NC(=CN=C4N=N3)C5=CN(N=C5)CCO)N=C1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PDMUGYOXRHVNMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H16N8O/c28-7-6-26-12-15(9-22-26)17-10-21-18-19(23-17)27(25-24-18)11-13-3-4-16-14(8-13)2-1-5-20-16/h1-5,8-10,12,28H,6-7,11H2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | PF-04217903 is a selective ATP-competitive c-Met inhibitor with IC50 of 4.8 nM, susceptible to oncogenic mutations (no activity to Y1230C mutant).
IC50 value: 4.8 nM [1]
Target:
in vitro: Being more selective than staurosporine or PF-02341066, PF-04217903 displays >1000-fold selectivity for c-Met over a panel of 208 kinases, although more susceptible to oncogenic mutations of c-Met that attenuate potency than PF-02341066. In addition to WT c-Met, PF-04217903 displays similar potency to inhibit the activity of c-Met-H1094R, c-Met-R988C, and c-Met-T1010I with IC50 of 3.1 nM, 6.4 nM, and 6.7 nM, respectively, but has no inhibitory activity against c-Met-Y1230C with IC50 of >10 μM [1]. PF-04217903 in combination with sunitinib significantly inhibits endothelial cells, but not the tumor cells B16F1, Tib6, EL4, and LLC [2] PF-04217903 significantly inhibits the clonogenic growth of LXFA 526L and LXFA 1647L with IC50 values of 16 nM, and 13 nM, respectively, yielding an additive effect when in combination with cetuximab [3].
in vivo: Although unable to inhibit tumor growth in the sunitinib-sensitive B16F1 and Tib6 tumor models, the combination of PF-04217903 and sunitinib significantly inhibits tumor growth in sunitinib-resistant EL4, and LLC tumor models compared with sunitinib or PF-04217903 alone by significantly blocking vascular expansion, indicating a functional role for HGF/c-Met axis in the sunitinib-resistant tumors [2]. References: | |||||

PF-04217903 Dilution Calculator

PF-04217903 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6854 mL | 13.4271 mL | 26.8543 mL | 53.7086 mL | 67.1357 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5371 mL | 2.6854 mL | 5.3709 mL | 10.7417 mL | 13.4271 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2685 mL | 1.3427 mL | 2.6854 mL | 5.3709 mL | 6.7136 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0537 mL | 0.2685 mL | 0.5371 mL | 1.0742 mL | 1.3427 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0269 mL | 0.1343 mL | 0.2685 mL | 0.5371 mL | 0.6714 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
PF-04217903 is an ATP-competitive small-molecule inhibitor of c-Met kinase with Ki value of 4.8 nM [1].
The c-Met kinase is a kind of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK) and plays critical roles in embryonic development and wound healing. Activation of c-Met by the exclusive ligand hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) triggers a serious of biological responses that collectively give rise to the invasive growth .In cancers, abnormal activation of c-METs correlates with tumor growth, formation of new blood vessels and subsequently poor prognosis. PF-04217903 is a highly selective inhibitor of c-Met. It showed antitumor activity in tumor models where c-Met is activated by mechanisms including c-Met gene amplification, HGF/c-Met autocrine loop formation or c-Met overexpression [1].
PF-04217903 showed more than 1000-fold greater selectivity against c-Met kinase over 150 other kinases. When evaluated in a panel of human tumor and endothelial cell lines such as GTL-16, H1993 and HT29 cells, PF-04217903 showed inhibition of c-Met with a mean IC50 value of 7.3 nM. PF-04217903 was also found to inhibit some mutant c-Met including R988C (IC50 value of 6.4 nM), V1092I (IC50 value of 16 nM), H1094R (IC50 value of 3.1 nM), M1250T (IC50 value of 24 nM) and T11010I (IC50 value of 6.7 nM). Besides that, PF-04217903 suppressed proliferation of c-Met-amplified GTL-16 and H1993cells with IC50 values of 12 and 30 nM, respectively. It induced apoptosis in GTL-16 cells [1 and 2].
In mice bearing injected GTL-16 tumors, administration of PF-04217903 showed dose-dependent c-Met phosphorylation inhibition and antitumor efficacy. It inhibited the phosphorylation of c-Met with EC50 value of 10 nM and suppressed tumor growth with EC50 value of 13 nM. Moreover, PF-04217903 was found to affect the downstream signal transduction of c-Met such as AKT, STAT5 and Gab-1 [1].
References:
[1] Zou H Y, Li Q, Lee J H, et al. Sensitivity of selected human tumor models to PF-04217903, a novel selective c-Met kinase inhibitor. Molecular cancer therapeutics, 2012, 11(4): 1036-1047.
[2] Cui J J, McTigue M, Nambu M, et al. Discovery of a Novel Class of Exquisitely Selective Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transition Factor (c-MET) Protein Kinase Inhibitors and Identification of the Clinical Candidate 2-(4-(1-(Quinolin-6-ylmethyl)-1 H-[1, 2, 3] triazolo [4, 5-b] pyrazin-6-yl)-1 H-pyrazol-1-yl) ethanol (PF-04217903) for the Treatment of Cancer. Journal of medicinal chemistry, 2012, 55(18): 8091-8109.
- Betamethasone hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4256
CAS No.:956901-32-9
- Euscaphin B
Catalog No.:BCN4507
CAS No.:956869-95-7
- 8beta,9alpha-Dihydroxylindan-4(5),7(11)-dien-8alpha,12-olide
Catalog No.:BCN8024
CAS No.:956707-04-3
- LDE225 (NVP-LDE225,Erismodegib)
Catalog No.:BCC5066
CAS No.:956697-53-3
- MM-22
Catalog No.:BCC6114
CAS No.:956605-71-3
- UNBS 5162
Catalog No.:BCC4008
CAS No.:956590-23-1
- Demethylsonchifolin
Catalog No.:BCN4551
CAS No.:956384-55-7
- Ranolazine 2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2503
CAS No.:95635-56-6
- Ranolazine
Catalog No.:BCC3847
CAS No.:95635-55-5
- Phoyunnanin C
Catalog No.:BCN3686
CAS No.:956344-38-0
- mavatrep
Catalog No.:BCC6457
CAS No.:956274-94-5
- TCS HDAC6 20b
Catalog No.:BCC2427
CAS No.:956154-63-5
- PF-04217903 methanesulfonate
Catalog No.:BCC1849
CAS No.:956906-93-7
- XL147
Catalog No.:BCC2487
CAS No.:956958-53-5
- Isolinderalactone
Catalog No.:BCN1252
CAS No.:957-66-4
- 7-Aminocephalosporanic acid
Catalog No.:BCC4617
CAS No.:957-68-6
- GDC-0941
Catalog No.:BCC3626
CAS No.:957054-30-7
- GDC-0941 dimethanesulfonate
Catalog No.:BCC1590
CAS No.:957054-33-0
- MK-3207 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4420
CAS No.:957116-20-0
- MK-3207
Catalog No.:BCC1759
CAS No.:957118-49-9
- SM-164
Catalog No.:BCC4002
CAS No.:957135-43-2
- NVP-QAV-572
Catalog No.:BCC4181
CAS No.:957209-68-6
- BTZ043 Racemate
Catalog No.:BCC2488
CAS No.:957217-65-1
- Hedyotisol A
Catalog No.:BCN4508
CAS No.:95732-59-5
A novel SND1-BRAF fusion confers resistance to c-Met inhibitor PF-04217903 in GTL16 cells through [corrected] MAPK activation.[Pubmed:22745804]
PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39653.
Targeting cancers with amplified or abnormally activated c-Met (hepatocyte growth factor receptor) may have therapeutic benefit based on nonclinical and emerging clinical findings. However, the eventual emergence of drug resistant tumors motivates the pre-emptive identification of potential mechanisms of clinical resistance. We rendered a MET amplified gastric cancer cell line, GTL16, resistant to c-Met inhibition with prolonged exposure to a c-Met inhibitor, PF-04217903 (METi). Characterization of surviving cells identified an amplified chromosomal rearrangement between 7q32 and 7q34 which overexpresses a constitutively active SND1-BRAF fusion protein. In the resistant clones, hyperactivation of the downstream MAPK pathway via SND1-BRAF conferred resistance to c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition. Combination treatment with METi and a RAF inhibitor, PF-04880594 (RAFi) inhibited ERK activation and circumvented resistance to either single agent. Alternatively, treatment with a MEK inhibitor, PD-0325901 (MEKi) alone effectively blocked ERK phosphorylation and inhibited cell growth. Our results suggest that combination of a c-Met tyrosine kinase inhibitor with a BRAF or a MEK inhibitor may be effective in treating resistant tumors that use activated BRAF to escape suppression of c-Met signaling.
Sensitivity of selected human tumor models to PF-04217903, a novel selective c-Met kinase inhibitor.[Pubmed:22389468]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 Apr;11(4):1036-47.
The c-Met pathway has been implicated in a variety of human cancers for its critical role in tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis. PF-04217903 is a novel ATP-competitive small-molecule inhibitor of c-Met kinase. PF-04217903 showed more than 1,000-fold selectivity for c-Met compared with more than 150 kinases, making it one of the most selective c-Met inhibitors described to date. PF-04217903 inhibited tumor cell proliferation, survival, migration/invasion in MET-amplified cell lines in vitro, and showed marked antitumor activity in tumor models harboring either MET gene amplification or a hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)/c-Met autocrine loop at well-tolerated dose levels in vivo. Antitumor efficacy of PF-04217903 was dose-dependent and showed a strong correlation with inhibition of c-Met phosphorylation, downstream signaling, and tumor cell proliferation/survival. In human xenograft models that express relatively high levels of c-Met, complete inhibition of c-Met activity by PF-04217903 only led to partial tumor growth inhibition (38%-46%) in vivo. The combination of PF-04217903 with Recepteur d'origine nantais (RON) short hairpin RNA (shRNA) knockdown in the HT29 model that also expresses activated RON kinase-induced tumor cell apoptosis and resulted in enhanced antitumor efficacy (77%) compared with either PF-04217903 (38%) or RON shRNA alone (56%). PF-04217903 also showed potent antiangiogenic properties in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, PF-04217903 strongly induced phospho-PDGFRbeta (platelet-derived growth factor receptor) levels in U87MG xenograft tumors, indicating a possible oncogene switching mechanism in tumor cell signaling as a potential resistance mechanism that might compromise tumor responses to c-Met inhibitors. Collectively, these results show the use of highly selective inhibition of c-Met and provide insight toward targeting tumors exhibiting different mechanisms of c-Met dysregulation.
Discovery of a novel class of exquisitely selective mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (c-MET) protein kinase inhibitors and identification of the clinical candidate 2-(4-(1-(quinolin-6-ylmethyl)-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-6-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1 -yl)ethanol (PF-04217903) for the treatment of cancer.[Pubmed:22924734]
J Med Chem. 2012 Sep 27;55(18):8091-109.
The c-MET receptor tyrosine kinase is an attractive oncology target because of its critical role in human oncogenesis and tumor progression. An oxindole hydrazide hit 6 was identified during a c-MET HTS campaign and subsequently demonstrated to have an unusual degree of selectivity against a broad array of other kinases. The cocrystal structure of the related oxindole hydrazide c-MET inhibitor 10 with a nonphosphorylated c-MET kinase domain revealed a unique binding mode associated with the exquisite selectivity profile. The chemically labile oxindole hydrazide scaffold was replaced with a chemically and metabolically stable triazolopyrazine scaffold using structure based drug design. Medicinal chemistry lead optimization produced 2-(4-(1-(quinolin-6-ylmethyl)-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-6-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1 -yl)ethanol (2, PF-04217903), an extremely potent and exquisitely selective c-MET inhibitor. 2 demonstrated effective tumor growth inhibition in c-MET dependent tumor models with good oral PK properties and an acceptable safety profile in preclinical studies. 2 progressed to clinical evaluation in a Phase I oncology setting.


