SM-164Anticancer agent CAS# 957135-43-2 |
- BV6
Catalog No.:BCC5372
CAS No.:1001600-56-1
- LCL161
Catalog No.:BCC1691
CAS No.:1005342-46-0
- Birinapant (TL32711)
Catalog No.:BCC2250
CAS No.:1260251-31-7
- Embelin
Catalog No.:BCN2678
CAS No.:550-24-3
- GDC-0152
Catalog No.:BCC2252
CAS No.:873652-48-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 957135-43-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 17756618 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C62H84N14O6 | M.Wt | 1121.42 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 5.2 mg/mL (4.64 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
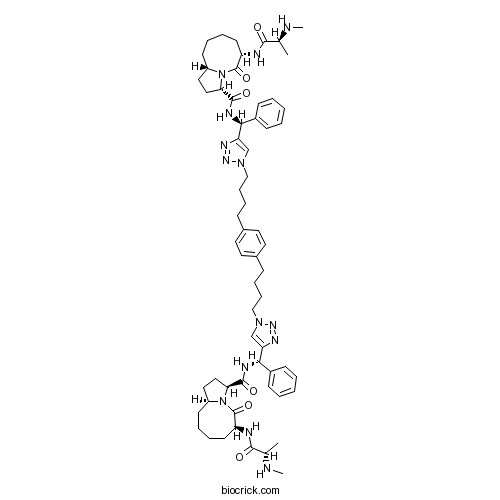
| Chemical Name | (3S,6S,10aS)-N-[(S)-[1-[4-[4-[4-[4-[(S)-[[(3S,6S,10aS)-6-[[(2S)-2-(methylamino)propanoyl]amino]-5-oxo-2,3,6,7,8,9,10,10a-octahydro-1H-pyrrolo[1,2-a]azocine-3-carbonyl]amino]-phenylmethyl]triazol-1-yl]butyl]phenyl]butyl]triazol-4-yl]-phenylmethyl]-6-[[(2S)-2-(methylamino)propanoyl]amino]-5-oxo-2,3,6,7,8,9,10,10a-octahydro-1H-pyrrolo[1,2-a]azocine-3-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(C(=O)NC1CCCCC2CCC(N2C1=O)C(=O)NC(C3=CC=CC=C3)C4=CN(N=N4)CCCCC5=CC=C(C=C5)CCCCN6C=C(N=N6)C(C7=CC=CC=C7)NC(=O)C8CCC9N8C(=O)C(CCCC9)NC(=O)C(C)NC)NC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LGYDZXNSSLRFJS-IOQQVAQYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C62H84N14O6/c1-41(63-3)57(77)65-49-27-13-11-25-47-33-35-53(75(47)61(49)81)59(79)67-55(45-21-7-5-8-22-45)51-39-73(71-69-51)37-17-15-19-43-29-31-44(32-30-43)20-16-18-38-74-40-52(70-72-74)56(46-23-9-6-10-24-46)68-60(80)54-36-34-48-26-12-14-28-50(62(82)76(48)54)66-58(78)42(2)64-4/h5-10,21-24,29-32,39-42,47-50,53-56,63-64H,11-20,25-28,33-38H2,1-4H3,(H,65,77)(H,66,78)(H,67,79)(H,68,80)/t41-,42-,47-,48-,49-,50-,53-,54-,55-,56-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Targets | IAP | ||||
| IC50 | 0.56 nM/0.31 nM/1.1 nM |
| Kinase experiment [1]: | |
| Fluorescence-polarization-based binding assays for XIAP, cIAP-1 and cIAP-2 proteins | To determine the binding affinities of SM-164 to XIAP containing both BIR2 andBIR3 domains, an FP-based competitive binding assay was established using a bivalent fluorescently tagged tracer, named Smac-1F. The Kd value of the bivalent tagged tracer to XIAP containing BIR2 and BIR3 domains was determined to be 2.3 nM. In competitive binding experiments, a tested compound was incubated with 3 nM of XIAP protein containing both BIR2 and BIR3 domain (residues 120-356) and 1 nM of in the same assay buffer. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
| Cell lines | MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell |
| Preparation method | Limited solubility. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 ℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
| Reacting condition | 12 h-48 h |
| Applications | 12 h 1 nmol/L SM-164 treatment induces 32%, 33%, and 37% of the MDA-MB-231, SK-OV-3 and MALME-3M cells to undergo apoptosis. SM-164 also leads to cIAP-1 degradation in resistant cancer cell line and effectively antagonizes cellular XIAP. Moreover, 3 to 10 nmol/L SM-164 induces cell death with or without TNFα in all these sensitive cancer cell lines. |
| Animal experiment [1]: | |
| Animal models | MDA-MB-231 xenograft tumor mice model |
| Dosage form | A single i.v. dose of SM-164 at 5 mg/kg. |
| Application | At the 3-hour time point, SM-164 induces prominent apoptosis in tumor tissues, and more than 50% of tumor cells were TUNEL positive at the 6-hour time point. SM-164 reduces the tumor volume from 147 ± 54 mm3 (day 25-start of the treatment) to 54 ± 32 mm3 (day 36-end of treatment), a 65% reduction. SM-164 treatment also shows no significant weight loss or sign of toxicity. |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: 1. Lu J, Bai L, Sun H, Nikolovska-Coleska Z et al.SM-164: a novel, bivalent Smac mimetic that induces apoptosis and tumor regression by concurrent removal of the blockade of cIAP-1/2 and XIAP. Cancer Res. 2008 Nov 15;68(22):9384-93. | |

SM-164 Dilution Calculator

SM-164 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.8917 mL | 4.4586 mL | 8.9173 mL | 17.8345 mL | 22.2932 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.1783 mL | 0.8917 mL | 1.7835 mL | 3.5669 mL | 4.4586 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.0892 mL | 0.4459 mL | 0.8917 mL | 1.7835 mL | 2.2293 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0178 mL | 0.0892 mL | 0.1783 mL | 0.3567 mL | 0.4459 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0089 mL | 0.0446 mL | 0.0892 mL | 0.1783 mL | 0.2229 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
SM-164 is a bivalent mimetic of Smac with Ki values of 0.31 nM, 1.1 nM and 0.56 nM for cIAP-1, cIAP-2 and XIAP, respectively 1.
SM-164 is developed as an anticancer agent. It plays its antitumor roles through inducing degradation of cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein (cIAP)-1/2, antagonizing X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) and inducing TNFα–dependent apoptosis in tumor cells. SM-164 is a bivalent mimetic containing two SM-122 analogues. It binds to cIAP-1 protein containing bothBIR2 and BIR3 domains, cIAP-2 BIR3 protein and XIAP protein containing both BIR2 and BIR3 domains with Ki values of 0.31 nM, 1.1 nM and 0.56 nM, respectively. In tumor cells, treatment of SM-164 significantly reduced cIAP-1 level to undetectable levels (1nM, 60min), effectively antagonized cellular XIAP and enhanced TNFα secretion. In the MDA-MB-231 xenograft model, administration of SM-164 at dose of 5mg/kg markedly decreased cIAP-1 level within 1 hour and activated caspase-8, caspase-9 and caspase-3 at 3 hour 1.
References:
1. Lu J, Bai L, Sun H, et al. SM-164: a novel, bivalent Smac mimetic that induces apoptosis and tumor regression by concurrent removal of the blockade of cIAP-1/2 and XIAP. Cancer research, 2008, 68(22): 9384-9393.
- MK-3207
Catalog No.:BCC1759
CAS No.:957118-49-9
- MK-3207 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4420
CAS No.:957116-20-0
- GDC-0941 dimethanesulfonate
Catalog No.:BCC1590
CAS No.:957054-33-0
- GDC-0941
Catalog No.:BCC3626
CAS No.:957054-30-7
- 7-Aminocephalosporanic acid
Catalog No.:BCC4617
CAS No.:957-68-6
- Isolinderalactone
Catalog No.:BCN1252
CAS No.:957-66-4
- XL147
Catalog No.:BCC2487
CAS No.:956958-53-5
- PF-04217903 methanesulfonate
Catalog No.:BCC1849
CAS No.:956906-93-7
- PF-04217903
Catalog No.:BCC2486
CAS No.:956905-27-4
- Betamethasone hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4256
CAS No.:956901-32-9
- Euscaphin B
Catalog No.:BCN4507
CAS No.:956869-95-7
- 8beta,9alpha-Dihydroxylindan-4(5),7(11)-dien-8alpha,12-olide
Catalog No.:BCN8024
CAS No.:956707-04-3
- NVP-QAV-572
Catalog No.:BCC4181
CAS No.:957209-68-6
- BTZ043 Racemate
Catalog No.:BCC2488
CAS No.:957217-65-1
- Hedyotisol A
Catalog No.:BCN4508
CAS No.:95732-59-5
- Daphnodorin B
Catalog No.:BCN7937
CAS No.:95733-02-1
- Nedaplatin
Catalog No.:BCC4807
CAS No.:95734-82-0
- FPH2 (BRD-9424)
Catalog No.:BCC5451
CAS No.:957485-64-2
- Charybdotoxin
Catalog No.:BCC6933
CAS No.:95751-30-7
- Fmoc-Phe(4-NO2)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3277
CAS No.:95753-55-2
- Fmoc-Phe(4-NH2)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3154
CAS No.:95753-56-3
- HIV-1 integrase inhibitor 2
Catalog No.:BCC1619
CAS No.:957890-42-5
- MPC-3100
Catalog No.:BCC2128
CAS No.:958025-66-6
- CPI-613
Catalog No.:BCC2287
CAS No.:95809-78-2
Therapy of Smac mimetic SM-164 in combination with gemcitabine for pancreatic cancer.[Pubmed:23142291]
Cancer Lett. 2013 Feb 1;329(1):118-24.
Pancreatic cancer (PC) is a lethal solid malignancy with resistance to traditional chemotherapy. We investigated therapy of PC with SM-164 and gemcitabine alone and in combination. Survival of PC cells was reduced as the dose of SM-164 increased. SM-164 and/or gemcitabine increased the number of apoptotic and dead PC cells, and expression of cleavage fragments of caspase-3 and PARP1, and inhibited tumor xenograft growth in nude mice. The inhibitory effect of combination treatment was greater and of longer duration than monotherapy. Neither combination nor monotherapy showed any significant toxicity in vivo. Apoptosis and necrosis, decreased expression of Ki67, and increased expression of cleaved caspase-3 were observed in xenograft tumor tissues in SM164/gemcitabine-treated mice. SM-164 could be a promising new agent for treatment of PC in combination with gemcitabine.
Therapeutic potential and molecular mechanism of a novel, potent, nonpeptide, Smac mimetic SM-164 in combination with TRAIL for cancer treatment.[Pubmed:21372226]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 May;10(5):902-14.
Smac mimetics are being developed as a new class of anticancer therapies. Because the single-agent activity of Smac mimetics is very limited, rational combinations represent a viable strategy for their clinical development. The combination of Smac mimetics with TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) may be particularly attractive because of the low toxicity of TRAIL to normal cells and the synergistic antitumor activity observed for the combination. In this study, we have investigated the combination synergy between TRAIL and a potent Smac mimetic, SM-164, in vitro and in vivo and the underlying molecular mechanism of action for the synergy. Our study shows that SM-164 is highly synergistic with TRAIL in vitro in both TRAIL-sensitive and TRAIL-resistant cancer cell lines of breast, prostate, and colon cancer. Furthermore, the combination of SM-164 with TRAIL induces rapid tumor regression in vivo in a breast cancer xenograft model in which either agent is ineffective. Our data show that X-linked IAP (XIAP) and cellular IAP 1 (cIAP1), but not cIAP2, work in concert to attenuate the activity of TRAIL; SM-164 strongly enhances TRAIL activity by concurrently targeting XIAP and cIAP1. Moreover, although RIP1 plays a minimal role in the activity of TRAIL as a single agent, it is required for the synergistic interaction between TRAIL and SM-164. This study provides a strong rationale to develop the combination of SM-164 and TRAIL as a new therapeutic strategy for the treatment of human cancer.
Smac mimetic SM-164 potentiates APO2L/TRAIL- and doxorubicin-mediated anticancer activity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.[Pubmed:23240027]
PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51461.
BACKGROUND: The members of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) family are key negative regulators of apoptosis. Overexpression of IAPs are found in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and can contribute to chemotherapy resistance and recurrence of HCC. Small-molecule Second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases (Smac) mimetics have recently emerged as novel anticancer drugs through targeting IAPs. The specific aims of this study were to 1) examine the anticancer activity of Smac mimetics as a single agent and in combination with chemotherapy in HCC cells, and 2) investigate the mechanism of anticancer action of Smac mimetics. METHODS: Four HCC cell lines, including SMMC-7721, BEL-7402, HepG2 and Hep3B, and 12 primary HCC cells were used in this study. Smac mimetic SM-164 was used to treat HCC cells. Cell viability, cell death induction and clonal formation assays were used to evaluate the anticancer activity. Western blotting analysis and a pancaspase inhibitor were used to investigate the mechanisms. RESULTS: Although SM-164 induced complete cIAP-1 degradation, it displayed weak inhibitory effects on the viability of HCC cells. Nevertheless, SM-164 considerably potentiated Apo2 ligand or TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (APO2L/TRAIL)- and Doxorubicin-mediated anticancer activity in HCC cells. Mechanistic studies demonstrated that SM-164 in combination with chemotherapeutic agents resulted in enhanced activation of caspases-9, -3 and cleavage of poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP), and also led to decreased AKT activation. CONCLUSIONS: Smac mimetics can enhance chemotherapeutic-mediated anticancer activity by enhancing apoptosis signaling and suppressing survival signaling in HCC cells. This study suggests Smac mimetics are potential therapeutic agents for HCC.
Smac-mimetic compound SM-164 induces radiosensitization in breast cancer cells through activation of caspases and induction of apoptosis.[Pubmed:21901386]
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 May;133(1):189-99.
Radiotherapy is a treatment choice for local control of breast cancer, particularly after the removal of tumor tissues by surgery. However, intrinsic radioresistance of cancer cells limits therapeutic efficacy. Here, we determined in breast cancer cells the potential radiosensitizing activity of SM-164, a small molecule compound, that mimics the activity of SMAC, a mitochondrial protein released during apoptosis to activate caspases by inhibiting cellular inhibitor of apoptosis proteins, cIAP-1, and XIAP. We found that SM-164 at nanomolar concentrations promoted degradation of cIAP-1, disrupted the inhibitory binding of XIAP to active caspase-9, and sensitized breast cancer cells to radiation with a sensitization enhancement ratio (SER) of 1.7-1.8. In one line of breast cancer cells resistant to SM-164 as a single agent, SM-164 radiosensitization was mediated by intrinsic apoptosis pathway through activation of caspases-9 and -3. In a line of breast cancer cells sensitive to SM-164 as a single agent, SM-164 radiosensitization was mediated by both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis pathways through activation of caspases-9, -8, and -3. Consistently, blockage of caspase activation, through siRNA knockdown or treatment with a pan-caspase inhibitor z-VAD-fmk, inhibited apoptosis and abrogated SM-164 radiosensitization. Our study demonstrates that IAPs are valid radiosensitizing targets in breast cancer cells and SM-164 could be further developed as a novel class of radiosensitizers for the treatment of radioresistant breast cancer.


