Phenformin HClbiguanidine drug with anti-diabetic activity CAS# 834-28-6 |
- Metformin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4799
CAS No.:1115-70-4
- Lenalidomide (CC-5013)
Catalog No.:BCC2245
CAS No.:191732-72-6
- Gliclazide
Catalog No.:BCC5002
CAS No.:21187-98-4
- Geniposide
Catalog No.:BCN5104
CAS No.:24512-63-8
- MEK inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1738
CAS No.:334951-92-7
- Imeglimin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4085
CAS No.:775351-61-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 834-28-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 13266 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C10H16ClN5 | M.Wt | 241.72 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Phenethylbiguanide hydrochloride | ||
| Solubility | H2O : 12.5 mg/mL (51.71 mM; Need ultrasonic) DMSO : < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) Ethanol : < 1 mg/mL (insoluble) DMF : < 1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
| Chemical Name | 1-(diaminomethylidene)-2-(2-phenylethyl)guanidine;hydrochloride | ||
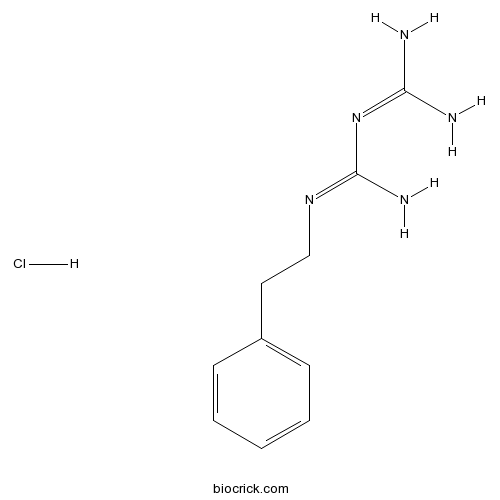
| SMILES | [H+].[Cl-].NC(N)=NC(N)=NCCc1ccccc1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YSUCWSWKRIOILX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H15N5.ClH/c11-9(12)15-10(13)14-7-6-8-4-2-1-3-5-8;/h1-5H,6-7H2,(H6,11,12,13,14,15);1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Phenformin (hydrochloride) is a hydrochloride salt of phenformin that is an anti-diabetic drug from the biguanide class, can activate AMPK activity.In Vitro:Phenformin stimulates the phosphorylation and activation of AMPKalpha1 and AMPKalpha2 without altering LKB1 activity[1]. Phenformin increases AMPK activity and phosphorylation in the isolated heart, the increase in AMPK activity is always preceded by and correlated with increased cytosolic [AMP][2]. Phenformin is a 50-fold more potent inhibitor of mitochondrial complex I than metformin. Phenformin robustly induces apoptosis in LKB1 deficient NSCLC cell lines. Phenformin at 2 mM similarly induces AMPK signaling as shown by increased P-AMPK and P-Raptor levels. Phenformin induces higher levels of cellular stress, triggering induction of P-Ser51 eIF2α and its downstream target CHOP, and markers of apoptosis at later times. Phenformin induces a significant increase in survival and therapeutic response in KLluc mice following long-term treatment[3]. Phenformin and AICAR increases AMPK activity in H441 cells in a dose-dependent fashion, stimulating the kinase maximally at 5-10 mm and 2 mm, respectively. Phenformin significantly decreases basal ion transport (measured as short circuit current) across H441 monolayers by approximately 50% compared with that of controls. Phenformin and AICAR significantly reduce amiloride-sensitive transepithelial Na+ transport compared with controls. Phenformin and AICAR suppress amiloride-sensitive Na+ transport across H441 cells via a pathway that includes activation of AMPK and inhibition of both apical Na+ entry through ENaC and basolateral Na+ extrusion via the Na+,K+-ATPase[4]. Phenformin-treated rats reveals a tendency towards a decrease in blood insulin level (radioimmunoassay)[5].In Vivo:Phenformin increases levels of P-eIF2α and its target BiP/Grp78 in normal lung as well as in lung tumors of mice[3]. References: | |||||

Phenformin HCl Dilution Calculator

Phenformin HCl Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.137 mL | 20.6851 mL | 41.3702 mL | 82.7404 mL | 103.4255 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8274 mL | 4.137 mL | 8.274 mL | 16.5481 mL | 20.6851 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4137 mL | 2.0685 mL | 4.137 mL | 8.274 mL | 10.3425 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0827 mL | 0.4137 mL | 0.8274 mL | 1.6548 mL | 2.0685 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0414 mL | 0.2069 mL | 0.4137 mL | 0.8274 mL | 1.0343 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Phenformin HCl is a hydrochloride salt of the biguanidine drug phenformin.
Phenformin is the biguanide class that displays anti-diabetic activity.
In 5 patients with diabetes mellitus, phenformin reduced the blood glucose values and glycosuria. In 4 of 5 patients, cholesterol and total lipid levels were dropped. Also, Phenformin had no impact on glucose, nor the insulin levels after intravenous glucose loading.
References:
[1]. Geldermans CA, Terpstra J, Krans HM. The effect of phenformin-HCl on patients with diabetes mellitus, studied under strict balance conditions. Diabetologia, 1975, 11(5): 475-482.
- PL 017
Catalog No.:BCC5864
CAS No.:83397-56-2
- Prenyl caffeate
Catalog No.:BCC8351
CAS No.:100884-13-7
- D609
Catalog No.:BCC1509
CAS No.:83373-60-8
- 25(R)-Hydroxyprotopanaxadiol
Catalog No.:BCN2493
CAS No.:83349-37-5
- 10-O-Caffeoyl-6-epiferetoside
Catalog No.:BCN4822
CAS No.:83348-22-5
- Dynorphin B
Catalog No.:BCC5987
CAS No.:83335-41-5
- (-)-Lariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN3418
CAS No.:83327-19-9
- 8(17),13-Labdadien-15,16-olide
Catalog No.:BCN4374
CAS No.:83324-51-0
- Bryostatin 1
Catalog No.:BCC7343
CAS No.:83314-01-6
- 7-Hydroxycoumarin-6-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4375
CAS No.:833-52-3
- Menisporphine
Catalog No.:BCN7902
CAS No.:83287-02-9
- Napabucasin
Catalog No.:BCC6525
CAS No.:83280-65-3
- ICI 154,129
Catalog No.:BCC5677
CAS No.:83420-94-4
- Boc-D-Prolinol
Catalog No.:BCC2707
CAS No.:83435-58-9
- Ebracteolata cpd B
Catalog No.:BCN3781
CAS No.:83459-37-4
- Ginsenoside Ra1
Catalog No.:BCN8392
CAS No.:83459-41-0
- Mifamurtide
Catalog No.:BCC5241
CAS No.:83461-56-7
- Voglibose
Catalog No.:BCC4750
CAS No.:83480-29-9
- Ginsenoside Rd2
Catalog No.:BCN8279
CAS No.:83480-64-2
- Grantaline
Catalog No.:BCN2083
CAS No.:83482-61-5
- 4-[4-(3-Hydroxyphenyl)-3-(4-methylphenyl)-6-oxo-1,4-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-d]pyrazol-5-yl]benzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6341
CAS No.:834903-43-4
- Leucosceptoside A
Catalog No.:BCN7457
CAS No.:83529-62-8
- Anisofolin A
Catalog No.:BCN4377
CAS No.:83529-71-9
- 2,2-Bis(3-amino-4-hydroxyphenyl)hexafluoropropane
Catalog No.:BCC8490
CAS No.:83558-87-6
The effect of phenformin-HCl on patients with diabetes mellitus, studied under strict balance conditions.[Pubmed:1181670]
Diabetologia. 1975 Oct;11(5):475-82.
Under strict balance conditions we studied the effect of phenformin in 5 patients with diabetes mellitus. In all cases phenformin lowered the blood glucose values, and all patients showed a reduction of glycosuria. Contrary to other reports body weight increased during phenformin treatment. This was accompanied by positive nitrogen, phosphorus and calcium balances. The weight gain can be explained by the positive caloric balance, mainly caused by the diminished glycosuria. No change in B.M.R. or R.Q. was seen. During phenformin treatment there was a drop in cholesterol and total lipid levels in 4 patients. No conclusions could be drawn about the effect of phenformin on triglycerides, phospholipids and lipoprotein spectra. Phenformin treatment did not affect the disappearance of glucose, nor the insulin levels after intravenous glucose loading. During oral glucose loading phenformin caused a significant fall in blood glucose levels, accompanied by an increased insulin response in one patient. In the other 4 patients phenformin had no effect on either parameter.


