PiperanineCAS# 23512-46-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 23512-46-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5320618 | Appearance | Powder |
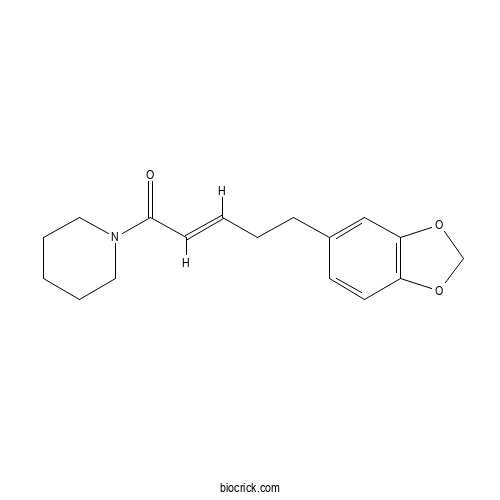
| Formula | C17H21NO3 | M.Wt | 287.4 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (E)-5-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-1-piperidin-1-ylpent-2-en-1-one | ||
| SMILES | C1CCN(CC1)C(=O)C=CCCC2=CC3=C(C=C2)OCO3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QHWOFMXDKFORMO-XVNBXDOJSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H21NO3/c19-17(18-10-4-1-5-11-18)7-3-2-6-14-8-9-15-16(12-14)21-13-20-15/h3,7-9,12H,1-2,4-6,10-11,13H2/b7-3+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Piperanine Dilution Calculator

Piperanine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4795 mL | 17.3974 mL | 34.7947 mL | 69.5894 mL | 86.9868 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6959 mL | 3.4795 mL | 6.9589 mL | 13.9179 mL | 17.3974 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3479 mL | 1.7397 mL | 3.4795 mL | 6.9589 mL | 8.6987 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0696 mL | 0.3479 mL | 0.6959 mL | 1.3918 mL | 1.7397 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0348 mL | 0.174 mL | 0.3479 mL | 0.6959 mL | 0.8699 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 2E-Decenoylpiperidide
Catalog No.:BCN0504
CAS No.:147030-02-2
- 2E,4E-Decadienoylpiperidide
Catalog No.:BCN0503
CAS No.:42997-42-2
- Isoorientin 2''-O-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN0502
CAS No.:50980-94-4
- Chingchengenamide A
Catalog No.:BCN0501
CAS No.:139906-29-9
- Retrofractamide B
Catalog No.:BCN0500
CAS No.:54794-74-0
- Guineensine
Catalog No.:BCN0499
CAS No.:55038-30-7
- 5α,8α-Epidioxyergost-6-en-3β-ol
Catalog No.:BCN0498
CAS No.:82227-99-4
- Sarmentine
Catalog No.:BCN0497
CAS No.:78910-33-5
- Muramine
Catalog No.:BCN0496
CAS No.:2292-20-8
- Uvamalol D
Catalog No.:BCN0495
CAS No.:545404-02-2
- 6-O-Veratroylcatalpol
Catalog No.:BCN0494
CAS No.:56973-43-4
- Piceatannol 4'-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN0493
CAS No.:116181-54-5
- (3R,5R)-1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-7-phenylheptane-3,5-diol
Catalog No.:BCN0506
CAS No.:112494-44-7
- Alpinin A
Catalog No.:BCN0507
CAS No.:2151847-03-7
- 4'-Hydroxy-5,6,7-trimethoxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN0508
CAS No.:72943-91-0
- 7-O-Methylaromadendrin
Catalog No.:BCN0509
CAS No.:37971-69-0
- 4-Formylphenyl(tetra-O-acetyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN0510
CAS No.:31873-42-4
- (3R,5R)-1-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)heptane-3,5-diol
Catalog No.:BCN0511
CAS No.:408324-13-0
- Methyl epi-dihydrophaseate
Catalog No.:BCN0512
CAS No.:57761-30-5
- Linarin 4'''-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN0513
CAS No.:79541-06-3
- Myricetin 3-O-beta-D-xylopyranosyl(1-2)-[alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-6)]-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN0514
CAS No.:
- Alpinin B
Catalog No.:BCN0515
CAS No.:2125947-85-3
- (R)-5-Hydroxy-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-phenylheptan-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN0516
CAS No.:1961196-24-6
- Desacetylripariochromene B
Catalog No.:BCN0517
CAS No.:69790-24-5
Cardioprotective effect of ethanol extracts of Sugemule-3 decoction on isoproterenol-induced heart failure in Wistar rats through regulation of mitochondrial dynamics.[Pubmed:34600079]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Sep 29:114669.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Sugemule-3 decoction (SD-3) is a commonly used prescription in Mongolian medicine which composed of the herbs Baidoukou (the fruit of Amomum compactum Sol. ex Maton), Baijusheng (the fruit of Lactuca sativa L.) and Biba (Piper longum L.). SD-3 has remarkable effect on the cardiovascular diseases, but its pharmacological mechanism has not been elucidated. AIM OF THIS STUDY: To evaluate the cardioprotective effects and the potential mechanisms of the ethanol extracts of SD-3 against isoproterenol (ISO)-induced heart failure (HF) in rats. MATERIAL AND METHODS: The ethanol extracts of SD-3 were prepared and analyzed by LC-ESI-MS/MS. One hundred male Wistar rats were randomly divided into five groups: control, ISO (HF) and different doses of SD-3 (0.4, 0.2, 0.1g/kg/d) groups. HF model rats were established by intraperitoneal injecting of ISO. The left ventricular function was evaluated by echocardiography. Myocardial injury and fibrosis were examined by hematoxylin-eosin (HE) and Masson staining. Western-blot analysis was performed to determine the protein expression of apoptosis and mitochondrial dynamics in all the groups. Moreover, the structural changes in the mitochondria of cardiomyocytes were also observed by transmission electron microscopy. RESULTS: Fifteen compounds were detected in the ethanol extracts of SD-3, include piperine, Piperanine, etc. Rats administered with ISO showed a significant decline in the left ventricular function. The cardiac histopathological changes such as local necrosis, interstitial oedema, and cardiac fibrosis were also observed in the ISO group. The treatment with SD-3 significantly inhibited these effects of ISO. ISO was found to increase the protein expression of Bax, cleaved-PARP and cleaved-caspase-3, -7 -9, destroy the balance between mitochondrial fusion and fission, and alter the mitochondrial morphology. The ethanol extracts of SD-3 could rebalance mitochondrial fusion and fission, and ameliorates the morphological abnormalities induced by ISO in mitochondria. CONCLUSION: The current study demonstrated that ethanol extracts of SD-3 improved isoprenaline-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis and regulating the mitochondrial dynamics.
Amide alkaloids characterization and neuroprotective properties of Piper nigrum L.: A comparative study with fruits, pericarp, stalks and leaves.[Pubmed:34474242]
Food Chem. 2021 Aug 10;368:130832.
Piper nigrum L. is commonly used worldwide and its pericarp, stalks, leaves will be major wastes materials. 42 amide alkaloids were identified in black, white pepper and pericarp by UHPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap HRMS method, followed by 40 constituents in stalks and 36 constituents in leaves. 8 amide alkaloids were reported for the first time in P. nigrum. An ultra-high-performance supercritical fluid chromatography (UHPSFC)-MS method was firstly applied to simultaneously determine 9 characteristic constituents (piperine, piperlonguminine, Piperanine, pipercallosine, dehydropipernonaline, pipernonatine, retrofractamide B, pellitorine and guineensine). The most abundant compound in each extract was piperine with a concentration from 0.10 to 12.37 mg/g of dry weight. The fruits, pericarp and leaves extracts could improve cell viability in 6-OHDA-induced SK-N-SH and SH-SY5Y cells. The results showed the characteristics of amide alkaloids of different parts of P. nigrum and evaluated their neuroprotective activities.
Identification of the stable and reactive metabolites of tetrahydropiperine using ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography combined with diode-array detection and high-resolution mass spectrometry.[Pubmed:33049799]
Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2021 Jan 30;35(2):e8975.
RATIONALE: Tetrahydropiperine is one of the natural arylpentanamide compounds isolated from Piper nigrum L., which has been demonstrated to have insecticidal activity. The aim of this study was to investigate the metabolic profiles of tetrahydropiperine in mouse, rat, dog, monkey and human hepatocytes. METHODS: The in vitro metabolism of tetrahydropiperine was elucidated via incubation with hepatocytes for 2 h at 37 degrees C. The samples were analyzed using ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography combined with diode-array detection and high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry operated in positive electrospray ionization mode. The structures of the metabolites were characterized using their retention times and their tandem mass spectrometric product ions. RESULTS: A total of 20 metabolites were detected and their structures were proposed. These metabolites were formed mainly through the following pathways: (1) 1,3-benzodioxole ring opening to form a catechol derivative (M12), which was prone to glucuronidation (M6 and M8), methylation (M17) and glutathione (GSH)-derived conjugation through an ortho-quinone intermediate (M4) or via an aldehyde intermediate (M7); (2) dehydrogenation to form a Piperanine (M15), which was subsequently subject to hydroxylation (M2 and M5) and GSH conjugation (M10 and M11) via Michael addition; (3) hydroxylation (M13, M14, M16, M18 and M19); and (4) direct GSH conjugation through an aldehyde intermediate (M3). CONCLUSIONS: The major metabolic pathways of tetrahydropiperine were hydroxylation, dehydrogenation, methylation, GSH conjugation and glucuronidation. Tetrahydropiperine was bioactivated through ortho-quinone, Michael receptor and aldehyde intermediates.
Molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation approach to screen natural compounds for inhibition of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae by targeting peptide deformylase.[Pubmed:31965918]
J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2021 Feb;39(3):823-840.
Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae (Xoo) causes bacterial leaf blight (BLB) of rice which results in a huge loss in production. Many chemicals are used to control BLB disease. However, these chemicals are toxic to the environments, animals and human beings. Thus, there is a demand to discover potential and safe natural pesticides to manage BLB disease successfully. Therefore, we screened a library of phytochemicals of different plants having antibacterial activity by targeting Peptide Deformylase (PDF) of Xoo using in silico techniques. A library of 318 phytochemicals was prepared and subjected to rigid and flexible molecular docking against PDF followed by molecular dynamics simulation and free energy analysis of protein-ligand complexes. The results of virtual screening showed that 14 compounds from different plants have good binding energy as compare to reference molecule (3 R)-2,3-dihydro[1,3] thiazolo [3,2 a]benzimidazol-3-ol) (-7.7 kcal mol(-1)). Out of 14 hit compounds, eight compounds that were selected based on binding energy were analyzed by Molecular dynamic (MD) simulation. Analysis of MD simulation revealed that eight compounds namely; Bisdemethoxycurcumin, Rosmarinic acid, Piperanine, Dihydropiperlonguminine, Piperdardine, Dihydrocurcumin and Lonhumosides B achieved good stability during the 80 ns MD simulation at 300 K in term of the RMSD. Further, we calculated RMSF, RG, SASA, and interaction energy after 40 ns due to showing the stability of complexes. From our results, we conclude that these natural compounds could inhibit Xoo by targeting PDF receptor and can be used as potential bactericidal candidates against BLB disease of rice against Xoo and other bacteria. Communicated by Ramaswamy H. Sarma.
[Quantitative Analysis of Piperine and the Derivatives in Long Pepper Extract by HPLC Using Relative Molar Sensitivity].[Pubmed:31956239]
Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi. 2019;60(5):134-143.
A novel method was developed for quantification of five major piperine derivatives (Piperanine, piperine, chavicine, isopiperine, and isochavicine) in a hot water extract of long pepper fruit (LPE) using the relative molar sensitivity (RMS) based on the combination of HPLC/UV and (1)H- quantitative NMR ((1)H-qNMR). The RMSs of Piperanine, chavicine, isopiperine, and isochavicine to piperine of which the absolute purity was determined by (1)H-qNMR were calculated to be 0.3693, 1.138, 0.9164, and 1.277, respectively. The total amount of piperine derivatives in LPE was quantified by both (1)H-qNMR and HPLC/UV based on the RMS using piperine as a single-reference material (RMS method). The relative difference in quantitation values of (1)H-qNMR and calibration curve method from the RMS method was 2.01% or less. The relative difference of the total cis-trans piperine isomers content between before and after photoirradiation in piperine solution was quantified to be 2.84% by the RMS method. In addition, the interlaboratory difference of the RMS method was confirmed in the range of 0.600 to 4.00 mug/g when analysis was performed on piperine derivatives in LPE containing tablets, while the total amount of piperine derivatives in the tablets was quantified at 606 mug/g. Our proposed method is a reliable tool for determining the contents of piperine and the derivatives in LPE and processed foods containing LPE.
Direct from solid natural products to pure compounds in a single step: Coupling online extraction with high-speed counter-current chromatography.[Pubmed:30073789]
J Sep Sci. 2018 Sep;41(18):3607-3613.
Extraction is the most important step in the purification of bioactive compounds from natural products. This study introduces a simple online extraction strategy coupled with high-speed counter-current chromatography for efficient extraction and purification of bioactive components from solid natural products. For online extraction strategy, 1.0 g of ground Mangnolia officinalis or Piper nigrum was loaded into a guard column, which was then positioned on the manual injection valve instead of the sample loop. Bioactive components were directly extracted by the mobile phase of high-speed counter-current chromatography, and then transferred into high-speed counter-current chromatography for purification. In addition, the compatibility of the developed methodology for direct purification of bioactive components from fresh M. officinalis was successfully demonstrated. Obviously, in comparison with traditional offline heat-reflux extraction, online extraction avoided the instrument, time, solvent, and energy consumption, and purified two phenolic compounds (honokiol and magnolol) from M. officinalis and three alkaloids (piperyline, piperine, and Piperanine) from P. nigrum with high extraction efficiency. The superiority of the developed methodology is to establish an easy, rapid, and efficient technique for the purification of a wide variety of bioactive components from solid natural products.
[Identify metabolites of Piper longum alkaloids in feces and urine of rat by HPLC-FT-MS].[Pubmed:29902888]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018 May;43(9):1798-1805.
The metabolites were detected in feces and urine of rats orally administrated alkaloids of Piper longum by using high performance liquid chromatography coupled with a Fourier Transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer (HPLC-FT-MS). According to the mass spectrometric data and reported literature, the structures of metabolites were identified. Several metabolites were analyzed and belonged to piperine, Piperanine, piperlonguminine, Deltaalpha,beta-dihydropiperlonguminine and pellitorine, respectively. The metabolites of alkaloids from P. longum alkaloids were produced through phase and phase metabolism reaction, and were excreted with urination and defecation. The approach provided a rapid method for characterizing the metabolites of P. longum alkaloids and gave the truly active structures and the action mechanism of their neuroprotective effects.
The Possibility of Using Isolated Alkaloid Compounds and Crude Extracts of Piper retrofractum (Piperaceae) as Larvicidal Control Agents for Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae) Larvae.[Pubmed:29796657]
J Med Entomol. 2018 Aug 29;55(5):1231-1236.
Culex quinquefasciatus is a common domestic mosquito that is widespread in many areas of Thailand and serves as a southeastern vector of Japanese encephalitis. The present study investigated the acute toxicity of crude extracts and alkaloid compounds of Piper retrofractum (Piperales: Piperaceae) in Cx. quinquefasciatus third instar larvae. P. retrofractum was sequentially extracted using hexane, dichloromethane, ethyl acetate, and methanol, and the crude extracts were tested on mosquito larvae. Detoxification and neuroenzymes were analyzed to establish the mode of action. Acute toxicity was assessed on Poecilia reticulata (Cyprinodontiformes: Poeciliidae) to determine the possibility of toxicity in a nontarget species. Our results showed crude hexane extract had the highest toxicity in Cx. quinquefasciatus (0.9 ppm). Piperine and Piperanine, which are alkaloid compounds from the crude hexane extract, showed LC50 values of 0.27 and 2.97 ppm, respectively, after 24 h of exposure. All the crude extracts showed low toxicity in P. reticulata compared with that in the mosquito larvae. The carboxylesterase, glutathione-S-transferase, and acetylcholinesterase activities in Cx. quinquefasciatus were reduced after treatment with all the extracts and the two alkaloid compounds. Thus, P. retrofractum shows larvicidal effects against Cx. quinquefasciatus and low toxicity for nontarget species. Thus, P. retrofractum could be a choice for controlling Cx. quinquefasciatus.
Identification and simultaneous quantification of five alkaloids in Piper longum L. by HPLC-ESI-MS(n) and UFLC-ESI-MS/MS and their application to Piper nigrum L.[Pubmed:25660876]
Food Chem. 2015 Jun 15;177:191-6.
A simple, effective and suitable UFLC-ESI-MS/MS method was firstly developed to simultaneously determine five characteristic constituents (piperine, piperlonguminine, Deltaalpha,beta-dihydropiperlonguminine, pellitorine and Piperanine) of Piper longum L. The total alkaloids of P. longum L. was prepared. The alkaloid contents of Piper nigrum L. and P. longum L. were compared. The analysis was carried out in multiple reaction monitoring scan mode. The method showed a good specificity, linearity (R(2)>0.995), stability (RSD<2.53%), repeatability (RSD<2.58%), and recovery (90.0-103.5%). The limits of detection and limits of quantification of five alkaloids were in the range of 0.02-0.03 and 0.05-0.10 ng/mL, respectively. The intra- and inter-day precision was less than 9.30% and 9.55%, respectively. The validation results confirmed that the method could simultaneously determine the target alkaloids in the sample. Furthermore, the identities of the alkaloids were verified by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS. Compared with P. nigrum, P. longum had lower piperine content but was enriched in the other four alkaloids.
Activation of TRPV1 and TRPA1 by black pepper components.[Pubmed:20460725]
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2010;74(5):1068-72.
We searched in this study for novel agonists of transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 1 (TRPV1) and transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily A, member 1 (TRPA1) in pepper, focusing attention on 19 compounds contained in black pepper. Almost all the compounds in HEK cells heterogeneously expressed TRPV1 or TRPA1, increased the intracellular Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)](i)) in a concentration-dependent manner. Among these, piperine, isopiperine, isochavicine, Piperanine, pipernonaline, dehydropipernonaline, retrofractamide C, piperolein A, and piperolein B relatively strongly activated TRPV1. The EC(50) values of these compounds for TRPV1 were 0.6-128 microM. Piperine, isopiperine, isochavicine, Piperanine, piperolein A, piperolein B, and N-isobutyl-(2E,4E)-tetradeca-2,4-diamide also relatively strongly activated TRPA1, the EC(50) values of these compounds for TRPA1 were 7.8-148 microM. The Ca(2+) responses of these compounds for TRPV1 and TRPA1 were significantly suppressed by co-applying each antagonist. We identified in this study new transient receptor potential (TRP) agonists present in black pepper and found that piperine, isopiperine, isochavicine, Piperanine, piperolein A, and piperolein B activated both TRPV1 and TRPA1.
Analysis by HPLC and LC/MS of pungent piperamides in commercial black, white, green, and red whole and ground peppercorns.[Pubmed:18386929]
J Agric Food Chem. 2008 May 14;56(9):3028-36.
Pepper plants accumulate pungent bioactive alkaloids called piperamides. To facilitate studies in this area, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry methods were developed and used to measure the following piperamides in 10 commercial whole (peppercorns) and in 10 ground, black, white, green, and red peppers: Piperanine, piperdardine, piperine, piperlonguminine, and piperettine. Structural identification of individual compounds in extracts was performed by associating the HPLC peak of each compound with the corresponding mass spectrum. The Piperanine content of the peppers (in mg/g piperine equivalents) ranged from 0.3 for the ground white pepper to 1.4 in black peppercorns. The corresponding range for piperdardine was from 0.0 for seven samples to 1.8 in black peppercorns; for four isomeric piperines, from 0.7 for red to 129 in green peppercorns; for piperlonguminine, from 0.0 in red peppercorns to 1.0 in black peppercorns; and for piperyline, from 0.9 in ground black pepper to 5.9 for red peppercorn. Four well-separated stereoisomeric forms of piperettine with the same molecular weight were present in 19 peppers. The sums of the piperamides ranged from 6.6 for red to 153 for green peppercorns. In contrast to large differences in absolute concentrations among the peppers, the ratios of piperines to total piperamide were quite narrow, ranging from 0.76 for black to 0.90 for white peppercorns, with an average value of 0.84 +/- 0.04 ( n = 19). Thus, on average, the total piperamide content of the peppers consists of 84% piperines and 16% other piperamides. These results demonstrate the utility of the described extraction and analytical methods used to determine the wide-ranging individual and total piperamide contents of widely consumed peppers.
Protective effects of amide constituents from the fruit of Piper chaba on D-galactosamine/TNF-alpha-induced cell death in mouse hepatocytes.[Pubmed:18289853]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008 Mar 15;18(6):2038-42.
The methanolic extract from the fruit of Piper chaba (Piperaceae) was found to have a hepatoprotective effect on D-galactosamine (D-GalN)/lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced liver injury in mice. From the ethyl acetate-soluble fraction, a new amide constituent named piperchabamide E together with twenty known amide constituents (e.g., piperine, piperchabamides A-D, and Piperanine) and two aromatic constituents were isolated as the hepatoprotective constituents. With regard to structure-activity relationships, the amide moiety and the 1,9-decadiene structure between the benzene ring and amide moiety were suggested to be important for strong inhibition of D-GalN/tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha)-induced death of hepatocytes. Furthermore, a principal amide constituent, piperine, dose-dependently inhibited increase in serum GPT and GOT levels at doses of 2.5-10 mg/kg (p.o.) in D-GalN/LPS-treated mice, and this inhibitory effect was suggested to depend on the reduced sensitivity of hepatocytes to TNF-alpha.
In vivo and in vitro activities of the seed extract of Piper guineense Schum. and Thonn. against skin and gill monogenean parasites of gold fish (Carassius auratus auratus).[Pubmed:15551399]
Phytother Res. 2004 Oct;18(10):793-7.
Methanol extracts of the seeds of Piper guineense (Piperaceae) were active against gold fish (Carassius auratus auratus L. Pisces Cyprinidae) monogenean parasites. The seed extract of P. guineense was administered at different concentrations (0.5-2.0 mg/L) under in vivo and in vitro conditions. There was a higher efficacy of the effects of the extracts against fish parasites under in vitro situations than under in vivo. Three major compounds (Piperanine, N-isobutyl (E,E)-2,4 decadienamide and Deltaalpha,beta-dihydrowasanine) were identified from the seed extract of Piper guineense by LC-MS analysis.
Preparative isolation and purification of amides from the fruits of Piper longum L. by upright counter-current chromatography and reversed-phase liquid chromatography.[Pubmed:15230526]
J Chromatogr A. 2004 Jun 25;1040(2):193-204.
A versatile counter-current chromatography (CCC) with upright type-J multilayer coil planet centrifuge, named upright CCC, was applied to the isolation and purification of amides from Piper longum L., which is widely used as an anodyne and a treatment for stomach disease in China. After the saponification by KOH of the ethanol extracts solution of 15 kg of crude drug "Piper Longi Fructus", the fruits of P. longum L., the solution was extracted with light petroleum and 500 g of red crude oil was obtained. Using 2.5 g of red crude oil as sample, the preparative upright CCC with a two-phase system composed of light petroleum (bp 60-90 degrees C)-ethyl acetate-tetrachloromethane-methanol-water (1:1:8:6:1, v/v) was successfully performed, which yielded nine fractions. Then these fractions were further purified by use of reversed-phase liquid chromatography (RPLC) with a glass column of 500 x 10 mm i.d. packed with reversed-phase silica gel. As a result, nine target amides with over 95% purity, i.e., 50 mg of (2E,4E)-N-isobutyl-eicosa-2,4-dienamide, 150 mg of (2E,4E,14Z)-N-isobutyl-eicosa-2,4,14-trienamide, 110 mg of (2E,4E,12Z)-N-isobutyl-ocatadeca-2,4,12-trienamide, 50 mg of guineensine, 60 mg of pipernonaline, 75 mg of pellitorine, 63 mg of piperine, 45 mg of Piperanine, and 40 mg of piperlonguminine were isolated, respectively. Structures of all compounds were identified by electrospray ionization MS, electron impact ionization MS, one- and two-dimensional NMR spectra.
New amides and gastroprotective constituents from the fruit of Piper chaba.[Pubmed:14994194]
Planta Med. 2004 Feb;70(2):152-9.
The 80 % aqueous acetone extract from the fruit of Piper chaba was found to show protective effects on ethanol- and indomethacin-induced gastric lesions in rats. From the aqueous acetone extract, four new amides named piperchabamides A ( 1), B ( 2), C ( 3), and D ( 4) were isolated, and their structures were determined on the basis of chemical and physicochemical evidence. In addition, the gastroprotective effects of the principal constituents, piperine ( 5), Piperanine ( 6), pipernonaline ( 7), dehydropipernonaline ( 8), piperlonguminine ( 9), retrofractamide B ( 10), guineensine ( 11), N-isobutyl-(2 E,4 E)-octadecadienamide ( 12), N-isobutyl-(2 E,4 E,14 Z)-eicosatrienamide ( 13), and methyl piperate ( 14), were examined. As a result, compounds 5 - 10 and 12 - 14 significantly inhibited ethanol-induced gastric lesions at a dose of 25 mg/kg, p. o., while 5, 7, 8, 10, 12, and 13 also significantly inhibited indomethacin-induced gastric lesions at the same dose.


