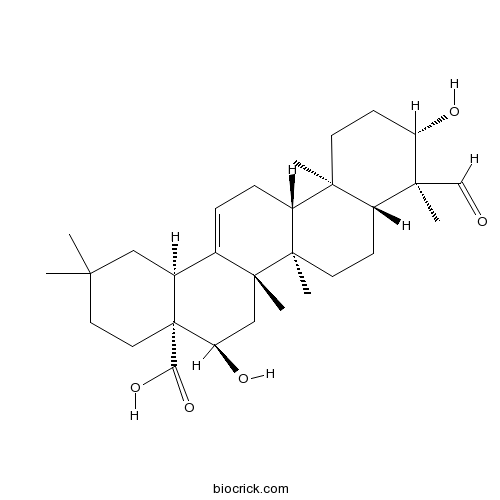
Quillaic acidCAS# 631-01-6 |
- Dexpramipexole dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1528
CAS No.:104632-27-1
- Dexpramipexole
Catalog No.:BCC1527
CAS No.:104632-28-2
- Cariprazine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1454
CAS No.:1083076-69-0
- Cariprazine
Catalog No.:BCC1453
CAS No.:839712-12-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 631-01-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 101810 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C30H46O5 | M.Wt | 486.68 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Quillaja sapogenin | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 41 mg/mL (84.24 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | (4aR,5R,6aR,6aS,6bR,8aR,9S,10S,12aR,14bS)-9-formyl-5,10-dihydroxy-2,2,6a,6b,9,12a-hexamethyl-1,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a,10,11,12,13,14b-tetradecahydropicene-4a-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC1(CCC2(C(C1)C3=CCC4C5(CCC(C(C5CCC4(C3(CC2O)C)C)(C)C=O)O)C)C(=O)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MQUFAARYGOUYEV-UAWZMHPWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C30H46O5/c1-25(2)13-14-30(24(34)35)19(15-25)18-7-8-21-26(3)11-10-22(32)27(4,17-31)20(26)9-12-28(21,5)29(18,6)16-23(30)33/h7,17,19-23,32-33H,8-16H2,1-6H3,(H,34,35)/t19-,20+,21+,22-,23+,26-,27-,28+,29+,30+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Quillaic acid elicits dose-dependent antinociceptive effects in two murine thermal models. 2. Quillaic acid exhibits strong topical anti-inflammatory activity in both models. |
| Targets | Immunology & Inflammation related |

Quillaic acid Dilution Calculator

Quillaic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0547 mL | 10.2737 mL | 20.5474 mL | 41.0948 mL | 51.3685 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4109 mL | 2.0547 mL | 4.1095 mL | 8.219 mL | 10.2737 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2055 mL | 1.0274 mL | 2.0547 mL | 4.1095 mL | 5.1368 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0411 mL | 0.2055 mL | 0.4109 mL | 0.8219 mL | 1.0274 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0205 mL | 0.1027 mL | 0.2055 mL | 0.4109 mL | 0.5137 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Quillaic acid(Quillaja sapogenin) is the major aglycone of the widely studied saponins of the Chilean indigenous tree Quillaja saponaria Mol; can elicit dose-dependent antinociceptive effects in two murine thermal models.
References:
[1]. Arrau S, et al. Antinociceptive activity of Quillaja saponaria Mol. saponin extract, quillaic acid and derivatives in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Jan 7;133(1):164-7.
[2]. Rodríguez-Díaz M, et al. Topical anti-inflammatory activity of quillaic acid from Quillaja saponaria Mol. and some derivatives. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011 May;63(5):718-24.
- (±)-threo-3-Methylglutamic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6804
CAS No.:63088-04-0
- Boc-Thr-OSu
Catalog No.:BCC3450
CAS No.:63076-44-8
- H-Val-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3142
CAS No.:6306-52-1
- Asunaprevir (BMS-650032)
Catalog No.:BCC1374
CAS No.:630420-16-5
- Estradiol-3-benzoate-17-butyrate
Catalog No.:BCC8963
CAS No.:63042-18-2
- H-Tle-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2658
CAS No.:63038-27-7
- Senkyunolide
Catalog No.:BCN8154
CAS No.:63038-10-8
- Hexacosyl (E)-ferulate
Catalog No.:BCN4170
CAS No.:63034-29-7
- Crenulatin
Catalog No.:BCN7791
CAS No.:63026-02-8
- Androstenone hydrazone
Catalog No.:BCC8830
CAS No.:63015-10-1
- AST 487
Catalog No.:BCC1373
CAS No.:630124-46-8
- PD 168077 maleate
Catalog No.:BCC6919
CAS No.:630117-19-0
- Beta-boswellic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2367
CAS No.:631-69-6
- NSC-41589
Catalog No.:BCC5477
CAS No.:6310-41-4
- Withanolide S
Catalog No.:BCN6728
CAS No.:63139-16-2
- Benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8848
CAS No.:6314-28-9
- 4-(Phenylthio)benzyl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCC8653
CAS No.:6317-56-2
- Methyl 2,5-dihydroxycinnamate
Catalog No.:BCC6702
CAS No.:63177-57-1
- 4-Acetoxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5364
CAS No.:6318-20-3
- H-D-Thr-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3108
CAS No.:632-20-2
- Rose Bengal
Catalog No.:BCC8024
CAS No.:632-69-9
- Wogonin
Catalog No.:BCN4171
CAS No.:632-85-9
- Pifithrin-α (PFTα)
Catalog No.:BCC2241
CAS No.:63208-82-2
- Cannabispirenone A
Catalog No.:BCN7603
CAS No.:63213-00-3
Topical anti-inflammatory activity of quillaic acid from Quillaja saponaria Mol. and some derivatives.[Pubmed:21492174]
J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011 May;63(5):718-24.
OBJECTIVES: Quillaic acid is the major aglycone of the widely studied saponins of the Chilean indigenous tree Quillaja saponaria Mol. The industrial availability of quillaja saponins and the extensive functionalization of this triterpenoid provide unique opportunities for structural modification and pose a challenge from the standpoint of selectivity in regard to one or the other secondary alcohol group, the aldehyde, and the carboxylic acid functions. The anti-inflammatory activity of this sapogenin has not been studied previously and it has never been used to obtain potential anti-inflammatory derivatives. METHODS: A series of Quillaic acid derivatives were prepared and subjected to topical assays for the inhibition of inflammation induced by arachidonic acid or phorbol ester. KEY FINDINGS: Quillaic acid exhibited strong topical anti-inflammatory activity in both models. Most of its derivatives were less potent, but the hydrazone 8 showed similar potency to Quillaic acid in the TPA assay. CONCLUSIONS: The structural modifications performed and the biological results suggest that the aldehyde and carboxyl groups are relevant to the anti-inflammatory activity in these models.
Antinociceptive activity of Quillaja saponaria Mol. saponin extract, quillaic acid and derivatives in mice.[Pubmed:20951193]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Jan 7;133(1):164-7.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Quillaja saponaria bark contains a high percentage of triterpene saponins and has been used for centuries as a cleansing and analgesic agent in Chilean folk medicine. AIM OF THE STUDY: The topical and systemic analgesic effects of a commercial partially purified saponin extract, 3beta,16alpha-dihydroxy-23-oxoolean-12-en-28-oic acid (Quillaic acid), methyl 3beta,16alpha-dihydroxy-23-oxoolean-12-en-28-oate and methyl 4-nor-3,16-dioxoolean-12-en-28-oate. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The samples were assessed in mice using the topical tail-flick and i.p. hot-plate tests, respectively. RESULTS: All the samples showed activity in both analgesic tests in a dose-dependent manner. The most active against tail flick test was commercial partially purified saponin extract (EC50 27.9 mg%, w/v) and more than the ibuprofen sodium. On hot-plate test, methyl 4-nor-3, 16-dioxoolean-12-en-28-oate was the most active (ED50 12.2 mg/kg) and more than the ibuprofen sodium. CONCLUSIONS: The results of the present study demonstrated that Quillaja saponaria saponins, Quillaic acid, its methyl ester, and one of the oxidized derivatives of the latter, elicit dose-dependent antinociceptive effects in two murine thermal models.
Analysis of bisdesmosidic saponins in Saponaria vaccaria L. by HPLC-PAD-MS: identification of new quillaic acid and gypsogenin 3-O-trisaccharides.[Pubmed:17144250]
Phytochem Anal. 2006 Nov-Dec;17(6):414-23.
A high-performance liquid chromatographic method using photodiode array and single quadrupole electrospray mass detection for analysis and profiling of bisdesmosidic saponins in Saponaria vaccaria seed was developed. Profiles of seed extract from three different plant sources were obtained and found to contain the same saponins, albeit in different proportions. Several known saponins were identified by selected ion extraction of quasi-molecular ions from the total ion chromatogram and confirmed by their mass spectra. Application of high cone voltages afforded mass spectra containing key diagnostic fragments and relatively strong singly charged quasi-molecular ions. In addition to previously identified saponins, several new Quillaic acid and gypsogenin bisdesmosides could be detected via mass spectral analysis. Five of these were tentatively identified as pentose homologues of known saponins, having an added xylosyl residue linked to the 3-O-glucuronyl group (1 --> 3). The stereochemistry and identity of the xylosyl linkage in the new saponins was determined by chemical means. Previously reported vaccaric or segetalic acid-type bisdesmosides could not be detected in any of the extracts.
Antiproliferative quillaic acid and gypsogenin saponins from Saponaria officinalis L. roots.[Pubmed:25534953]
Phytochemistry. 2015 May;113:108-20.
Nine Quillaic acid and five gypsogenin bisdesmosides were isolated from roots of Saponaria officinalis L. (Caryophyllaceae). Seven of the Quillaic acid saponins possessed a 3-O-beta-D-galactopyranosyl-(1 --> 2)-[beta-D-xylopyranosyl-(1 --> 3)]-beta-D-glucuronopyranosyl unit, but differed from each other in oligosaccharide units linked to the C-28 ester. The five gypsogenin saponins isolated from the roots all possessed the 3-O-beta-D-galactopyranosyl-(1 --> 2)-[beta-D-xylopyranosyl-(1 --> 3)]-beta-D-glucuronopyranosyl unit, with their oligosaccharide units linked to the C-28 ester differing. Structures were elucidated by extensive 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. The saponins were evaluated for growth inhibitory activity in two human cancer cell lines and hemolytic activity in sheep red blood cells.


