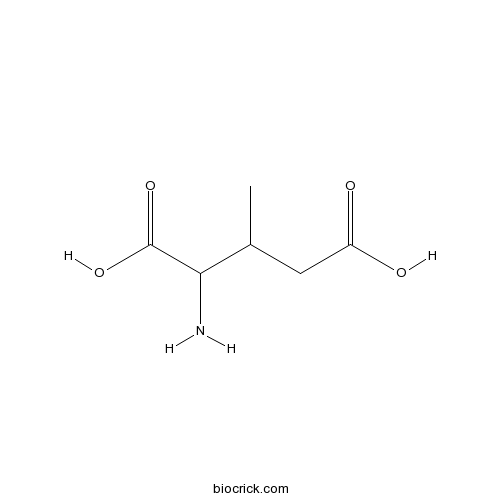
(±)-threo-3-Methylglutamic acidEAAT2 and EAAT4 blocker CAS# 63088-04-0 |
- BMS-708163 (Avagacestat)
Catalog No.:BCC2104
CAS No.:1146699-66-2
- DAPT (GSI-IX)
Catalog No.:BCC3618
CAS No.:208255-80-5
- YO-01027 (Dibenzazepine, DBZ)
Catalog No.:BCC2100
CAS No.:209984-56-5
- MK-0752
Catalog No.:BCC2090
CAS No.:471905-41-6
- MRK 560
Catalog No.:BCC2345
CAS No.:677772-84-8
- PF-03084014
Catalog No.:BCC1848
CAS No.:865773-15-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 63088-04-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 237657 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C6H11NO4 | M.Wt | 161.16 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in 1eq. NaOH | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-amino-3-methylpentanedioic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(CC(=O)O)C(C(=O)O)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FHJNAFIJPFGZRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C6H11NO4/c1-3(2-4(8)9)5(7)6(10)11/h3,5H,2,7H2,1H3,(H,8,9)(H,10,11) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | A potent blocker of glutamate transport; selective for EAAT2 and EAAT4 (IC50 values are 90, 109, 1600 and 1080 μM for EAAT2, EAAT4, EAAT1 and EAAT3 respectively). |

(±)-threo-3-Methylglutamic acid Dilution Calculator

(±)-threo-3-Methylglutamic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.205 mL | 31.0251 mL | 62.0501 mL | 124.1003 mL | 155.1253 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.241 mL | 6.205 mL | 12.41 mL | 24.8201 mL | 31.0251 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6205 mL | 3.1025 mL | 6.205 mL | 12.41 mL | 15.5125 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1241 mL | 0.6205 mL | 1.241 mL | 2.482 mL | 3.1025 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0621 mL | 0.3103 mL | 0.6205 mL | 1.241 mL | 1.5513 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Boc-Thr-OSu
Catalog No.:BCC3450
CAS No.:63076-44-8
- H-Val-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3142
CAS No.:6306-52-1
- Asunaprevir (BMS-650032)
Catalog No.:BCC1374
CAS No.:630420-16-5
- Estradiol-3-benzoate-17-butyrate
Catalog No.:BCC8963
CAS No.:63042-18-2
- H-Tle-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2658
CAS No.:63038-27-7
- Senkyunolide
Catalog No.:BCN8154
CAS No.:63038-10-8
- Hexacosyl (E)-ferulate
Catalog No.:BCN4170
CAS No.:63034-29-7
- Crenulatin
Catalog No.:BCN7791
CAS No.:63026-02-8
- Androstenone hydrazone
Catalog No.:BCC8830
CAS No.:63015-10-1
- AST 487
Catalog No.:BCC1373
CAS No.:630124-46-8
- PD 168077 maleate
Catalog No.:BCC6919
CAS No.:630117-19-0
- MRS 2500 tetraammonium salt
Catalog No.:BCC5881
CAS No.:630103-23-0
- Quillaic acid
Catalog No.:BCC5310
CAS No.:631-01-6
- Beta-boswellic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2367
CAS No.:631-69-6
- NSC-41589
Catalog No.:BCC5477
CAS No.:6310-41-4
- Withanolide S
Catalog No.:BCN6728
CAS No.:63139-16-2
- Benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8848
CAS No.:6314-28-9
- 4-(Phenylthio)benzyl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCC8653
CAS No.:6317-56-2
- Methyl 2,5-dihydroxycinnamate
Catalog No.:BCC6702
CAS No.:63177-57-1
- 4-Acetoxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5364
CAS No.:6318-20-3
- H-D-Thr-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3108
CAS No.:632-20-2
- Rose Bengal
Catalog No.:BCC8024
CAS No.:632-69-9
- Wogonin
Catalog No.:BCN4171
CAS No.:632-85-9
- Pifithrin-α (PFTα)
Catalog No.:BCC2241
CAS No.:63208-82-2
Pharmacological characterization of threo-3-methylglutamic acid with excitatory amino acid transporters in native and recombinant systems.[Pubmed:11299317]
J Neurochem. 2001 Apr;77(2):550-7.
The glutamate analog (+/-) threo-3-methylglutamate (T3MG) has recently been reported to inhibit the EAAT2 but not EAAT1 subtype of high-affinity, Na(+)-dependent excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT). We have examined the effects of T3MG on glutamate-elicited currents mediated by EAATs 1-4 expressed in Xenopus oocytes and on the transport of radiolabeled substrate in mammalian cell lines expressing EAATs 1-3. T3MG was found to be an inhibitor of EAAT2 and EAAT4 but a weak inhibitor of EAAT1 and EAAT3. T3MG competitively inhibited uptake of D-[(3)H]-aspartate into both cortical and cerebellar synaptosomes with a similar potency, consistent with its inhibitory activity on the cloned EAAT2 and EAAT4 subtypes. In addition, T3MG produced substrate-like currents in oocytes expressing EAAT4 but not EAAT2. However, T3MG was unable to elicit heteroexchange of preloaded D-[(3)H]-aspartate in cerebellar synaptosomes, inconsistent with the behavior of a substrate inhibitor. Finally, T3MG acts as a poor ionotropic glutamate receptor agonist in cultured hippocampal neurons: concentrations greater than 100 microM T3MG were required to elicit significant NMDA receptor-mediated currents. Thus, T3MG represents a pharmacological tool for the study of not only the predominant EAAT2 subtype but also the EAAT4 subtype highly expressed in cerebellum.
Identification of functional domains of the human glutamate transporters EAAT1 and EAAT2.[Pubmed:9614067]
J Biol Chem. 1998 Jun 12;273(24):14698-706.
Glutamate transporters serve the important function of mediating removal of glutamate released at excitatory synapses and maintaining extracellular concentrations below excitotoxic levels. Excitatory amino acid transporter subtypes EAAT1 and EAAT2 have a high degree of sequence homology and similar predicted topology and yet display a number of functional differences. Several recombinant chimeric transporters were generated to identify domains that contribute to functional differences between EAAT1 and EAAT2. Wild-type transporters and chimeric transporters were expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes, and electrogenic transport was studied under voltage clamp conditions. The differential sensitivity of EAAT1 and EAAT2 to transport blockers, kainate, threo-3-methylglutamate, and (2S, 4R)-4-methylglutamate as well as L-serine-O-sulfate transport and chloride permeability were employed to characterize chimeric transporters. One particular region, transmembrane domains 9 and 10, plays an important role in defining these functional differences. The intracellular carboxyl-terminal region may also play a minor role in conferring an effect on chloride permeability. This study provides important insight into the identification of functional domains that determine differences among glutamate transporter subtypes.
Contrasting modes of action of methylglutamate derivatives on the excitatory amino acid transporters, EAAT1 and EAAT2.[Pubmed:9145919]
Mol Pharmacol. 1997 May;51(5):809-15.
We have investigated the mechanism of action of a series of glutamate derivatives on the cloned excitatory amino acid transporters 1 and 2 (EAAT1 and EAAT2), expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. The compounds were tested as substrates and competitive blockers of the glutamate transporters. A number of compounds showed contrasting mechanisms of action on EAAT1 compared with EAAT2. In particular, (2S,4R)-4-methylglutamate and 4-methylene-glutamate were transported by EAAT1, with Km values of 54 microM and 391 microM, respectively, but potently blocked glutamate transport by EAAT2, with Kb values of 3.4 microM and 39 microM, respectively. Indeed, (2S,4R)-4-methylglutamate is the most potent blocker of EAAT2 yet described. (+/-)-Threo-3-methylglutamate also potently blocked glutamate transport by EAAT2 (Kb = 18 microM), but was inactive on EAAT1 as either a substrate or a blocker at concentrations up to 300 microM. In contrast to (2S,4R)-4-methylglutamate, L-threo-4-hydroxyglutamate was a substrate for both EAAT1 and EAAT2, with Km values of 61 microM and 48 microM, respectively. It seems that the chemical nature and also the orientation of the group at the 4-position of the carbon backbone of glutamate is crucial in determining the pharmacological activity. The conformations of these molecules have been modeled to understand the structural differences between, firstly, compounds that are blockers versus substrates of EAAT2 and, secondly, the pharmacological differences between EAAT1 and EAAT2.


