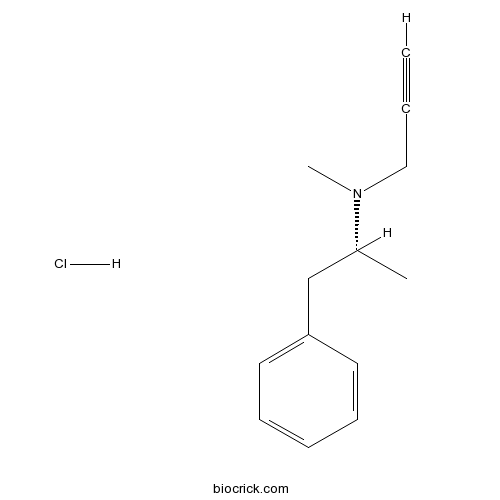
R-(-)-Deprenyl hydrochlorideMAO-B inhibitor CAS# 14611-52-0 |
- Anguizole
Catalog No.:BCC1365
CAS No.:442666-98-0
- Asunaprevir (BMS-650032)
Catalog No.:BCC1374
CAS No.:630420-16-5
- Balapiravir
Catalog No.:BCC1396
CAS No.:690270-29-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 14611-52-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 26758 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C13H18ClN | M.Wt | 223.74 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Selegiline | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in water | ||
| Chemical Name | (2R)-N-methyl-1-phenyl-N-prop-2-ynylpropan-2-amine;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CC(CC1=CC=CC=C1)N(C)CC#C.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IYETZZCWLLUHIJ-UTONKHPSSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H17N.ClH/c1-4-10-14(3)12(2)11-13-8-6-5-7-9-13;/h1,5-9,12H,10-11H2,2-3H3;1H/t12-;/m1./s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective inhibitor of monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). |

R-(-)-Deprenyl hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

R-(-)-Deprenyl hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.4695 mL | 22.3474 mL | 44.6947 mL | 89.3895 mL | 111.7368 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8939 mL | 4.4695 mL | 8.9389 mL | 17.8779 mL | 22.3474 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4469 mL | 2.2347 mL | 4.4695 mL | 8.9389 mL | 11.1737 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0894 mL | 0.4469 mL | 0.8939 mL | 1.7878 mL | 2.2347 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0447 mL | 0.2235 mL | 0.4469 mL | 0.8939 mL | 1.1174 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
R-(-)-Deprenyl Hydrochloride is a selective inhibitor of monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B).
- Z-Arg(Z)2-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3574
CAS No.:14611-34-8
- Pulchinenoside E1
Catalog No.:BCN8185
CAS No.:146100-02-9
- Dihydromarein
Catalog No.:BCN8406
CAS No.:
- MSDC-0160
Catalog No.:BCC5343
CAS No.:146062-49-9
- Tauroursodeoxycholic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6953
CAS No.:14605-22-2
- SC 51089
Catalog No.:BCC7773
CAS No.:146033-02-5
- SC 51322
Catalog No.:BCC5941
CAS No.:146032-79-3
- Tropine nonanoate
Catalog No.:BCN1925
CAS No.:146018-90-8
- 2-Fluoroadenosine
Catalog No.:BCC8576
CAS No.:146-78-1
- 2-Chloroadenosine
Catalog No.:BCC7575
CAS No.:146-77-0
- Yohimbine
Catalog No.:BCN2293
CAS No.:146-48-5
- Cycloart-23-ene-3,25-diol
Catalog No.:BCN2640
CAS No.:14599-48-5
- Chlorajapolide F
Catalog No.:BCN6425
CAS No.:1461760-59-7
- N-Methyllidocaine iodide
Catalog No.:BCC6905
CAS No.:1462-71-1
- SR 48692
Catalog No.:BCC7763
CAS No.:146362-70-1
- Desmethylrocaglamide
Catalog No.:BCN7735
CAS No.:146408-78-8
- Lactose
Catalog No.:BCN8387
CAS No.:14641-93-1
- Flavopiridol
Catalog No.:BCC1577
CAS No.:146426-40-6
- Camaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN1650
CAS No.:146450-83-1
- Pralatrexate
Catalog No.:BCC2304
CAS No.:146464-95-1
- 1-Methylpsilocin
Catalog No.:BCC7536
CAS No.:1465-16-3
- Complanatoside A
Catalog No.:BCN6282
CAS No.:146501-37-3
- WR 1065
Catalog No.:BCC2417
CAS No.:14653-77-1
- Tyrphostin AG 1296
Catalog No.:BCC1195
CAS No.:146535-11-7
In vitro interactions of amantadine hydrochloride, R-(-)-deprenyl hydrochloride and valproic acid sodium salt with antifungal agents against filamentous fungal species causing central nervous system infection.[Pubmed:23134606]
Acta Biol Hung. 2012 Dec;63(4):490-500.
The mortality rates of fungal infections that affect the central nervous system are high in consequence of the absence of effective antifungal drugs with good penetration across the blood-brain barrier and the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier. In the present work in vitro antifungal activities of three good penetrating non-antifungal drugs (amantadine hydrochloride, R-(-)-Deprenyl hydrochloride, valproic acid sodium salt) and their combinations with three antifungal agents (amphotericin B, itraconazole, terbinafine) were tested with broth microdilution method against eight fungal isolates belonging to Zygomycetes (Lichtheimia corymbifera, Rhizomucor miehei, Rhizopus microsporus var. rhizopodiformis, Saksenaeavasiformis) and Aspergillus genus (A. flavus, A. fumigatus, A. nidulans, A. terreus). These are known to be possible agents of central nervous fungal infections (CNFI). When used alone, the investigated nonantifungal drugs exerted slight antifungal effects. In their combinations with antifungal agents they acted antagonistically, additively and synergistically against zygomyceteous isolates. Primarily antagonistic interactions were revealed between the investigated drugs in case of Aspergilli, but additive and synergistic interactions were also observed. The additive and synergistic combinations allowed the usage of reduced concentrations of antifungal agents to inhibit the fungal growth in our study. These combinations would be a basis of an effective, less toxic therapy for treatment of CNFI.
Effect of selegiline on dopamine concentration in the striatum of a primate.[Pubmed:9974121]
Brain Res. 1999 Jan 2;815(1):44-50.
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) has two subtypes, A and B, that have different distributions between the rodent and the human. In the striatum, dopamine (DA) of the rat seems to be metabolized by MAO A, and DA of the human is largely deaminated by MAO B. MAO in the striatum of common marmosets is also type B. Using in vivo microdialysis, we investigated the pharmacological activity of selegiline, a selective irreversible inhibitor of MAO B, in the striatum of marmosets. Intraperitoneal co-administration of selegiline (1 mg kg-1, i.p.) with levodopa/carbidopa (10/2.5 mg kg-1, i.p.) did not significantly increase extracellular concentration of DA in the striatum of common marmosets compared with control animals receiving levodopa/carbidopa alone. Daily pretreatment with 0.1 mg kg-1 (i.p.) selegiline for two weeks, however, dramatically increased extracellular concentration of DA to about seven times that of control animals treated with levodopa/carbidopa alone in marmosets. Such an increase in extracellular concentrations of DA could not be observed in a similar study with Wistar rats. This study showed that chronic administration of a small dose of selegiline caused a marked increase in extracellular DA concentration in the striatum of primates, but not in the rodents.
Deprenyl decreases an endogenous parkinsonism-inducing compound, 1-benzyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline in mice: in vivo and in vitro studies.[Pubmed:9518683]
Brain Res. 1998 Mar 23;787(2):341-3.
We examined the effect of deprenyl, a promising drug for the therapy of Parkinson's disease on the formation of a parkinsonism-inducing compound, 1-benzyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline (1BnTIQ). The 1BnTIQ content was significantly decreased in the brain of deprenyl-treated mouse in vivo, and deprenyl also inhibited 1BnTIQ formation from phenethylamine by a mouse brain homogenate supernatant in vitro. In vivo, the content of a parkinsonism-preventing compound, 1-methyl-1,2,3, 4-tetrahydroisoquinoline (1MeTIQ) was slightly increased in mice injected with deprenyl. The marked decrease of the ratio of 1BnTIQ to 1MeTIQ might play a role in the clinical effect of deprenyl.
Modification of levodopa responses by deprenyl (selegiline): an electrophysiological and behavioral study in the rat relevant to Parkinson's disease.[Pubmed:9585355]
Ann Neurol. 1998 May;43(5):613-7.
From using in vitro intracellular recordings from mesencephalic neurons and monoamine-depleted rats, we report that the functions of levodopa in the brain are greatly enhanced and prolonged by high doses of the monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor deprenyl. Dopaminergic neurons were hyperpolarized and inhibited by levodopa application. These effects of levodopa were largely potentiated by pretreatment with nonselective doses of deprenyl. Furthermore, when locomotor activity induced by levodopa was examined on a rodent model of Parkinson's disease, pretreatment of the animals with nonselective doses of deprenyl caused an enhancement of the antiparkinsonian action of levodopa. The great increase in levodopa responses by deprenyl suggests a likely therapeutic use of this dopamine precursor with a higher dosage of the MAO inhibitor, to reduce effectively the daily levodopa requirements in Parkinson's disease patients.
The molecular pharmacology of L-deprenyl.[Pubmed:1639115]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jun 5;226(2):97-108.
L-Deprenyl, the selective inhibitor of monoamine oxidase type B (MAO-B), has gained wide acceptance as a useful form of adjunct therapeutic drug in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. This review summarizes the molecular pharmacology of L-deprenyl, and the advances in our understanding of its possible mode of action in Parkinson's disease. L-Deprenyl belongs to the class of enzyme-activated irreversible inhibitors also described as 'suicide' inhibitors, because the compound acts as a substrate for the target enzyme, whose action on the compound results in irreversible inhibition. L-Deprenyl first of all forms a noncovalent complex with MAO as an initial, reversible step. The subsequent interaction of L-deprenyl with MAO leads to a reduction of the enzyme-bound flavin-adenine dinucleotide (FAD), and concomitant oxidation of the inhibitor. This oxidized inhibitor then reacts with FAD at the N-5-position in a covalent manner. The observed in vitro selectivity of L-deprenyl for MAO-B may be accounted for by differences in the affinities of the two MAO subtypes for reversible interaction with L-deprenyl, differences in the rates of reaction within the noncovalent complexes to form the irreversibly inhibited adduct, or a combination of both these factors. However, if selective inhibition is to be maintained in vivo, correct dosage schedules are critically important, since all selective MAO inhibitors described up to now lack selectivity at high doses. In experimental animals L-deprenyl is protective against the damaging effects of several neurotoxins, including the dopaminergic agents 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) and 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) and the noradrenergic neurotoxin N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-ethyl-2-bromobenzylamine (DSP-4). Beside MAO-B inhibition, which above all explains the prevention of neurotoxic action of MPTP by preventing its metabolism, L-deprenyl appears to exhibit other mechanisms of action which are independent of its action on MAO-B.


