2-ChloroadenosineAdenosine receptor agonist CAS# 146-77-0 |
- (24R)-MC 976
Catalog No.:BCC1289
CAS No.:112828-09-8
- (24S)-MC 976
Catalog No.:BCC1291
CAS No.:112849-14-6
- 1alpha, 25-Dihydroxy VD2-D6
Catalog No.:BCC1299
CAS No.:216244-04-1
- 1alpha, 24, 25-Trihydroxy VD2
Catalog No.:BCC1298
CAS No.:457048-34-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 146-77-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 8974 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C10H12ClN5O4 | M.Wt | 301.69 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 2-CADO | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 25 mM in water and to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
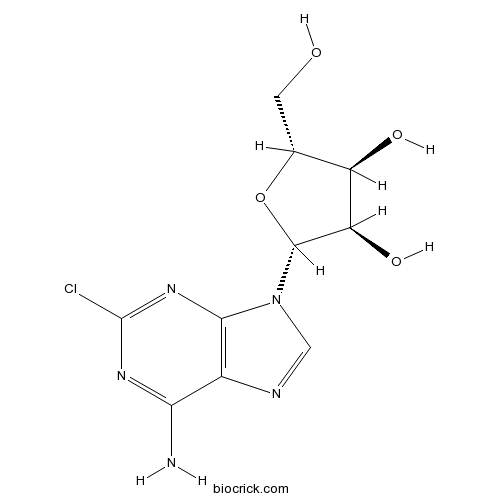
| Chemical Name | (2R,3R,4S,5R)-2-(6-amino-2-chloropurin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol | ||
| SMILES | C1=NC2=C(N1C3C(C(C(O3)CO)O)O)N=C(N=C2N)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BIXYYZIIJIXVFW-UUOKFMHZSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H12ClN5O4/c11-10-14-7(12)4-8(15-10)16(2-13-4)9-6(19)5(18)3(1-17)20-9/h2-3,5-6,9,17-19H,1H2,(H2,12,14,15)/t3-,5-,6-,9-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Metabolically stable analog of adenosine that behaves as an adenosine receptor agonist (Ki values are 300, 80 and 1900 nM for A1, A2A and A3 receptors respectively). Anticonvulsive in vivo. |

2-Chloroadenosine Dilution Calculator

2-Chloroadenosine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3147 mL | 16.5733 mL | 33.1466 mL | 66.2932 mL | 82.8665 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6629 mL | 3.3147 mL | 6.6293 mL | 13.2586 mL | 16.5733 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3315 mL | 1.6573 mL | 3.3147 mL | 6.6293 mL | 8.2867 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0663 mL | 0.3315 mL | 0.6629 mL | 1.3259 mL | 1.6573 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0331 mL | 0.1657 mL | 0.3315 mL | 0.6629 mL | 0.8287 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Yohimbine
Catalog No.:BCN2293
CAS No.:146-48-5
- Cycloart-23-ene-3,25-diol
Catalog No.:BCN2640
CAS No.:14599-48-5
- Jasminoid A
Catalog No.:BCN7605
CAS No.:1459784-57-6
- Laccaic acid E
Catalog No.:BCN1807
CAS No.:14597-16-1
- N,N,N-Trimethyl-2-aminoethylphosphonate
Catalog No.:BCN1560
CAS No.:14596-57-7
- 2-Dimethylaminoethylphosphonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1764
CAS No.:14596-56-6
- 2-(Methylamino)ethylphosphonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1763
CAS No.:14596-55-5
- 3-Amino-3-phenyl-1-propanol
Catalog No.:BCC8608
CAS No.:14593-04-5
- 7,8,9,9-Tetradehydroisolariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN1649
CAS No.:145918-59-8
- CGP 53353
Catalog No.:BCC7363
CAS No.:145915-60-2
- CGP 52411
Catalog No.:BCC7667
CAS No.:145915-58-8
- Brachynoside
Catalog No.:BCN3749
CAS No.:145898-87-9
- 2-Fluoroadenosine
Catalog No.:BCC8576
CAS No.:146-78-1
- Tropine nonanoate
Catalog No.:BCN1925
CAS No.:146018-90-8
- SC 51322
Catalog No.:BCC5941
CAS No.:146032-79-3
- SC 51089
Catalog No.:BCC7773
CAS No.:146033-02-5
- Tauroursodeoxycholic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6953
CAS No.:14605-22-2
- MSDC-0160
Catalog No.:BCC5343
CAS No.:146062-49-9
- Dihydromarein
Catalog No.:BCN8406
CAS No.:
- Pulchinenoside E1
Catalog No.:BCN8185
CAS No.:146100-02-9
- Z-Arg(Z)2-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3574
CAS No.:14611-34-8
- R-(-)-Deprenyl hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5196
CAS No.:14611-52-0
- Chlorajapolide F
Catalog No.:BCN6425
CAS No.:1461760-59-7
- N-Methyllidocaine iodide
Catalog No.:BCC6905
CAS No.:1462-71-1
Intravenous 2-chloroadenosine protects BALB/c mice from Klebsiella pneumoniae B5055-induced sepsis by modulating the pro-inflammatory immune response.[Pubmed:20071287]
J Chemother. 2009 Dec;21(6):639-45.
Sepsis is a severe inflammatory immune response of the host against an infectious agent or its product i.e. lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Therefore, targeting the immune system during sepsis may lower the morbidity and mortality associated with sepsis. The present study shows the protective immunomodulatory action of 2-Chloroadenosine (2-CADO) in K. pneumoniae B5055 induced sepsis in male BALB/c mice. Sepsis was induced by implanting the fibrin-thrombin clot containing known amount (10(2)cfu) of Klebsiella pneumoniae B5055 into the peritoneal cavity of mice. 100% mortality with in the 5 post infection days (PIDs) was observed in control group animals. Intravenous 2-CADO (10 microg/kg/day) treatment increased in survival of animals by 70% without significantly (p>0.05) decreasing the blood bacterial load. But a significant (p<0.05) decrease in the level of inflammatory markers (TNF-alpha, il-1alpha, MDA, NO) responsible for sepsis was observed. However, serum il-10 levels were found to be significantly (p<0.05) increased with 2-CADO treatment.
Effects of 2-chloroadenosine on cortical epileptic afterdischarges in immature rats.[Pubmed:20360616]
Pharmacol Rep. 2010 Jan-Feb;62(1):62-7.
Adenosine may represent an endogenous anticonvulsant in the brain. This study focused on the possible anticonvulsant action of an adenosine agonist, 2-Chloroadenosine, against cortical epileptic afterdischarges (ADs) in immature rats. Three age groups of rat pups with implanted electrodes were studied: 12-, 18- and 25-days-old. The compound, 2-Chloroadenosine, was injected after the first successful stimulation at doses of 1, 4 or 10 mg/kg intraperitoneally, and stimulation at the same intensity was repeated three more times. Movements directly elicited by stimulation, as well as clonic seizures accompanying electroencephalography (EEG) ADs, were markedly suppressed in only the 18-day-old animals. The effects in the 12- and especially the 25-day-old rats were moderate. The duration of the ADs decreased in all three age groups with 2-Chloroadenosine treatment, and the shortest AD duration was seen in the treated, 12-day-old rats. The AD suppression also lasted longer in this age group than it did in the older animals. After a brief suppression of the second AD, the treated, 25-day-old group exhibited a significant AD rebound during the third and fourth stimulations. Taken together, our data show that 2-Chloroadenosine exhibits an anticonvulsant effect that is dose- and age-dependent.
Anticonvulsant action of 2-chloroadenosine against pentetrazol-induced seizures in immature rats is due to activation of A1 adenosine receptors.[Pubmed:20809069]
J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2010 Nov;117(11):1269-77.
Potentiation of adenosinergic inhibitory modulation is one of possible strategies to develop new antiepileptic drugs. Nonspecific receptor agonist 2-Chloroadenosine was tested against pentetrazol-induced convulsions in immature (7, 12, 18 and 25 days old) and adult rats. Doses of 1-15 mg/kg i.p. suppressed tonic phase of generalized tonic-clonic seizures (GTCS) in the two youngest groups, whereas GTCS were abolished in older rats. Minimal clonic seizures in 18-day and older rats were suppressed by high doses of 2-Chloroadenosine. The role of A1 and A2A adenosine receptors was studied in 12- and 25-day-old rats. Action of an agonist of A1 receptors CCPA is similar to that of 2-Chloroadenosine. An agonist of A2A receptors CGS 21680 exhibits an anticonvulsant action only in the dose-inducing catalepsy; an A2A antagonist ZM 241385 moderately suppressed tonic phase of GTCS only in 12-day-old animals. Anticonvulsant action of adenosine agonists is due to their effects on A1 receptors.
2-Chloroadenosine (2-CADO) treatment modulates the pro-inflammatory immune response to prevent acute lung inflammation in BALB/c mice suffering from Klebsiella pneumoniae B5055-induced pneumonia.[Pubmed:20189776]
Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2010 Jun;35(6):599-602.
Acute lung inflammation (ALI) is a life-threatening pathology and can develop during the course of several clinical conditions such as pneumonia, acid aspiration or sepsis. Adenosine plays a significant role in controlling acute inflammation via binding to A(2A) receptors on inflammatory cells, i.e. neutrophils or macrophages. The present study was designed to evaluate the anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of 2-Chloroadenosine (2-CADO), alone or in combination with amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (AMC), in Klebsiella pneumoniae B5055-induced acute lung infection in mice. Acute lung infection in mice was induced by directly instilling the selected dose (10(4) colony-forming units/mL) of bacteria intranasally. Histopathological examination of the lungs was performed to reveal neutrophil infiltration into the lung alveoli. In addition to the major pro-inflammatory cytokines tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNFalpha) and interleukin (IL)-1alpha, levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 were also determined. Intranasal instillation of bacteria caused profound neutrophil infiltration into the lung alveoli as well as a significant increase in the levels of pro-inflammatory mediators (i.e. TNFalpha and IL-1alpha). However, intravenous administration of 2-CADO 10 microg/kg/day, alone or in combination with an antibiotic (i.e. AMC), significantly decreased neutrophil infiltration into the lung alveoli. A significant decrease in TNFalpha and IL-1alpha along with elevation of IL-10 levels in the lung homogenate of mice with acute lung infection was observed upon treatment with 2-CADO alone, with no significant decrease in bacterial counts. Moreover, in combination with AMC, 2-CADO exhibited its immunomodulatory action in acute lung infection and prevented ALI, whilst an antibacterial action was exhibited by AMC.
The protective effect of 2-chloroadenosine against the development of amygdala kindling and on amygdala-kindled seizures.[Pubmed:9178649]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1997 May 12;326(1):7-14.
The influence of 2-Chloroadenosine, a non-metabolizable adenosine A1 receptor agonist, was tested on the development of electrically kindled amygdala and on the seizure responses of fully kindled rats. Focal intra-amygdaloid injection of 2-Chloroadenosine (1-10 nmol/0.5 microl) 20 min before applying the daily kindling stimulus prevented the development of the kindling process. The behavioural seizure score and the afterdischarge duration were reduced below their initial values. The antiepileptogenic effects of 1 and 10 nmol of 2-Chloroadenosine were reversible 8-10 days after withdrawal of the drug. When 2-Chloroadenosine was tested on fully developed stage 5 amygdala-kindled seizures, it increased the generalised seizure threshold in a dose-dependent manner. A maximum efficiency of 125% (P < 0.001) was achieved with 5 nmol and the median effective dose was 0.55 nmol. Higher doses resulted in the reduced anticonvulsant effect (P < 0.05). With the same daily stimulation, 2-Chloroadenosine 5 nmol in 0.5 microl vehicle, significantly reduced the maximum seizure score by 90%, the afterdischarge duration by 88% and completely blocked the generalised seizure duration. The antiseizure activity of the drug lasted for 3 days. In conclusion, 2-Chloroadenosine not only acts as an anticonvulsant against electrically induced kindled seizures as described here, and against audiogenic seizures, electroshock and a variety of chemical convulsants as described by others, it prevents the development of the epileptic state by kindling-stimulation, i.e., it is antiepileptogenic. We theorise here that this is due to its blockade of presynaptic glutamate release.
Intra-amygdala infusion of 2-chloroadenosine suppresses amygdala-kindled seizures.[Pubmed:9439826]
Brain Res. 1997 Nov 14;775(1-2):37-42.
The seizure-modulating effects of 2-Chloroadenosine (2-CLA) infused directly into the amygdala were investigated. Different groups of amygdala-kindled rats were infused (1 microliter) with 2-CLA (0.25, 1, 10 and 25 nM), caffeine (200 microM and 2 mM), a combination of the two or artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF) applied directly through a cannula located in the amygdala. Infusion of 2-CLA dramatically suppressed seizure stage (SS), after discharge duration (ADD) and stage 5 seizure duration (S5D), while the latency to bilateral forelimb clonus (S4L) was significantly prolonged. These anticonvulsant effects were evident after 5 min, reached a maximum at the 60 min time point and were still detectable 360 min post-2-CLA infusion. Pretreatment with caffeine blocked the anticonvulsant effects of 2-CLA dose-dependently. These results may suggest that in amygdaloid-kindled rats, adenosine receptors located in the amygdala play a major role in the expression of the anticonvulsant activity of 2-CLA.
Pharmacokinetic-haemodynamic relationships of 2-chloroadenosine at adenosine A1 and A2a receptors in vivo.[Pubmed:8735640]
Br J Pharmacol. 1996 May;118(2):369-77.
1. The purpose of the present study was to develop an experimental strategy for the quantification of the cardiovascular effects of non-selective adenosine receptor ligands at the adenosine A1 and A2a receptor in vivo. 2-Chloroadenosine (CADO) was used as a model compound. 2. Three groups of normotensive conscious rats received an short intravenous infusion of 1.4 mg kg-1 CADO during constant infusions of the A1-selective antagonist, 8-cyclopentyltheophylline (CPT; 20 micrograms min-1 kg-1), the A2a-selective antagonist, 8-(3-chlorostyryl) caffeine (CSC; 32 micrograms min-1 kg-1) or the vehicle. The heart rate (HR) and mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) were recorded continuously during the experiment and serial arterial blood samples were taken for analysis of drug concentrations. The ratio MAP/HR was also calculated, which may reflect changes in total peripheral resistance on the assumption that no changes in stroke volume occur. 3. During the infusion of CPT, CADO produced a reduction in both blood pressure and MAP/HR by activation of the A2a receptor. The concentration-effect relationships were described according to the sigmoidal Emax model, yielding potencies based on free drug concentrations (EC50,u) of 61 and 68 ng ml-1 (202 and 225 nM) for the reduction of blood pressure and MAP/HR, respectively. During the infusion of CSC, an EC50,u value of 41 ng ml-1 (136 nM) was observed for the A1 receptor-mediated reduction in heart rate. The in vivo potencies correlated with reported receptor affinities (Ki(A1) = 300 nM and Ki(A2a) = 80 nM). The maximal reductions in MAP/HR and heart rate were comparable to those of full agonists, with the Emax values of -12 +/- 1 x 10(-2) mmHg b.p.m.-1 and -205 b.p.m. respectively. 4. It is concluded that this integrated pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic approach can be used to obtain quantitative information on the potency and intrinsic activity of new non-selective adenosine receptor agonists at different receptor subtypes in vivo.


