SU6656Src tyrosine kinases inhibitor CAS# 330161-87-0 |
- PP 1
Catalog No.:BCC3630
CAS No.:172889-26-8
- Dasatinib (BMS-354825)
Catalog No.:BCC1281
CAS No.:302962-49-8
- Saracatinib (AZD0530)
Catalog No.:BCC1166
CAS No.:379231-04-6
- ZM 306416
Catalog No.:BCC3964
CAS No.:690206-97-4
- NVP-BHG712
Catalog No.:BCC3963
CAS No.:940310-85-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 330161-87-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5353978 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H21N3O3S | M.Wt | 371.45 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 20 mg/mL (53.84 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
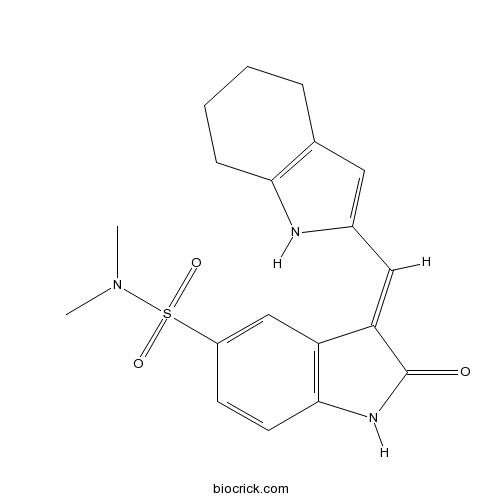
| Chemical Name | (3E)-N,N-dimethyl-2-oxo-3-(4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-indol-2-ylmethylidene)-1H-indole-5-sulfonamide | ||
| SMILES | CN(C)S(=O)(=O)C1=CC2=C(C=C1)NC(=O)C2=CC3=CC4=C(N3)CCCC4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LOGJQOUIVKBFGH-MHWRWJLKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H21N3O3S/c1-22(2)26(24,25)14-7-8-18-15(11-14)16(19(23)21-18)10-13-9-12-5-3-4-6-17(12)20-13/h7-11,20H,3-6H2,1-2H3,(H,21,23)/b16-10+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | SU 6656 is a selective inhibitor of Src kinases, Including Src, Yes, Lyn, and Fyn (IC50 = 280, 20, 130, 170 nM, respectively).
IC50 value:
Target: Src kinases inhibitor
in vitro: By comparing PDGF-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation events in untreated and SU6656-treated cells, we found that some substrates (for example, c-Cbl, and protein kinase C delta) were Src family substrates whereas others (for example, phospholipase C-gamma) were not [1]. Selective inhibition of SFKs with SU6656 delocalized E-cadherin and disrupted cellular junctions without affecting E-cadherin expression and this effect was phenocopied by knockdown of Src or Yes [2]. Inhibiting Src kinase activity by SU6656 suppressed TGFβ-induced RhoA and ATF2 activation but not Smad2 phosphorylation [3]. SU6656, the selective inhibitor of the Src kinase activity, decreased up-regulation of the mTORC1 signalling and moreover, unlike rapamycin, it did not induce the activation of Akt/PKB and its downstream targets in HBL melanoma cells [4].
in vivo: Ischemic postconditioning induced neuroprotective effects were significantly attenuated by pre-treatment of selective Src Kinase inhibitors SU-6656 (4 mg/kg i.p.) and PP1 (0.2 mg/kg i.p.) [5]. SU6656 and SKI-606 (bosutinib) enhanced immunotoxin killing of mesothelin-expressing cells by SS1P and CD22-expressing cells by HA22 (moxetumomab pasudotox). SU6656 also enhanced the antitumor effects of SS1P and HA22 in mouse xenograft tumor models [6]. References: | |||||

SU6656 Dilution Calculator

SU6656 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6922 mL | 13.4608 mL | 26.9215 mL | 53.843 mL | 67.3038 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5384 mL | 2.6922 mL | 5.3843 mL | 10.7686 mL | 13.4608 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2692 mL | 1.3461 mL | 2.6922 mL | 5.3843 mL | 6.7304 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0538 mL | 0.2692 mL | 0.5384 mL | 1.0769 mL | 1.3461 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0269 mL | 0.1346 mL | 0.2692 mL | 0.5384 mL | 0.673 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
SU6656 is a small-molecule, potent and selective inhibitor of Src tyrosine kinases.
Src (proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase) is a non-receptor protein tyrosine kinase family including 9 members and promotes survival, angiogenesis, and proliferation and invasion pathways.
In NIH 3T3 cell, SU6656 inhibits PDGF-/Src-driven mitogenesis and PDGF-stimulated c-Myc induction. [1] In UT-7/TPO, SU6656 cause ceased cell division but DNA continues accumulating by endomitosis. It also increased CD41 and CD61 expression on the cell surface in. [2] SU6656 in combination with radiation decrease clonogenic survival of endothelial cells. Src family kinase inhibition by SU6656 attenuated radiation-induced Akt phosphorylation and increased radiation-induced apoptosis and vascular endothelium destruction. [3]
In vivo, SU6656 administered prior to irradiation significantly promotes radiation-induced destruction of blood vessels within the tumor windows. It also facilitates tumor growth delay when administered during fractionated irradiation. [3]
References:
1. Blake RA, Broome MA, Liu X et al. SU6656, a selective src family kinase inhibitor, used to probe growth factor signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Dec;20(23):9018-27.
2. Lannutti BJ, Blake N, Gandhi MJ et al. Induction of polyploidization in leukemic cell lines and primary bone marrow by Src kinase inhibitor SU6656. Blood. 2005 May 15;105(10):3875-8.
3. Cuneo KC, Geng L, Tan J et al. SRC family kinase inhibitor SU6656 enhances antiangiogenic effect of irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006 Mar 15;64(4):1197-203.
- Cyanidin-3-O-sambubioside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3150
CAS No.:33012-73-6
- ent-16beta,17-Dihydroxy-19-kauranoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1457
CAS No.:3301-61-9
- Kumatakenin
Catalog No.:BCN5252
CAS No.:3301-49-3
- Nicarbazin
Catalog No.:BCC9101
CAS No.:330-95-0
- 3,4-Secocucurbita-4,24-diene-3,26,29-trioic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1458
CAS No.:329975-47-5
- TTP 22
Catalog No.:BCC2017
CAS No.:329907-28-0
- Viomycin
Catalog No.:BCC3930
CAS No.:32988-50-4
- Tobramycin
Catalog No.:BCC4739
CAS No.:32986-56-4
- 10-Deacetylbaccatin III
Catalog No.:BCN5251
CAS No.:32981-86-5
- Methyl (2R,3S)-3-(benzoylamino)-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoate
Catalog No.:BCN8520
CAS No.:32981-85-4
- Cinaciguat
Catalog No.:BCC1484
CAS No.:329773-35-5
- 2-Acetyl-3-ethylpyrazine
Catalog No.:BCC8512
CAS No.:32974-92-8
- TC HSD 21
Catalog No.:BCC6228
CAS No.:330203-01-5
- Boc-β-Ala-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3051
CAS No.:3303-84-2
- Aloe-emodin-8-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1456
CAS No.:33037-46-6
- H-Orn(Z)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3003
CAS No.:3304-51-6
- Peramivir
Catalog No.:BCC1846
CAS No.:330600-85-6
- TCTU
Catalog No.:BCC2689
CAS No.:330641-16-2
- HCTU
Catalog No.:BCC2818
CAS No.:330645-87-9
- KH 7
Catalog No.:BCC7787
CAS No.:330676-02-3
- Paclitaxel
Catalog No.:BCN4650
CAS No.:33069-62-4
- Avanafil
Catalog No.:BCC2288
CAS No.:330784-47-9
- PCI 29732
Catalog No.:BCC4100
CAS No.:330786-25-9
- MRT 10
Catalog No.:BCC7950
CAS No.:330829-30-6
Simultaneous inhibition of Src and Aurora kinases by SU6656 induces therapeutic synergy in human synovial sarcoma growth, invasion and angiogenesis in vivo.[Pubmed:22244830]
Eur J Cancer. 2012 Oct;48(15):2417-30.
Synovial sarcoma is an obstinate, high-grade malignancy because of its modest responses to radiotherapy and chemotherapy; the identification of effective therapeutics for this sarcoma is therefore necessary. Inhibition of Src family kinases (SFKs) suppresses the proliferation of synovial sarcoma cells in vitro, as we have previously reported. In this study, to validate the efficacy of Src inhibition in vivo, we employed SU6656, which was originally identified as a specific SFK inhibitor. SU6656 treatment significantly impaired the growth of established, existing tumours formed by synovial sarcoma cells in mice. Tumour cell invasion into the surrounding tissues was also abolished by SU6656. It is noteworthy that SU6656 but not PP2 induced a defect in cleavage furrow formation during cytokinesis, resulting in G2/M accumulation and subsequent apoptosis. Intriguingly, SU6656 abrogated the catalytic activities of Aurora kinases and led to the down-regulation of phosphorylated histone H3 coincidently with p53 accumulation, as did the Aurora kinase inhibitor VX-680. Structural comparison indicated an extensive similarity between the catalytic domains of SFKs and Aurora kinases. The structural analysis also revealed the potential binding mode of SU6656 to the ATP-binding cleft of Aurora B via four hydrogen bonds. SU6656 prevented angiogenesis within the tumours by attenuating vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) production by tumour cells and the subsequent chemotaxis of endothelial cells; these effects were the result of the inhibition of SFKs but not Aurora kinases. Based on these results, we hereby report a novel property of SU6656 as a dual inhibitor of SFKs and Aurora kinases, the suppression of both of which effectively abrogates tumour development and the progression of synovial sarcoma in vivo.
Dual inhibition of Src family kinases and Aurora kinases by SU6656 modulates CTGF (connective tissue growth factor) expression in an ERK-dependent manner.[Pubmed:24275091]
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Jan;46:39-48.
Src kinases are regulators of the expression of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN2), which plays a role in fibrotic injuries. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the potential of SU6656, a dual inhibitor of Src family and Aurora kinases, to interfere with the synthesis of this pro-fibrotic factor. SU6656 impaired TGF-beta-mediated upregulation of CTGF mRNA and protein in proximal epithelial HKC-8 cells, and also reduced CTGF expression in cells exposed to autocrine growth factors. In association with the inhibition of Src family kinases and diminished focal adhesion kinase activity, adherence of the cells was reduced. Furthermore, SU6656 interfered with Aurora kinase activity resulting in inhibition of cell division and formation multilobular nuclei after 24h. Comparable alterations were observed in primary tubular cells. When cell division was inhibited by SU6656 or ZM447439, a specific inhibitor of Aurora kinases, CTGF levels were back to control or even increased after 48h. The activity of RhoA-Rho kinase and ERK signaling was analyzed to delineate the signaling pathways responsible for the biphasic regulation of CTGF. While Rho kinase was not significantly altered by SU6656, ERK activity was inhibited in the early phase and increased after 24-48h. ERK activity correlated with secreted CTGF. As ZM447439 increased ERK activity only after 48h, cellular reorganization is likely responsible for triggering the ERK-dependent upregulation of CTGF. Taken together, in non-transformed epithelial cells, SU6656 modulates the expression of the pro-fibrotic factor CTGF in a time-dependent manner by inhibition of Src kinases and Aurora kinases.
Inhibition of p21 and Akt potentiates SU6656-induced caspase-independent cell death in FRO anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells.[Pubmed:23386415]
Horm Metab Res. 2013 Jun;45(6):408-14.
SU6656 is a small-molecule indolinone that selectively inhibits Src family kinase and induces death of cancer cells. The aim of the present study was to investigate the influence of SU6656 on cell survival and to assess the role of p21 and PI3K/Akt signaling in cell survival resulting from SU6656 treatment in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC) cells. When 8505C, CAL62, and FRO ATC cells were treated with SU6656, the viability of 8505C and CAL62 ATC cells decreased only after treatment with SU6656 at a dosage of 100 muM for 72 h, while the viability of FRO ATC cells decreased after treatment with SU6656 in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. Cell viability was not changed by pretreatment with the broad-spectrum caspase inhibitor z-VAD-fmk. Phospho-Src protein levels were reduced, and p21 protein levels were elevated. Phospho-ERK1/2 protein levels were multiplied without alteration of total ERK1/2, total Akt, and phospho-Akt protein levels. Regarding FRO ATC cells, the decrement of cell viability, the increment of cleaved PARP-1 protein levels, and the decrement of phospho-Src protein levels were shown in p21 siRNA- or LY294002-pretreated cells compared to SU6656-treated control cells. ERK1/2 siRNA transfection did not affect cell viability and protein levels of cleaved PARP-1, p21, and Akt. In conclusion, these results suggest that SU6656 induces caspase-independent death of FRO ATC cells by overcoming the resistance mechanism involving p21 and Akt. Suppression of p21 and Akt enhances the cytotoxic effect of SU6656 in FRO ATC cells.
Inhibition of mTORC1 by SU6656, the selective Src kinase inhibitor, is not accompanied by activation of Akt/PKB signalling in melanoma cells.[Pubmed:24093774]
Folia Biol (Praha). 2013;59(4):162-7.
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a Ser/Thr protein kinase conserved in all eukaryotes that plays a key role in cell growth and is a central effector of several pathways regulating essential cell functions. Hyperactivation of the mTORdependent signalling pathway occurs in many human diseases and may be a selective target for their therapy. However, the dual nature of mTOR, existing in two multiprotein complexes mTORC1 and mTORC2 driven by different feedback loops, decreases the therapeutic effects of rapamycin, the specific mTOR inhibitor. In the present study we demonstrate that the mTORC1 signalling pathway is highly activated in human melanoma cells and that up-regulation of this pathway along with the growth and malignity of these cells could be suppressed by disruption of the Src activity. SU6656, the selective inhibitor of the Src kinase activity, decreased up-regulation of the mTORC1 signalling and moreover, unlike rapamycin, it did not induce the activation of Akt/PKB and its downstream targets in HBL melanoma cells. The Src protein was found to be associated with raptor in the mTORC1 complex immunoprecipitated from these cells, suggesting that the Src activity might be a new attractive target for monotherapeutic inhibition of the up-regulated mTORC1 signalling pathway.


