Salvinorin ACAS# 83729-01-5 |
- Guanfacine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1609
CAS No.:29110-48-3
- (R,R)-Formoterol
Catalog No.:BCC1293
CAS No.:67346-49-0
- Doxazosin Mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC1257
CAS No.:77883-43-3
- Medetomidine
Catalog No.:BCC1736
CAS No.:86347-14-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

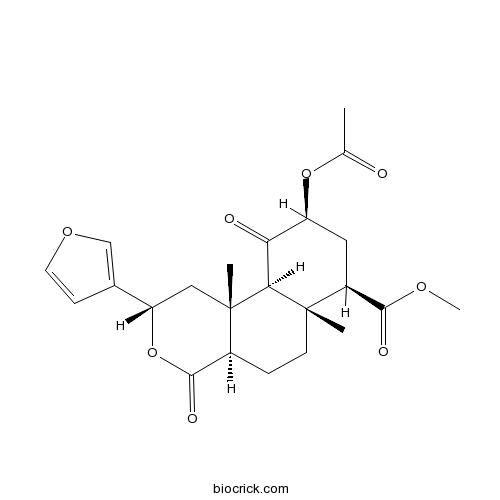
| Cas No. | 83729-01-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 128563 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H28O8 | M.Wt | 432.47 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 10 mM in ethanol | ||
| Chemical Name | methyl (2S,4aR,6aR,7R,9S,10aS,10bR)-9-acetyloxy-2-(furan-3-yl)-6a,10b-dimethyl-4,10-dioxo-2,4a,5,6,7,8,9,10a-octahydro-1H-benzo[f]isochromene-7-carboxylate | ||
| SMILES | CC(=O)OC1CC(C2(CCC3C(=O)OC(CC3(C2C1=O)C)C4=COC=C4)C)C(=O)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OBSYBRPAKCASQB-AGQYDFLVSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H28O8/c1-12(24)30-16-9-15(20(26)28-4)22(2)7-5-14-21(27)31-17(13-6-8-29-11-13)10-23(14,3)19(22)18(16)25/h6,8,11,14-17,19H,5,7,9-10H2,1-4H3/t14-,15-,16-,17-,19-,22-,23-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent naturally occuring non-nitrogenous κ-opioid selective agonist that displays high affinity at both native (Ki = 4.3 nM) and cloned (Ki = 16 nM) κ-opioid receptors. Also exhibits allosteric modulation of μ-opioid receptor binding. Reported to be brain-penetrant and displays psychoactive properties.. |

Salvinorin A Dilution Calculator

Salvinorin A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3123 mL | 11.5615 mL | 23.123 mL | 46.246 mL | 57.8075 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4625 mL | 2.3123 mL | 4.6246 mL | 9.2492 mL | 11.5615 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2312 mL | 1.1561 mL | 2.3123 mL | 4.6246 mL | 5.7807 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0462 mL | 0.2312 mL | 0.4625 mL | 0.9249 mL | 1.1561 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0231 mL | 0.1156 mL | 0.2312 mL | 0.4625 mL | 0.5781 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 3alpha-Acetoxy-20(29)-lupene-23,28-dioic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7508
CAS No.:83725-41-1
- Pomolic acid 28-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN1334
CAS No.:83725-24-0
- Ilexside I
Catalog No.:BCN3244
CAS No.:83725-19-3
- Dihydrosesamin
Catalog No.:BCN6616
CAS No.:83708-70-7
- (R)-AMPA
Catalog No.:BCC6582
CAS No.:83654-13-1
- RHC 80267
Catalog No.:BCC8083
CAS No.:83654-05-1
- CGRP (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5712
CAS No.:83651-90-5
- (S)-AMPA
Catalog No.:BCC6583
CAS No.:83643-88-3
- Cyclosporin H
Catalog No.:BCC6448
CAS No.:83602-39-5
- Cropodine
Catalog No.:BCN2073
CAS No.:83601-85-8
- Regorafenib hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1883
CAS No.:835621-07-3
- 2,2-Bis(3-amino-4-hydroxyphenyl)hexafluoropropane
Catalog No.:BCC8490
CAS No.:83558-87-6
- WH-4-023
Catalog No.:BCC8051
CAS No.:837422-57-8
- YM 244769
Catalog No.:BCC6222
CAS No.:837424-39-2
- Fmoc-Arg(Tos)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3076
CAS No.:83792-47-6
- Fmoc-Ser(Bzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3542
CAS No.:83792-48-7
- Falecalcitriol
Catalog No.:BCC1570
CAS No.:83805-11-2
- 2-Ethylhexyl trans-4-methoxycinnamate
Catalog No.:BCN1333
CAS No.:83834-59-7
- 4-Benzoyl 4'-methyldiphenyl sulfide
Catalog No.:BCC8694
CAS No.:83846-85-9
- Angeloylgomisin O
Catalog No.:BCN7361
CAS No.:83864-69-1
- Angeloylisogomisin O
Catalog No.:BCN4379
CAS No.:83864-70-4
- Obovatol
Catalog No.:BCN8265
CAS No.:83864-78-2
- Cetirizine
Catalog No.:BCC1469
CAS No.:83881-51-0
- Cetirizine DiHCl
Catalog No.:BCC4517
CAS No.:83881-52-1
A (-)-kolavenyl diphosphate synthase catalyzes the first step of salvinorin A biosynthesis in Salvia divinorum.[Pubmed:28204567]
J Exp Bot. 2017 Feb 1;68(5):1109-1122.
Salvia divinorum (Lamiaceae) is an annual herb used by indigenous cultures of Mexico for medicinal and ritual purposes. The biosynthesis of Salvinorin A, its major bioactive neo-clerodane diterpenoid, remains virtually unknown. This investigation aimed to identify the enzyme that catalyzes the first reaction of Salvinorin A biosynthesis, the formation of (-)-kolavenyl diphosphate [(-)-KPP], which is subsequently dephosphorylated to afford (-)-kolavenol. Peltate glandular trichomes were identified as the major and perhaps exclusive site of Salvinorin Accumulation in S. divinorum. The trichome-specific transcriptome was used to identify candidate diterpene synthases (diTPSs). In vitro and in planta characterization of a class II diTPS designated as SdKPS confirmed its activity as (-)-KPP synthase and its involvement in Salvinorin A biosynthesis. Mutation of a phenylalanine into histidine in the active site of SdKPS completely converts the product from (-)-KPP into ent-copalyl diphosphate. Structural elements were identified that mediate the natural formation of the neo-clerodane backbone by this enzyme and suggest how SdKPS and other diTPSs may have evolved from ent-copalyl diphosphate synthase.
A unique natural selective kappa-opioid receptor agonist, salvinorin A, and its roles in human therapeutics.[Pubmed:28190678]
Phytochemistry. 2017 May;137:9-14.
Until the mid-60s, only the Mazatecs, an indigenous group from Oaxaca, Mexico, used Salvia Divinorum (S. divinorum) due to its hallucinogen properties. Later it was found that the hallucinogen effects of this plant were caused by the presence of a neoclerodane diterpene Salvinorin A (Salvinorin A), which is a highly selective agonist of kappa-opioid receptor (KOR) that cause more intense hallucinations than the common hallucinogens as lysergic acid, mushrooms, ecstasy and others. In fact, smoking of only 200-500 mug of S. divinorum leaves is enough to produce these effects thus making it the most potent natural occurring hallucinogen known. Due to its legal status in various countries, this compound has gained a worldwide popularity as a drug of abuse with an easy access through smartshops and internet. Furthermore, Salvinorin A gathered an increased interest in the scientific community thanks to its unique structure and properties, and various studies demonstrated that Salvinorin A has antinociceptive, antidepressant, in some circumstances pro-depressant and anti-addictive effects that have yielded potential new avenues for research underlying Salvinorin A and its semi-synthetic analogs as therapeutic agents.
Addressing Structural Flexibility at the A-Ring on Salvinorin A: Discovery of a Potent Kappa-Opioid Agonist with Enhanced Metabolic Stability.[Pubmed:28376298]
J Med Chem. 2017 May 11;60(9):3866-3878.
Previous structure-activity studies on the neoclerodane diterpenoid Salvinorin A have demonstrated the importance of the acetoxy functionality on the A-ring in its activity as a kappa-opioid receptor agonist. Few studies have focused on understanding the role of conformation in these interactions. Herein we describe the synthesis and evaluation of both flexible and conformationally restricted compounds derived from Salvinorin A. One such compound, spirobutyrolactone 14, was synthesized in a single step from salvinorin B and had similar potency and selectivity to Salvinorin A (EC50 = 0.6 +/- 0.2 nM at kappa; >10000 nM at mu and delta). Microsomal stability studies demonstrated that 14 was more metabolically resistant than Salvinorin A. Evaluation of analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties revealed similar in vivo effects between 14 and Salvinorin A. To our knowledge, this study represents the first example of bioisosteric replacement of an acetate group by a spirobutyrolactone to produce a metabolically resistant derivative.
Synergistic blockade of alcohol escalation drinking in mice by a combination of novel kappa opioid receptor agonist Mesyl Salvinorin B and naltrexone.[Pubmed:28263712]
Brain Res. 2017 May 1;1662:75-86.
Mesyl Salvinorin B (MSB) is a potent selective kappa opioid receptor (KOP-r) agonist that has potential for development as an anti-psychostimulant agent with fewer side-effects (e.g., sedation, depression and dysphoria) than classic KOP-r agonists. However, no such study has been done on alcohol. We investigated whether MSB alone or in combination with naltrexone (mu-opioid receptor antagonist) altered voluntary alcohol drinking in both male and female mice. Mice, subjected to 3weeks of chronic escalation drinking (CED) in a two-bottle choice paradigm with 24-h access every other day, developed rapid escalation of alcohol intake and high preference. We found that single, acute administration of MSB dose-dependently reduced alcohol intake and preference in mice after 3-week CED. The effect was specific to alcohol, as shown by the lack of any effect of MSB on sucrose or saccharin intake. We also used the drinking-in-the-dark (DID) model with limited access (4h/day) to evaluate the pharmacological effect of MSB after 3weeks of DID. However, MSB had no effect on alcohol drinking after 3-week DID. Upon investigation of potential synergistic effects between naltrexone and MSB, we found that acute administration of a combination of MSB and naltrexone reduced alcohol intake profoundly after 3-week CED at doses lower than those individual effective doses. Repeated administrations of this combination showed less tolerance development than repeated MSB alone. Our study suggests that the novel KOP-r agonist MSB both alone and in combination with naltrexone shows potential in alcoholism treatment models.


