2-Ethylhexyl trans-4-methoxycinnamateCAS# 83834-59-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 83834-59-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5355130 | Appearance | Oil |
| Formula | C18H26O3 | M.Wt | 290.4 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-ethylhexyl (E)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate | ||
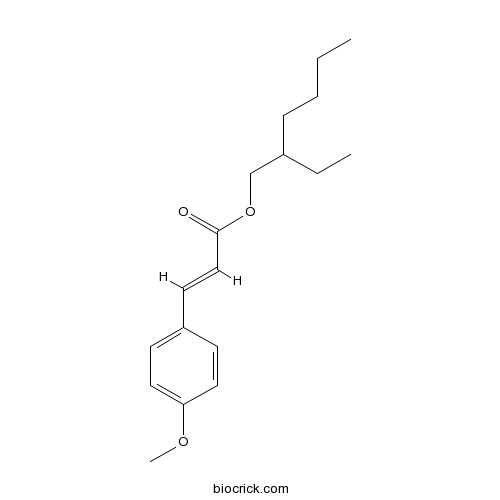
| SMILES | CCCCC(CC)COC(=O)C=CC1=CC=C(C=C1)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YBGZDTIWKVFICR-JLHYYAGUSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 2-Ethylhexyl-p-methoxycinnamate is a sunscreen agent. |
| In vitro | Energy efficiency for the removal of non-polar pollutants during ultraviolet irradiation, visible light photocatalysis and ozonation of a wastewater effluent.[Pubmed: 23863371]Water Res. 2013 Oct 1;47(15):5546-56.This study aims to assess the removal of a set of non-polar pollutants in biologically treated wastewater using ozonation, ultraviolet (UV 254 nm low pressure mercury lamp) and visible light (Xe-arc lamp) irradiation as well as visible light photocatalysis using Ce-doped TiO2.
The compounds tracked include UV filters, synthetic musks, herbicides, insecticides, antiseptics and polyaromatic hydrocarbons. |
| Structure Identification | J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2002 Nov 7;30(4):1181-9.Comparative studies of the influence of cyclodextrins on the stability of the sunscreen agent, 2-ethylhexyl-p-methoxycinnamate.[Pubmed: 12408908]The effects of beta-cyclodextrin (beta-CD) and hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin (HP-beta-CD) on the base-catalyzed degradation and light-induced decomposition of the sunscreen agent, trans-2-ethylhexyl-p-methoxycinnamate (2-Ethylhexyl trans-4-methoxycinnamate,trans-EHMC) were investigated. |

2-Ethylhexyl trans-4-methoxycinnamate Dilution Calculator

2-Ethylhexyl trans-4-methoxycinnamate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4435 mL | 17.2176 mL | 34.4353 mL | 68.8705 mL | 86.0882 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6887 mL | 3.4435 mL | 6.8871 mL | 13.7741 mL | 17.2176 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3444 mL | 1.7218 mL | 3.4435 mL | 6.8871 mL | 8.6088 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0689 mL | 0.3444 mL | 0.6887 mL | 1.3774 mL | 1.7218 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0344 mL | 0.1722 mL | 0.3444 mL | 0.6887 mL | 0.8609 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Falecalcitriol
Catalog No.:BCC1570
CAS No.:83805-11-2
- Fmoc-Ser(Bzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3542
CAS No.:83792-48-7
- Fmoc-Arg(Tos)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3076
CAS No.:83792-47-6
- YM 244769
Catalog No.:BCC6222
CAS No.:837424-39-2
- WH-4-023
Catalog No.:BCC8051
CAS No.:837422-57-8
- Salvinorin A
Catalog No.:BCC5875
CAS No.:83729-01-5
- 3alpha-Acetoxy-20(29)-lupene-23,28-dioic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7508
CAS No.:83725-41-1
- Pomolic acid 28-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN1334
CAS No.:83725-24-0
- Ilexside I
Catalog No.:BCN3244
CAS No.:83725-19-3
- Dihydrosesamin
Catalog No.:BCN6616
CAS No.:83708-70-7
- (R)-AMPA
Catalog No.:BCC6582
CAS No.:83654-13-1
- RHC 80267
Catalog No.:BCC8083
CAS No.:83654-05-1
- 4-Benzoyl 4'-methyldiphenyl sulfide
Catalog No.:BCC8694
CAS No.:83846-85-9
- Angeloylgomisin O
Catalog No.:BCN7361
CAS No.:83864-69-1
- Angeloylisogomisin O
Catalog No.:BCN4379
CAS No.:83864-70-4
- Obovatol
Catalog No.:BCN8265
CAS No.:83864-78-2
- Cetirizine
Catalog No.:BCC1469
CAS No.:83881-51-0
- Cetirizine DiHCl
Catalog No.:BCC4517
CAS No.:83881-52-1
- WIKI4
Catalog No.:BCC2455
CAS No.:838818-26-1
- TCS 2312
Catalog No.:BCC7541
CAS No.:838823-31-7
- Azithromycin
Catalog No.:BCC4385
CAS No.:83905-01-5
- Gramodendrine
Catalog No.:BCN2155
CAS No.:83905-67-3
- 12-Acetoxyabietic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4380
CAS No.:83905-81-1
- 13-Hydroxylabda-8(17),14-dien-18-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1332
CAS No.:83915-59-7
Energy efficiency for the removal of non-polar pollutants during ultraviolet irradiation, visible light photocatalysis and ozonation of a wastewater effluent.[Pubmed:23863371]
Water Res. 2013 Oct 1;47(15):5546-56.
This study aims to assess the removal of a set of non-polar pollutants in biologically treated wastewater using ozonation, ultraviolet (UV 254 nm low pressure mercury lamp) and visible light (Xe-arc lamp) irradiation as well as visible light photocatalysis using Ce-doped TiO2. The compounds tracked include UV filters, synthetic musks, herbicides, insecticides, antiseptics and polyaromatic hydrocarbons. Raw wastewater and treated samples were analyzed using stir-bar sorptive extraction coupled with comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography (SBSE-CG x GC-TOF-MS). Ozone treatment could remove most pollutants with a global efficiency of over 95% for 209 muM ozone dosage. UV irradiation reduced the total concentration of the sixteen pollutants tested by an average of 63% with high removal of the sunscreen 2-Ethylhexyl trans-4-methoxycinnamate (EHMC), the synthetic musk 7-acetyl-1,1,3,4,4,6-hexamethyltetrahydronaphthalene (tonalide, AHTN) and several herbicides. Visible light Ce-TiO2 photocatalysis reached ~70% overall removal with particularly high efficiency for synthetic musks. In terms of power usage efficiency expressed as nmol kJ(-1), the results showed that ozonation was by far the most efficient process, ten-fold over Xe/Ce-TiO2 visible light photocatalysis, the latter being in turn considerably more efficient than UV irradiation. In all cases the efficiency decreased along the treatments due to the lower reaction rate at lower pollutant concentration. The use of photocatalysis greatly improved the efficiency of visible light irradiation. The collector area per order decreased from 9.14 +/- 5.11 m(2) m(-3) order(-1) for visible light irradiation to 0.16 +/- 0.03 m(2) m(-3) order(-1) for Ce-TiO2 photocatalysis. The toxicity of treated wastewater was assessed using the green alga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Ozonation reduced the toxicity of treated wastewater, while UV irradiation and visible light photocatalysis limited by 20-25% the algal growth due to the accumulation of reaction by-products. Three transformation products were identified and tracked along the treatments.


