Sodium DanshensuCAS# 67920-52-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 67920-52-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 23711819 | Appearance | White-beige powder |
| Formula | C9H9O5Na | M.Wt | 220.2 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Sodium Danshensu; (±)-DanShenSu sodium sal | ||
| Solubility | H2O : 100 mg/mL (454.24 mM; Need ultrasonic) DMSO : 100 mg/mL (454.24 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
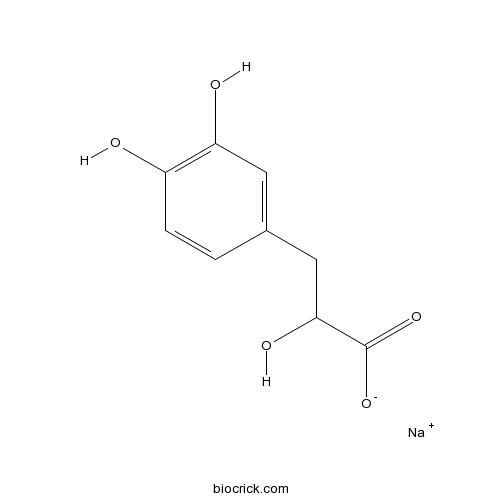
| Chemical Name | sodium;3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxypropanoate | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C=C1CC(C(=O)[O-])O)O)O.[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZMMKVDBZTXUHFO-UHFFFAOYSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C9H10O5.Na/c10-6-2-1-5(3-7(6)11)4-8(12)9(13)14;/h1-3,8,10-12H,4H2,(H,13,14);/q;+1/p-1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Sodium danshensu (SDSS), the sodium salt of danshensu (DSS), has the neuroprotective effect against cerebral I/R injury, and the potential mechanism might to inhibition of apoptosis through activating the PI3K/Akt signal pathway. SDSS has a protective effect against the genotoxicity of cigarette smoke,it shows a biphasic effects on vessel tension, while low dosage of sodium danshensu produces small contraction possibly through transient enhancement of Ca(2+) influx, high dosage produces significant vasodilation mainly through promoting the opening of non-selective K(+) channels and small-conductance calcium-sensitive K(+) channels in the vascular smooth muscle cells. |
| Targets | Calcium Channel | Potassium Channel | Akt | GSK-3 | Bcl-2/Bax | PI3K |
| In vitro | Protection of flavonoid components baicalein,quercetin,or sodium danshensu on cytotoxicity and cellular DNA damage induced by cigarette smoke[Reference: WebLink]Drugs & Clinic, 2014, 29(1):21-6.To evaluate the protective effect of flavonoid components baicalein, quercetin or Sodium Danshensu on cytotoxicity and cellular DNA damage induced by cigarette smoke. Methods Two kinds of eukaryotic cells B-16 cells and oral buccal mucosal cells in liquid were attacked by the mainstream smoke produced via on-line cigarette smoking according to FTC with or without baicalein, quercetin or Sodium Danshensu. The cytotoxicity and cellular DNA damage were respectively assessed by MTT method and single cell gel electrophoresis. Results The cytotoxicity of B-16 cells and DNA damage of two kinds of cells induced by on-line cigarette smoking were obvious. A positive relationship was observed between the exposure time in smoke and the tail moment and olive tail moment of comet cells. Baicalein, quercetin, or Sodium Danshensu(1 mmol/L) could relieve the cytotoxicity by about 50% and decrease the DNA damage by more than 60%. Conclusion There is a positive relationship between the exposure of cells in smoke and the cellular DNA damage, and the flavonoid components baicalein, quercetin, or Sodium Danshensu have a protective effect against the genotoxicity of cigarette smoke. |
| In vivo | Biphasic effects of sodium danshensu on vessel function in isolated rat aorta.[Pubmed: 20228827]Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010 Apr;31(4):421-8.To investigate the effects of Sodium Danshensu on vessel function in isolated rat aortic ring.
|
| Animal Research | Neuroprotective effect and underlying mechanism of sodium danshensu [3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl) lactic acid from Radix and Rhizoma Salviae miltiorrhizae = Danshen] against cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats.[Pubmed: 25765834 ]Phytomedicine. 2015 Feb 15;22(2):283-9.Sodium Danshensu (SDSS), the sodium salt of danshensu (DSS), has the same pharmacological effects as DSS.
|

Sodium Danshensu Dilution Calculator

Sodium Danshensu Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.5413 mL | 22.7066 mL | 45.4133 mL | 90.8265 mL | 113.5332 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9083 mL | 4.5413 mL | 9.0827 mL | 18.1653 mL | 22.7066 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4541 mL | 2.2707 mL | 4.5413 mL | 9.0827 mL | 11.3533 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0908 mL | 0.4541 mL | 0.9083 mL | 1.8165 mL | 2.2707 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0454 mL | 0.2271 mL | 0.4541 mL | 0.9083 mL | 1.1353 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Danshensu (sodium salt) is odium salt of danshensu from the widely used Chinese herb Danshen. It can inhibited phenylephrine- and CaCl2-induced vasoconstriction in Ca2+-free medium. In vitro: Sodium danshensu showed a biphasic effects on vessel tension. While low dosage of sodium danshensu produced small contraction possibly through transient enhancement of Ca2+ influx, high dosage produced significant vasodilation mainly through promoting the opening of non-selective K+ channels and small-conductance calcium-sensitive K+ channels in the vascular smooth muscle cells.[1]In vivo: Danshensu did not change the expression of AGEs but partly blocked the increased expression of RAGE in the hippocampus of diabetic mice. Danshensu could ameliorate the cognitive decline in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice by attenuating advanced glycation end product-mediated neuroinflammation.[2]
References:
[1]. Zhang N. Biphasic effects of sodium danshensu on vessel function in isolated rat aorta. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2010 Apr, 31(4):421-8.
[2]. Tian Wang et al. Danshensu ameliorates the cognitive decline in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice by attenuating advanced glycation end product-mediated neuroinflammation. J Neuroimmunol, 2012 Apr, 245(1-2):79-86.
- 1,6-Dihydro-4,7'-epoxy-1-methoxy-3',4'-methylenedioxy-6-oxo-3,8'-lignan
Catalog No.:BCN6584
CAS No.:67920-48-3
- Mesaconine
Catalog No.:BCC8339
CAS No.:6792-09-2
- Macusine B
Catalog No.:BCN6471
CAS No.:6792-07-0
- Homobaldrinal
Catalog No.:BCN2681
CAS No.:67910-07-0
- Dehydroevodiamine
Catalog No.:BCN2974
CAS No.:67909-49-3
- Aluminum n-octacosoxide
Catalog No.:BCC8099
CAS No.:67905-27-5
- Ambrox
Catalog No.:BCN6907
CAS No.:6790-58-5
- Scutebarbatine K
Catalog No.:BCN3223
CAS No.:960302-86-7
- Cyclo(Pro-Trp)
Catalog No.:BCN2422
CAS No.:67889-75-2
- Gigantol
Catalog No.:BCN8382
CAS No.:67884-30-4
- n-Butyl-β-D-fructopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCC9097
CAS No.:67884-27-9
- Martynoside
Catalog No.:BCN4236
CAS No.:67884-12-2
- Aurantio-obtusin
Catalog No.:BCN1222
CAS No.:67979-25-3
- N-(5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoyl)taurine
Catalog No.:BCN1755
CAS No.:679834-28-7
- N-(15-Methyl-9-hexadecenoyl)taurine
Catalog No.:BCN1754
CAS No.:679834-30-1
- BMS 193885
Catalog No.:BCC7613
CAS No.:679839-66-8
- Sodium citrate
Catalog No.:BCC7588
CAS No.:68-04-2
- Vitamin B12
Catalog No.:BCC4878
CAS No.:68-19-9
- Norethindrone
Catalog No.:BCC4811
CAS No.:68-22-4
- Vitamin A
Catalog No.:BCN8349
CAS No.:68-26-8
- Sulfadiazine
Catalog No.:BCC3859
CAS No.:68-35-9
- Hydroxyzine
Catalog No.:BCC5209
CAS No.:68-88-2
- Metamizole sodium
Catalog No.:BCC9024
CAS No.:68-89-3
- Hypoxanthine
Catalog No.:BCC5324
CAS No.:68-94-0
Biphasic effects of sodium danshensu on vessel function in isolated rat aorta.[Pubmed:20228827]
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010 Apr;31(4):421-8.
AIM: To investigate the effects of Sodium Danshensu on vessel function in isolated rat aortic ring. METHODS: Thoracic aortae from normal rats were isolated and equilibrated in organ bath with Krebs-Henseleit buffer and ring tension was recorded. Effects of Sodium Danshensu on basal tonus of the vessel and its effects on vessel contraction and relaxation with or without endothelium were observed. RESULTS: In thoracic arteries under basal tonus, Sodium Danshensu (0.3-3 g/L) produced a dose-dependent transient contraction. In phenylephrine-precontracted thoracic arteries with or without endothelium, low concentration (0.1-0.3 g/L) of Sodium Danshensu produced a weak contraction, while high concentrations (1-3 g/L) produced a pronounced vasodilator after a transient vasocontraction. Pre-incubation with Sodium Danshensu could inhibit vessel contraction induced by phenylephrine and potassium chloride in a concentration-dependent way. Sodium Danshensu inhibited phenylephrine- and CaCl(2)-induced vasoconstriction in Ca(2+)-free medium. Pre-incubation with tetraethylammonium, a non-selective K(+) channel blocker, and apamin, a small-conductance calcium-activated K(+) channel blocker partially antagonized the relaxation response induced by Sodium Danshensu. However, iberiotoxin (big-conductance calcium-sensitive K(+) channel blocker), barium chloride (inward rectifier K(+) channel blocker), and glibencalmide (ATP-sensitive K(+) channel blocker) had no influence on the vasodilation effect of Sodium Danshensu. CONCLUSION: Sodium Danshensu showed a biphasic effects on vessel tension. While low dosage of Sodium Danshensu produced small contraction possibly through transient enhancement of Ca(2+) influx, high dosage produced significant vasodilation mainly through promoting the opening of non-selective K(+) channels and small-conductance calcium-sensitive K(+) channels in the vascular smooth muscle cells.
Neuroprotective effect and underlying mechanism of sodium danshensu [3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl) lactic acid from Radix and Rhizoma Salviae miltiorrhizae = Danshen] against cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats.[Pubmed:25765834]
Phytomedicine. 2015 Feb 15;22(2):283-9.
Sodium Danshensu (SDSS), the sodium salt of danshensu (DSS), has the same pharmacological effects as DSS. In the present study, we aimed to investigate the neuroprotective effect and possible mechanism of SDSS against cerebral ischemic/reperfusion injury. Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into four groups: sham, control, 30 mg/kg and 60 mg/kg SDSS. Cerebral ischemia was induced by 2 h of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). Neurological functional deficits were evaluated according to the modified neurological severity score (mNSS); cerebral infarct volume and histological damage were measured by TTC or H-E staining. In addition, the number of apoptotic cells and caspase 3/7 activity were assessed by TUNEL or Caspase-Glo assay. And the expression of apoptosis-regulatory proteins and the PI3K/Akt pathway were investigated by western blotting. Our results showed that treatment with SDSS for 5 days after MCAO remarkably improved neurologic deficits and survival rate, reduced infarct volume and the number of dead neurons. SDSS also decreased the number of apoptotic cells, regulated the expression of Bcl-2 and Bax, and increased the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax. Further study revealed that treatment with SDSS also increased the level of p-Akt and p-GSK-3beta. Taken together, our results suggest that SDSS has the neuroprotective effect against cerebral I/R injury, and the potential mechanism might to inhibition of apoptosis through activating the PI3K/Akt signal pathway.


