TAK-242TLR 4 signaling inhibitor CAS# 243984-11-4 |
- Resiquimod (R-848)
Catalog No.:BCC4073
CAS No.:144875-48-9
- TAK-242 S enantiomer
Catalog No.:BCC1978
CAS No.:243984-10-3
- Imiquimod maleate
Catalog No.:BCC4197
CAS No.:896106-16-4
- Imiquimod hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4196
CAS No.:99011-78-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 243984-11-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11703255 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H17ClFNO4S | M.Wt | 361.82 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Resatorvid | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (276.38 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
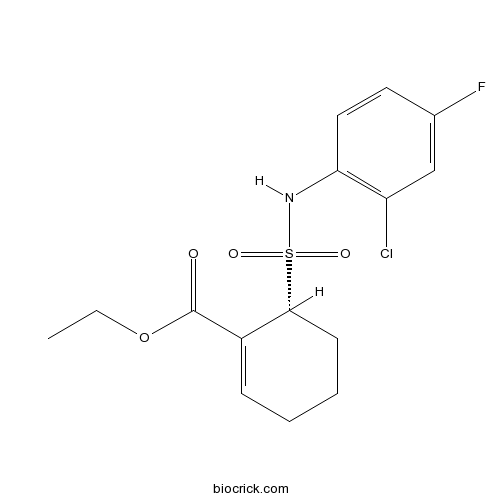
| Chemical Name | ethyl (6R)-6-[(2-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)sulfamoyl]cyclohexene-1-carboxylate | ||
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)C1=CCCCC1S(=O)(=O)NC2=C(C=C(C=C2)F)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LEEIJTHMHDMWLJ-CQSZACIVSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H17ClFNO4S/c1-2-22-15(19)11-5-3-4-6-14(11)23(20,21)18-13-8-7-10(17)9-12(13)16/h5,7-9,14,18H,2-4,6H2,1H3/t14-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | TAK-242 is a potent TLR4 signaling inhibitor, selectively inhibits the TLR4-mediated production of cytokines and NO.In Vitro:In RAW264.7 cells and mouse peritoneal macrophages, TAK-242 suppresses lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced production of NO, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin (IL)-6, with IC50 of 1.1 to 11 nM. TAK-242 also suppresses the production of these cytokines from LPS-stimulated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) at IC50 values from 11 to 33 nM[1].In Vivo:TAK-242 apparently reduces the serum anti-dsDNA levels in both genotype mice. Alternatively, IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-1β production is markedly inhibited by TAK-242, but their concentrations are still greatly higher than those in NS-treated counterparts[2]. TAK-242 pre-stress administration prevents the accumulation of potentially deleterious inflammatory and oxidative/nitrosative mediators in the brain frontal cortex of rats. TAK-242 i.v. administration at the beginning of the stress session completely blocks TLR-4 mRNA and protein upregulation after stress exposure[3]. References: | |||||

TAK-242 Dilution Calculator

TAK-242 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7638 mL | 13.819 mL | 27.6381 mL | 55.2761 mL | 69.0951 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5528 mL | 2.7638 mL | 5.5276 mL | 11.0552 mL | 13.819 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2764 mL | 1.3819 mL | 2.7638 mL | 5.5276 mL | 6.9095 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0553 mL | 0.2764 mL | 0.5528 mL | 1.1055 mL | 1.3819 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0276 mL | 0.1382 mL | 0.2764 mL | 0.5528 mL | 0.691 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: With IC50 of 1.1 to 11 nM, TAK-242 inhibited LPS-induced NO production, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin (IL)-6 in RAW264.7 cells and mouse peritoneal macrophages [1].
Toll, a member of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family, was identified as a gene product essential for the development of embryonic dorsoventral polarity in Drosophila melanogaster, moreover, it has been also found to play a critical role in the antifungal response of flies. TAK-242 (resatorvid), a cyclohexene derivative, is recongnizred as a novel small-molecule compound selectively inhibiting TLR4 signaling.
In vitro: A previous in-vitro study showed that TAK-242 could inhibit the production of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory mediators by binding to the intracellular domain of TLR4 using coimmunoprecipitation approach. Among 10 different human TLRs, TAK-242 selectively bound to TLR4. These findings suggested that TAK-242 could selectively bind to TLR4 and disrupted the interaction of TLR4 with adaptor molecules, thereby inhibiting TLR4 signal transduction and its downstream signaling [2].
In vivo: Preclinical animal study demonostrated that the acute restraint stress exposure upregulateed TLR-4 expression both at the mRNA and protein level in rat. TAK-242 pre-stress administration prevented the accumulation of potentially deleterious inflammatory and oxidative/nitrosative mediators in the brain frontal cortex of rats. These finding s indicated that the use of TAK-242 or other TLR-4 signalling pathway inhibitory compounds could be considered as a potential therapeutic adjuvant strategy to constrain the inflammatory process taking place after stress exposure and in stress-related neuropsychiatric diseases [3].
Clinical trial: To evaluate whether TAK-242, a small-molecule inhibitor of Toll-like receptor-4–mediated signaling, suppresses cytokine levels and improves 28-day all-cause mortality rates in patients with severe sepsis has been conducted in Japan, the U.S. and Europe by Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited ("Takeda"). However, following a thorough review of development strategy, Takeda has concluded that TAK-242’s profile does not meet the criteria to support continuation of further development activities. This decision has not been influenced by any concerns over the safety or efficacy of the compound [4].
References:
[1] Ii M, Matsunaga N, Hazeki K, Nakamura K, Takashima K, Seya T, Hazeki O, Kitazaki T, Iizawa Y. A novel cyclohexene derivative, ethyl (6R)-6-[N-(2-Chloro-4-fluorophenyl)sulfamoyl]cyclohex- 1-ene-1-carboxylate (TAK-242), selectively inhibits toll-like receptor 4-mediated cytokine production through suppression of intracellular signaling. Mol Pharmacol. 2006;69(4):1288-95.
[2] Naoko Matsunaga, Noboru Tsuchimori, Tatsumi Matsumoto, and Masayuki Ii. TAK-242 (Resatorvid), a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Toll-Like Receptor (TLR) 4 Signaling, Binds Selectively to TLR4 and Interferes with Interactions between TLR4 and Its Adaptor Molecules. Mol Pharmacol 79:34–41, 2011
[3] Iciar Gárate, Borja García-Bueno, José Luis Mu?oz Madrigal, Javier R Caso, Luis Alou, María Luisa Gómez-Lus and Juan Carlos Leza. Toll-like 4 receptor inhibitor TAK-242 decreases neuroinflammation in rat brain frontal cortex after stress. Journal of Neuroinflammation 2014, 11:8
[4] Todd W. Rice; Arthur P. Wheeler; Gordon R. Bernard; Jean-Louis Vincent; Derek C. Angus; Naoki Aikawa; Ignace Demeyer; Stephen Sainati; Nicholas Amlot; Charlie Cao; Masayuki Ii; Hideyasu Matsuda; Kouji Mouri; Jon Cohen. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of TAK-242 for the treatment of severe sepsis. Crit Care Med 2010 Vol. 38, No. 8: 1-10
- TAK-242 S enantiomer
Catalog No.:BCC1978
CAS No.:243984-10-3
- TCS 401
Catalog No.:BCC2469
CAS No.:243967-42-2
- Cnicin
Catalog No.:BCN8546
CAS No.:24394-09-0
- Ethyl 4-methoxycinnamate
Catalog No.:BCN5028
CAS No.:24393-56-4
- Kynurenic acid sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7754
CAS No.:2439-02-3
- 5-Iodotubercidin
Catalog No.:BCC1312
CAS No.:24386-93-4
- Glycoside L-F2
Catalog No.:BCN2158
CAS No.:243857-99-0
- pep4c
Catalog No.:BCC5783
CAS No.:243843-43-8
- pep2m
Catalog No.:BCC5782
CAS No.:243843-42-7
- L-(-)-Fucose
Catalog No.:BCN8326
CAS No.:2438-80-4
- Bufexamac
Catalog No.:BCC4427
CAS No.:2438-72-4
- (-)-alpha-Pinene
Catalog No.:BCC8295
CAS No.:2437-95-8
- beta-D-glucose
Catalog No.:BCN8171
CAS No.:492-61-5
- (+)-Epipinoresinol
Catalog No.:BCN3255
CAS No.:24404-50-0
- Beta-Rotunol
Catalog No.:BCN6628
CAS No.:24405-57-0
- L-798,106
Catalog No.:BCC7654
CAS No.:244101-02-8
- Taxumairol R
Catalog No.:BCN6939
CAS No.:244167-04-2
- L-748,337
Catalog No.:BCC7475
CAS No.:244192-94-7
- Pulchinenoside E2
Catalog No.:BCN8186
CAS No.:244202-36-6
- Celaphanol A
Catalog No.:BCN5101
CAS No.:244204-40-8
- JTC-801
Catalog No.:BCC3800
CAS No.:244218-51-7
- LFM-A13
Catalog No.:BCC6472
CAS No.:244240-24-2
- 3,5,7,15-Tetraacetoxy-9-nicotinoyloxy-6(17),11-jatrophadien-14-one
Catalog No.:BCN6592
CAS No.:244277-75-6
- Nonivamide
Catalog No.:BCN2325
CAS No.:2444-46-4
TAK-242 treatment ameliorates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting TLR4 signaling pathway in a swine model of Maastricht-category-III cardiac death.[Pubmed:27685793]
Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Dec;84:495-501.
OBJECTIVES: This study aims to test the effects of TAK-242 on liver transplant viability in a model of swine Maastricht-category-III cardiac death. METHODS: A swine DCD Maastricht-III model of cardiac death was established, and TAK-242 was administered prior to the induction of cardiac death. The protein and mRNA level of TLR4 signaling pathway molecules and cytokines that are important in mediating immune and inflammatory responses were assessed at different time points following the induction of cardiac death. RESULTS: After induction of cardiac death, both the mRNA and protein levels of key molecules (TLR4, TRAF6, NF-varkappaB, ICAM-1, MCP-1 and MPO), TNF-alpha and IL-6 increased significantly. Infusion of TAK-242 1h before induction of cardiac death blocked the increase of immune and inflammatory response molecules. However, the increase of TLR4 level was not affected by infusion of TAK-242. Histology study showed that infusion of TAK-242 protect liver tissue from damage during cardiac death. CONCLUSIONS: These results indicates that TLR4 signaling pathway may contribute to ischemia/reperfusion injury in the liver grafts, and blocking TLR4 pathway with TAK-242 may reduce TLR4-mediated tissue damage.
The toll-like receptor 4 antagonist transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase(TAK)-242 attenuates taurocholate-induced oxidative stress through regulating mitochondrial function in mice pancreatic acinar cells.[Pubmed:27884323]
J Surg Res. 2016 Dec;206(2):298-306.
BACKGROUND: Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a commonly occurring and potentially life-threatening disease. Recently, toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) has been considered as a new clue for studying the pathogenesis of AP due to its important role in inflammatory response cascade. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The aim of this study was to investigate the potential protective effect of transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase (TAK)-242, a novel TLR4 antagonist, in taurocholate-treated mice pancreatic acinar cells. The protective effects were measured by cell viability, lactate dehydrogenase release and apoptosis, and oxidative stress was assayed by lipid peroxidation and oxidative enzyme activities. To determine the potential underlying mechanisms, mitochondrial cytochrome c release, swelling, and calcium buffering capacity were measured in isolated mitochondria, and mitochondrial biogenesis and expression of mitochondrial dynamic proteins were detected by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and Western blot. RESULTS: Treatment with 6-mM taurocholate significantly increased the expression of TLR4 at both mRNA and protein levels. TAK-242 markedly increased cell viability, decreased lactate dehydrogenase release, and inhibited apoptotic cell death as measured by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining in pancreatic acinar cells. These protective effects were accompanied by the suppressed lipid peroxidation and enhanced endogenous antioxidative enzyme activity. Using isolated and purified mitochondria from pancreatic acinar cells, we found that TAK-242 treatment also inhibited cytochrome c release into the cytoplasm, mitochondrial swelling, and decrease in mitochondrial Ca(2+) buffering capacity after taurocholate exposure. In addition, TAK-242 significantly promoted mitochondrial biogenesis, as evidenced by increased mtDNA and upregulated mitochondrial transcription factors. The results of Western blot analysis showed that TAK-242 also differently regulated the expression of mitochondrial fusion and fission proteins. CONCLUSIONS: All these data strongly indicated that blocking TLR4 activity via TAK-242 exerts protective effects in an in vitro AP model, and it could be a possible strategy to improve clinical outcome in AP patients.
TAK-242 Protects Against Apoptosis in Coronary Microembolization-Induced Myocardial Injury in Rats by Suppressing TLR4/NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway.[Pubmed:28359050]
Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(4):1675-1683.
BACKGROUND/AIMS: Myocardial apoptosis is heavily implicated in the myocardial injury caused by coronary microembolization (CME), and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is considered to be involved in this apoptotic cascade. Therefore, the present study was designed to investigate the role of TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway regulated by TAK-242, a selective TLR4 signal transduction inhibitor, in the myocardial apoptosis after CME in rats. METHODS: Forty-five rats were randomized (random number) into three groups: sham, CME and CME + TAK-242 (n = 15 per group).CME was induced by injecting polyethylene microspheres (42microm) into the left ventricular except the sham group. CME + TAK-242 group was treated with TAK-242 (2mg/kg) via the tail vein 30 minutes before CME modeling. Cardiac function was evaluated 6 hours after operation. Tissue biopsy was stained with HBFP to measure the size of micro-infarction area. TUNEL staining was used to detect myocardial apoptosis. Western blot and qPCR were used to evaluate the expression of TLR4, MyD88, NF-kappaB p65, p-IkappaBalpha and Cleaved caspase-3. RESULTS: Cardiac function in the CME group and CME + TAK-242 group were significantly decreased compared with the sham group (P < 0.05) and the micro-infarction area, the apoptotic index, the expression of TLR4, NF-kappaB p65, p-IkappaBalpha and Cleaved caspase-3 were increased significantly (P < 0.05). Cardiac function in the CME + TAK-242 group was significantly improved compared with the CME group (P < 0.05) and the micro-infarction area, the apoptotic index, the expression of TLR4, MyD88, NF-kappaB p65, p-IkappaBalpha and Cleaved caspase-3 were decreased significantly (P < 0.05). CONCLUSIONS: TAK-242 can effectively improve CME-induced cardiac dysfunction by regulating TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway and then reducing the myocardial apoptosis.
Toll-like receptor 4 antagonist TAK-242 inhibits autoinflammatory symptoms in DITRA.[Pubmed:28196704]
J Autoimmun. 2017 Jun;80:28-38.
BACKGROUND: IL36RN encodes the IL-36 receptor antagonist (IL-36Ra), and loss-of-function mutations in IL36RN define a recessively inherited autoinflammatory disease named "deficiency of IL-36Ra" (DITRA). DITRA causes systemic autoinflammatory diseases, including generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP), an occasionally life-threatening disease that is characterized by widespread sterile pustules on the skin, fever and other systemic symptoms. GPP can present at any age, and provocative factors include various infections, medicines and pregnancy. OBJECTIVE: We aimed to elucidate the role of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling in DITRA and to innovate an efficient treatment for DITRA. METHODS: We generated Il36rn(-/-) mice and treated them with TLR4 agonist to establish DITRA model mice. Furthermore, we administrated TLR4 antagonist TAK-242 to the model mice to inhibit the DITRA symptoms. RESULT: Il36rn(-/-) mice treated by TLR4 agonist showed autoinflammatory symptoms in skin, articulation and liver. Thus, we established model mice for DITRA or GPP that show cutaneous, articular, and hepatic autoinflammatory symptoms typical of DITRA or GPP: sterile pustules on the skin, liver abscesses and enthesitis of the hind paws. Additionally, these symptoms were canceled by TAK-242 administration. We demonstrated the inhibitory effects of the TLR4 antagonist TAK-242 on the autoinflammatory symptoms exhibited by the DITRA models. CONCLUSION: We suggested that blockage of TLR4 signaling is a promising treatment for DITRA and GPP.


