TAK-593VEGFR2 inhibitor CAS# 1005780-62-0 |
- ML-7 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1770
CAS No.:110448-33-4
- Istaroxime
Catalog No.:BCC1660
CAS No.:203737-93-3
- Dynasore
Catalog No.:BCC1088
CAS No.:304448-55-3
- Istaroxime hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1661
CAS No.:374559-48-5
- 20-HETE
Catalog No.:BCC1301
CAS No.:79551-86-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1005780-62-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 24767976 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H23N7O3 | M.Wt | 445.47 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 48.5 mg/mL (108.87 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
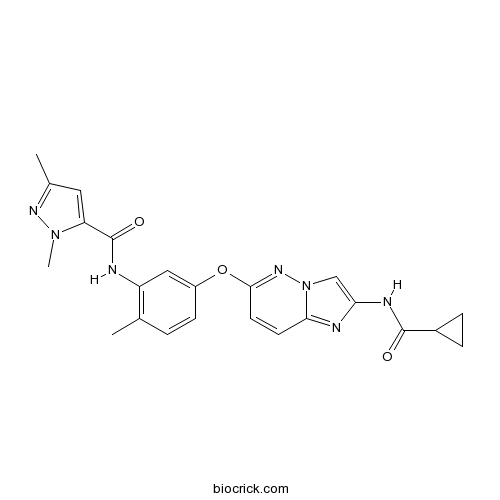
| Chemical Name | N-[5-[2-(cyclopropanecarbonylamino)imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazin-6-yl]oxy-2-methylphenyl]-2,5-dimethylpyrazole-3-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C=C(C=C1)OC2=NN3C=C(N=C3C=C2)NC(=O)C4CC4)NC(=O)C5=CC(=NN5C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DZFZXPPHBWCXPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H23N7O3/c1-13-4-7-16(11-17(13)24-23(32)18-10-14(2)27-29(18)3)33-21-9-8-20-25-19(12-30(20)28-21)26-22(31)15-5-6-15/h4,7-12,15H,5-6H2,1-3H3,(H,24,32)(H,26,31) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | TAK-593 is a potent VEGFR and PDGFR family inhibitor with IC50s of 3.2, 0.95, 1.1, 4.3 and 13 nM for VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3, PDFGRα and PDFGRβ, respectively.In Vitro:TAK-593 inhibits growth of HUVEC with an IC50 of 0.30 nM. It shows potent inhibitory activity against VEGFR (VEGFR1-3: IC50=3.2, 0.95, 1.1 nM) and PDGFR (PDGFRα, β: IC50=4.3, 13 nM) families. Against other kinases, the IC50 values of TAK-593 are above 100 nM, except for Fms (IC50=10 nM) and Ret (IC50=18 nM) kinases[1]. TAK-593 potently inhibits VEGF- and PDGF-stimulated cellular phosphorylation and proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and human coronary artery smooth muscle cells. TAK-593 also potently inhibits VEGF-induced tube formation of endothelial cells co-cultured with fibroblasts[2].In Vivo:TAK-593 inhibits growth of HUVEC with an IC50 of 0.30 nM. It shows potent inhibitory activity against VEGFR (VEGFR1-3: IC50=3.2, 0.95, 1.1 nM) and PDGFR (PDGFRα, β: IC50=4.3, 13 nM) families. Against other kinases, the IC50 values of TAK-593 are above 100 nM, except for Fms (IC50=10 nM) and Ret (IC50=18 nM) kinases[1]. TAK-593 potently inhibits VEGF- and PDGF-stimulated cellular phosphorylation and proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and human coronary artery smooth muscle cells. TAK-593 also potently inhibits VEGF-induced tube formation of endothelial cells co-cultured with fibroblasts[2]. References: | |||||

TAK-593 Dilution Calculator

TAK-593 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2448 mL | 11.2241 mL | 22.4482 mL | 44.8964 mL | 56.1205 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.449 mL | 2.2448 mL | 4.4896 mL | 8.9793 mL | 11.2241 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2245 mL | 1.1224 mL | 2.2448 mL | 4.4896 mL | 5.6121 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0449 mL | 0.2245 mL | 0.449 mL | 0.8979 mL | 1.1224 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0224 mL | 0.1122 mL | 0.2245 mL | 0.449 mL | 0.5612 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
TAK-593 is a highly potent inhibitor of VEGFR2 with IC50 value of 0.95nM [1].
TAK-593 is an imidazo [1, 2-b] pyridazine derivative. It is found to inhibit VEGFR2 with a highly potent effect in the non-RI assay using the AlphaScreen system. And in the cell proliferation assay, TAK-593 suppresses VEGF-stimulated cell growth of HUVEC with IC50 value of 0.3nM. TAK-593 is a slow-binding inhibitor and it has a long residence time on VEGFR2. Besides that, TAK-593 also has efficacy on other receptor kinases. It gives the IC50 values of 3.2nM, 1.1nM, 4.3nM and 13nM for VEGFR1, VEGFR3, PDGFRα and PDGFRβ, respectively. Moreover, TAK-593 shows significant anti-tumor efficacy in the mouse xenograft model using A549 human lung adenocarcinoma epithelial cells. Oral administration of TAK-593 twice daily at doses of 0.25mg/kg for two weeks potently inhibits tumor growth with T/C value of 34% [1].
References:
[1] Miyamoto N, Sakai N, Hirayama T, Miwa K, Oguro Y, Oki H, Okada K, Takagi T, Iwata H, Awazu Y, Yamasaki S, Takeuchi T, Miki H, Hori A, Imamura S. Discovery of N-[5-({2-[(cyclopropylcarbonyl)amino]imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazin-6-yl}oxy)-2-methylphenyl]-1,3-dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxamide (TAK-593), a highly potent VEGFR2 kinase inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013 Apr 15;21(8):2333-45.
- TC ASK 10
Catalog No.:BCC6301
CAS No.:1005775-56-3
- Monomethylsulochrin
Catalog No.:BCN7255
CAS No.:10056-14-1
- Tirasemtiv
Catalog No.:BCC5183
CAS No.:1005491-05-3
- LCL161
Catalog No.:BCC1691
CAS No.:1005342-46-0
- CVT 10216
Catalog No.:BCC5606
CAS No.:1005334-57-5
- Gelomulide N
Catalog No.:BCN6641
CAS No.:1005212-02-1
- Aeruginolactone
Catalog No.:BCN3695
CAS No.:1005208-88-7
- TCS 2002
Catalog No.:BCC6074
CAS No.:1005201-24-0
- Blasticidin A
Catalog No.:BCN1830
CAS No.:100513-53-9
- Sterigmatocystin
Catalog No.:BCN6885
CAS No.:10048-13-2
- Gastrin I (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5958
CAS No.:10047-33-3
- Rosiridin
Catalog No.:BCN5970
CAS No.:100462-37-1
- NF 546
Catalog No.:BCC7804
CAS No.:1006028-37-0
- MK-2894
Catalog No.:BCC1757
CAS No.:1006036-87-8
- MK-2894 sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC1758
CAS No.:1006036-88-9
- (-)-Epipinoresinol
Catalog No.:BCN3377
CAS No.:10061-38-8
- Desloratadine
Catalog No.:BCC4540
CAS No.:100643-71-8
- Ganoderenic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN3208
CAS No.:100665-40-5
- Ganoderenic acid B
Catalog No.:BCN7966
CAS No.:100665-41-6
- Ganoderenic acid C
Catalog No.:BCN3210
CAS No.:100665-42-7
- Ganoderenic acid D
Catalog No.:BCN2445
CAS No.:100665-43-8
- Deacetyl ganoderic acid F
Catalog No.:BCN2870
CAS No.:100665-44-9
- 3-(Hydroxymethyl)cyclopentanol
Catalog No.:BCN5822
CAS No.:1007125-14-5
- CH5132799
Catalog No.:BCC4991
CAS No.:1007207-67-1
Anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor effects of TAK-593, a potent and selective inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase.[Pubmed:23305239]
Cancer Sci. 2013 Apr;104(4):486-94.
We recently reported that TAK-593, a novel imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazine derivative, is a highly potent and selective inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and platelet derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor tyrosine kinase families. Moreover, TAK-593 exhibits a uniquely long-acting inhibitory profile towards VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2) and PDGF receptor beta (PDGFRbeta). In this study, we demonstrated that TAK-593 potently inhibits VEGF- and PDGF-stimulated cellular phosphorylation and proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and human coronary artery smooth muscle cells. TAK-593 also potently inhibits VEGF-induced tube formation of endothelial cells co-cultured with fibroblasts. Oral administration of TAK-593 exhibited strong anti-tumor effects against various human cancer xenografts along with good tolerability despite a low level of plasma exposure. Even after the blood and tissue concentrations of TAK-593 decreased below the detectable limit, a pharmacodynamic marker (phospho VEGFR2) was almost completely suppressed, indicating that its long duration of enzyme inhibition might contribute to the potent activity of TAK-593. Immunohistochemical staining indicated that TAK-593 showed anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects on tumors along with a decrease of vessel density and inhibition of pericyte recruitment to microvessels in vivo. Furthermore, dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging revealed that TAK-593 reduced tumor vessel permeability prior to the onset of anti-tumor activity. In conclusion, TAK-593 is an extremely potent VEGFR/PDGFR kinase inhibitor whose potent anti-angiogenic activity suggests therapeutic potential for the treatment of solid tumors.
Discovery of N-[5-({2-[(cyclopropylcarbonyl)amino]imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazin-6-yl}oxy)-2-methylph enyl]-1,3-dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxamide (TAK-593), a highly potent VEGFR2 kinase inhibitor.[Pubmed:23498918]
Bioorg Med Chem. 2013 Apr 15;21(8):2333-2345.
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) plays important roles in tumor angiogenesis, and the inhibition of its signaling pathway is considered an effective therapeutic option for the treatment of cancer. In this study, we describe the design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of 2-acylamino-6-phenoxy-imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazine derivatives. Hybridization of two distinct imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazines 1 and 2, followed by optimization led to the discovery of N-[5-({2-[(cyclopropylcarbonyl)amino]imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazin-6-yl}oxy)-2-methylph enyl]-1,3-dimethyl-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxamide (23a, TAK-593) as a highly potent VEGF receptor 2 kinase inhibitor with an IC50 value of 0.95 nM. The compound 23a strongly suppressed proliferation of VEGF-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells with an IC50 of 0.30 nM. Kinase selectivity profiling revealed that 23a inhibited platelet-derived growth factor receptor kinases as well as VEGF receptor kinases. Oral administration of 23a at 1 mg/kg bid potently inhibited tumor growth in a mouse xenograft model using human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells (T/C=8%).
Biochemical characterization of TAK-593, a novel VEGFR/PDGFR inhibitor with a two-step slow binding mechanism.[Pubmed:21182308]
Biochemistry. 2011 Feb 8;50(5):738-51.
Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis leads to a lack of oxygen and nutrients in the tumor and therefore has become a standards of care for many solid tumor therapies. Dual inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) and platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) protein kinase activities is a popular strategy for targeting tumor angiogenesis. We discovered that TAK-593, a novel imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazine derivative, potently inhibits tyrosine kinases from the VEGFR and PDGFR families. TAK-593 was highly selective for these families, with an IC(50) >1 muM when tested against more than 200 protein and lipid kinases. TAK-593 displayed competitive inhibition versus ATP. In addition, TAK-593 inhibited VEGFR2 and PDGFRbeta in a time-dependent manner, classifying it as a type II kinase inhibitor. Analysis of enzyme-inhibitor preincubation experiments revealed that the binding of TAK-593 to VEGFR2 and PDGFRbeta occurs via a two-step slow binding mechanism. Dissociation of TAK-593 from VEGFR2 was extremely slow (t(1/2) >17 h), and the affinity of TAK-593 at equilibrium (K(i)*) was less than 25 pM. Ligand displacement analysis with a fluorescent tracer confirmed the slow dissociation of TAK-593. The dissociation rate constants were in good agreement between the activity and ligand displacement data, and both analyses supported slow dissociation of TAK-593. The long residence time of TAK-593 may achieve an extended pharmacodynamic effect on VEGFR2 and PDGFRbeta kinases in vivo that differs substantially from its observed pharmacokinetic profile.


