Artemisia argyi
Artemisia argyi
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.

Natural products/compounds from Artemisia argyi
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
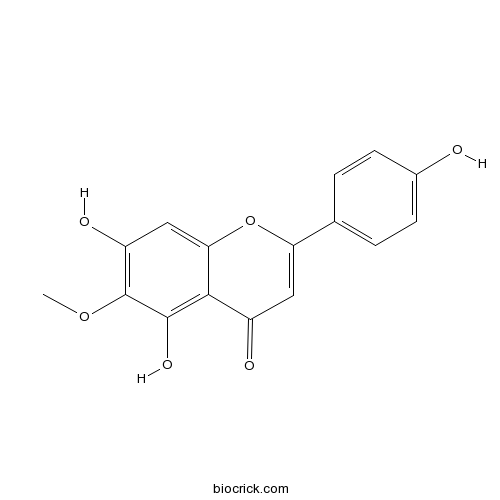
BCN6250
Hispidulin1447-88-7
Instructions
-
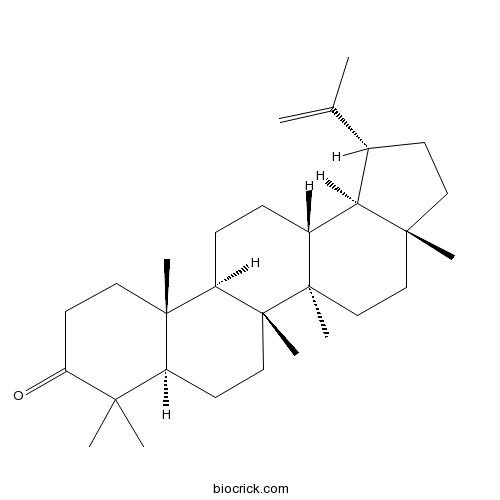
BCN1717
Lupenone1617-70-5
Instructions
-
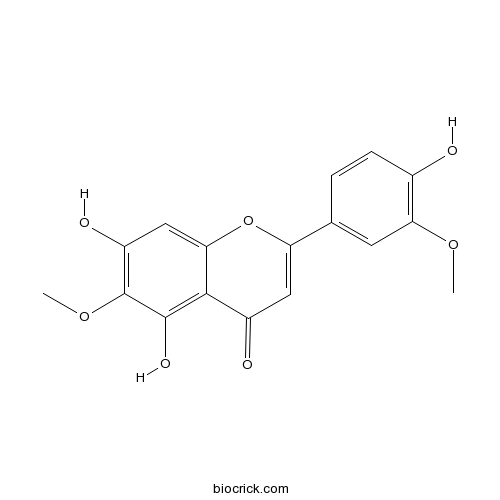
BCN2529
Jaceosidin18085-97-7
Instructions
-
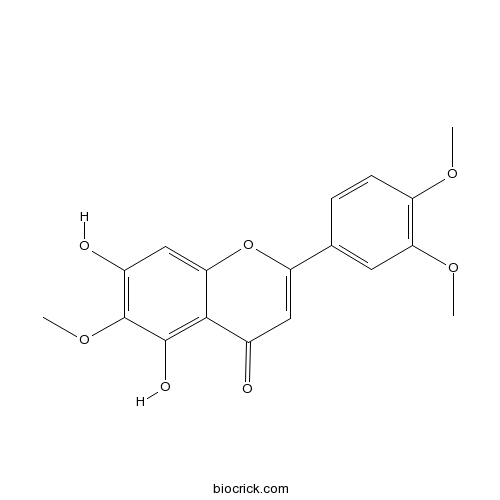
BCN2336
Eupatilin22368-21-4
Instructions
-
BCN5906
Chlorogenic acid327-97-9
Instructions
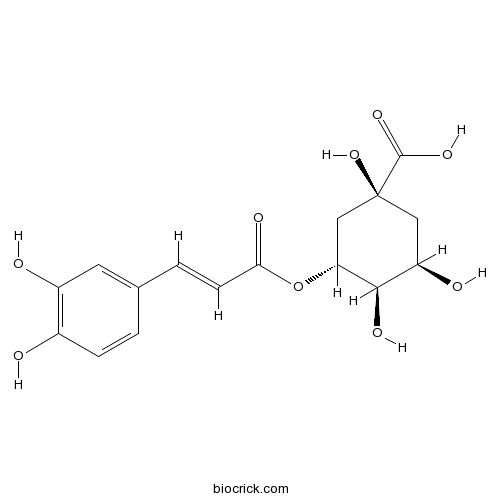
-
BCN7834
Clemaphenol A362606-60-8
Instructions
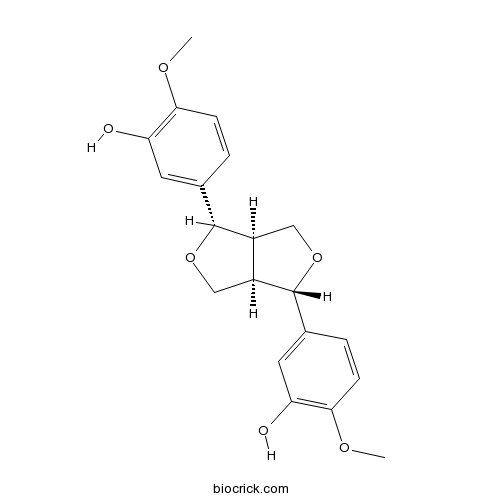
-
BCN5554
Linarin480-36-4
Instructions

-
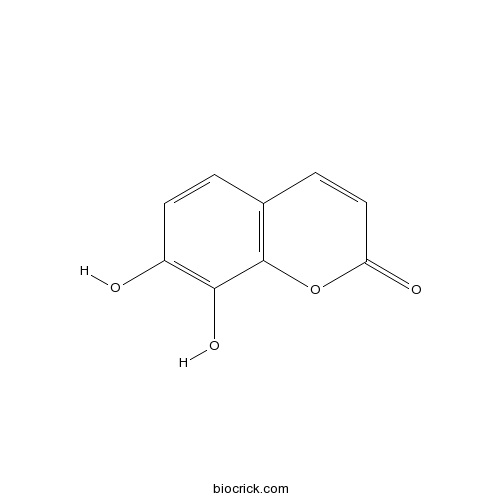
BCN1051
Daphnetin486-35-1
Instructions
-
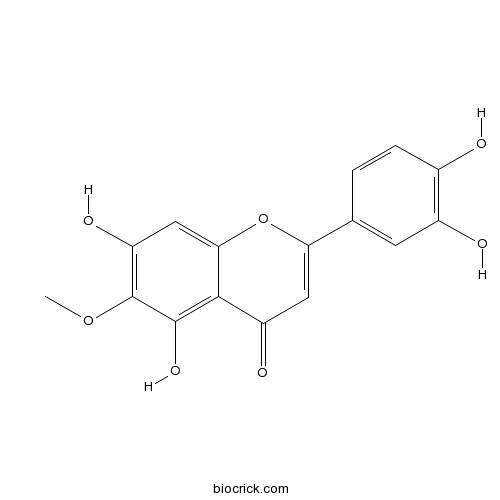
BCN3613
6-Methoxyluteolin520-11-6
Instructions
-
BCN2707
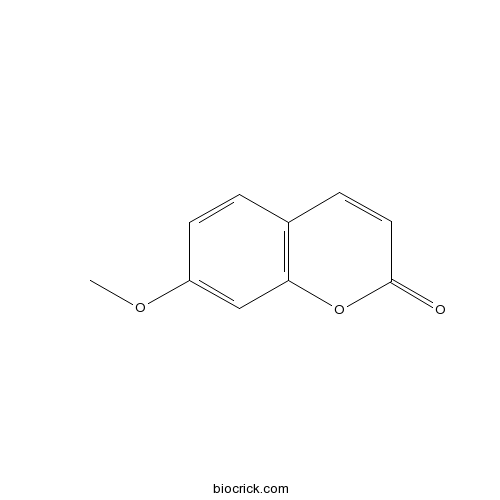
7-Methoxycoumarin531-59-9
Instructions
-
BCN8390
Myristic acid544-63-8
Instructions

-
BCN1209
Eriodictyol552-58-9
Instructions

-
BCN8297
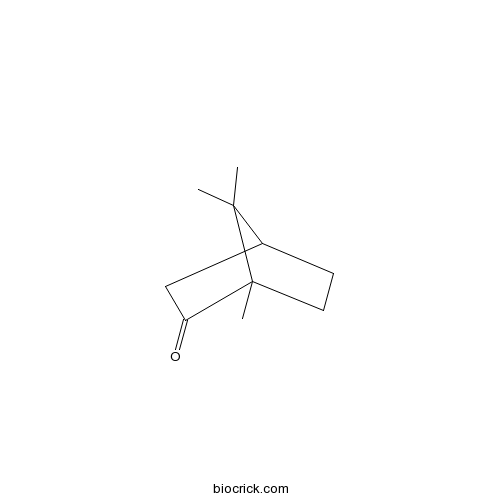
Camphor76-22-2
Instructions
-
BCN4582
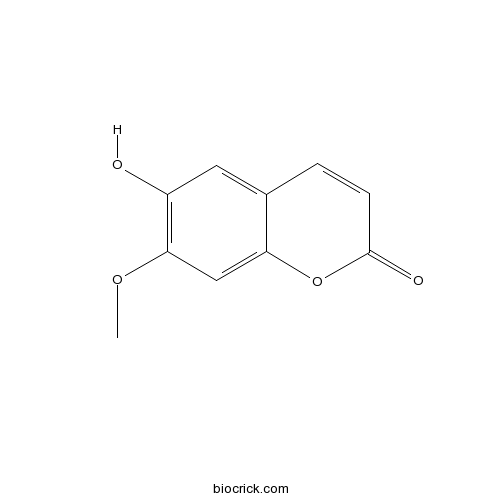
Isoscopoletin776-86-3
Instructions
-
BCN4405
Eupatorin855-96-9
Instructions

-
BCN2644
trans-Caryophyllene87-44-5
Instructions

-
BCN9045
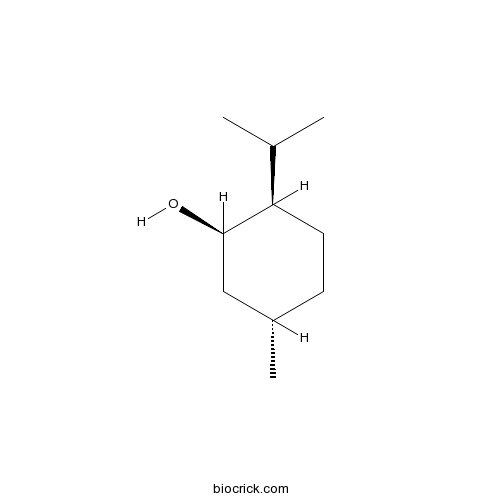
Menthol89-78-1
Instructions
-
BCN4450
Neochlorogenic acid906-33-2
Instructions

-
BCN4470
Scopoletin92-61-5
Instructions

-
BCN4477
Umbelliferone93-35-6
Instructions

-
BCN5964
Eugenol97-53-0
Instructions
Sesquiterpene lactone from Artemisia argyi induces gastric carcinoma cell apoptosis via activating NADPH oxidase/reactive oxygen species/mitochondrial pathway.[Pubmed: 30075222]
Apoptosis is an essential type of programmed cell death. Previous studies have demonstrated that a wide range of natural-derived anticancer agents induce apoptosis by trigging oxidative stress. Artemisia argyi is a traditional Chinese herb for treating diverse diseases including dyspepsia, arthroncus, and anaphylactic disease. In this study, sesquiterpene lactone 3 (SL3), a bioactive ingredient isolated from Artemisia argyi was found to show obvious inhibitory effect on two gastric carcinoma cells. Mechanism study revealed that SL3 promoted the membrane translocation of p47, activated nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADPH) oxidase, and evaluated intracellular reactive oxygen species production, leading to the activation of mitochondria-dependent caspase apoptosis pathway. Collectively, these findings show that SL3 is a promising anticancer candidate against gastric carcinoma by activating NADPH oxidase/reactive oxygen species/mitochondrial pathway.
[Quality evaluation of Artemisiae Argyi Folium based on fingerprint analysis and quantitative analysis of multicomponents].[Pubmed: 29676097]
Artemisiae Argyi Folium, the dried leaves of Artemisia argyi, has been widely used in traditional Chinese and folk medicines for treatment of hemorrhage, pain, and skin itch. Phytochemical studies indicated that volatile oil, organic acid and flavonoids were the main bioactive components in Artemisiae Argyi Folium. Compared to the volatile compounds, the research of nonvolatile compounds in Artemisiae Argyi Folium are limited. In the present study, an accurate and reliable fingerprint approach was developed using HPLC for quality control of Artemisiae Argyi Folium. A total of 10 common peaks were marked,and the similarity of all the Artemisiae Argyi Folium samples was above 0.940. The established fingerprint method could be used for quality control of Artemisiae Argyi Folium. Furthermore, an HPLC method was applied for simultaneous determination of seven bioactive compounds including five organic acids and two flavonoids in Artemisiae Argyi Folium and Artemisiae Lavandulaefoliae Folium samples. Moreover, chemometrics methods such as hierarchical clustering analysis and principal component analysis were performed to compare and discriminate the Artemisiae Argyi Folium and Artemisiae Lavandulaefoliae Folium based on the quantitative data of analytes. The results indicated that simultaneous quantification of multicomponents coupled with chemometrics analysis could be a well-acceptable strategy to identify and evaluate the quality of Artemisiae Argyi Folium.
De novo assembly and analysis of the Artemisia argyi transcriptome and identification of genes involved in terpenoid biosynthesis.[Pubmed: 29643397]
Artemisia argyi Lev. et Vant. (A. argyi) is widely utilized for moxibustion in Chinese medicine, and the mechanism underlying terpenoid biosynthesis in its leaves is suggested to play an important role in its medicinal use. However, the A. argyi transcriptome has not been sequenced. Herein, we performed RNA sequencing for A. argyi leaf, root and stem tissues to identify as many as possible of the transcribed genes. In total, 99,807 unigenes were assembled by analysing the expression profiles generated from the three tissue types, and 67,446 of those unigenes were annotated in public databases. We further performed differential gene expression analysis to compare leaf tissue with the other two tissue types and identified numerous genes that were specifically expressed or up-regulated in leaf tissue. Specifically, we identified multiple genes encoding significant enzymes or transcription factors related to terpenoid synthesis. This study serves as a valuable resource for transcriptome information, as many transcribed genes related to terpenoid biosynthesis were identified in the A. argyi transcriptome, providing a functional genomic basis for additional studies on molecular mechanisms underlying the medicinal use of A. argyi.
Gastro-protective effect of edible plant Artemisia argyi in ethanol-induced rats via normalizing inflammatory responses and oxidative stress.[Pubmed: 29273436]
Artemisia argyi, a kind of ethnic drug, has a long-term use on gastric diseases and syndromes.
[Activity of essential oil extracted from Artemisia argyi in inducing apoptosis of Candida albicans].[Pubmed: 29218944]
To explore the activity of essential oil extracted from Artemisia argyi (AAEO) in inducing the apoptosis of Candida albicans SC5314. The effect of AAEO on reactive oxygen species(ROS) and mitochondria membrane potential(MMP) of C. albicans SC5314 was detected by flow cytometry. Phosphatidylserine externalization was observed under fluorescence microscopic with Annexin-V/PI staining at the early stage of apoptosis in C. albicans. Metacaspase activity was observed under fluorescence microscopic with FITC-VAD-FMK staining at the early stage of apoptosis in C. albicans. C. albicans morphology was observed by DAPI nuclear staining and fluorescence microscopy. After intervention with 0.5 mL•L⁻¹ AAEO, apoptosis of C. albicans significantly increased, metacaspase activity increased, nuclear pyknosis and fragmentation, and intracellular ROS were significantly increased, and mitochondrial membrane potential decreased significantly. The certain concentrations of AAEO could induce the apoptosis of C. albicans.
[Quantative analysis of eupatilin and jaceosidin in folium of Artemisia argyi from different areas in China by RP-HPLC based on ancient medicine books].[Pubmed: 29218934]
In order to evaluate the quality of Artemisia argyi from Qichun, Ningbo, Anguo and Nanyang, the contents of eupatilin and jaceosidin were determined by RP-HPLC. The determination was performed on Agilent Eclipse XDB-C₁₈ (4.6 mm×250 mm, 5 μm) with mobile phase consisted of acetonitrile-0.2% phosphoric acid(35∶65) at the flow rate 1.0 mL•min ⁻¹. The detection wavelength was 350 nm and the column temperature was 25 ℃. The results showed that the amount of eupatilin and jaceosidin had a clear linear relationship in the range of 0.003-0.126 g•L ⁻¹ (r=0.999 9) and 0.005-0.200 g•L ⁻¹ (r=0.999 9), and the average recovery rates for them were 99.14% (n=6, RSD 1.2%) and 99.40% (n=6, RSD=0.73%), respectively. The results showed that RP-HPLC can be used for the quantification of eupatilin and jaceosidin in the folium of A. argyi. With this method, we found there was no significant difference of jaceosidin content within all the samples collected, but the content of eupatilin was significantly higher in samples from Qichun, Ningbo, Xiangyang and Nanyang, located in the south of Huaihe River compared with these from other areas.


