Morinda officinalis
Morinda officinalis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
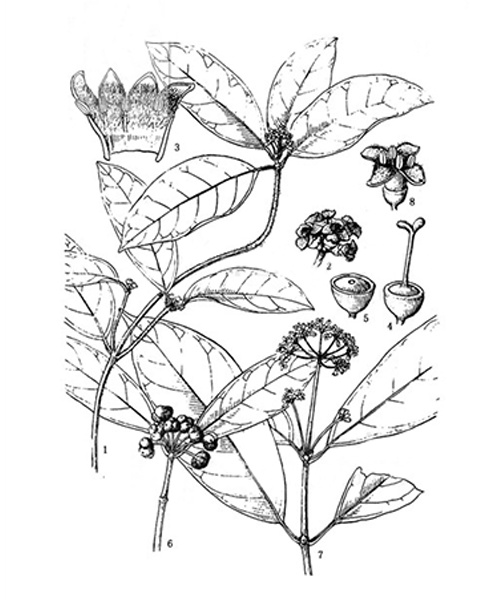
Natural products/compounds from Morinda officinalis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
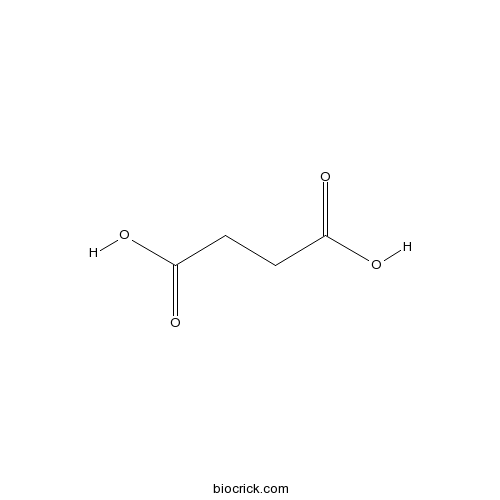
BCN5890
Succinic acid110-15-6
Instructions
-
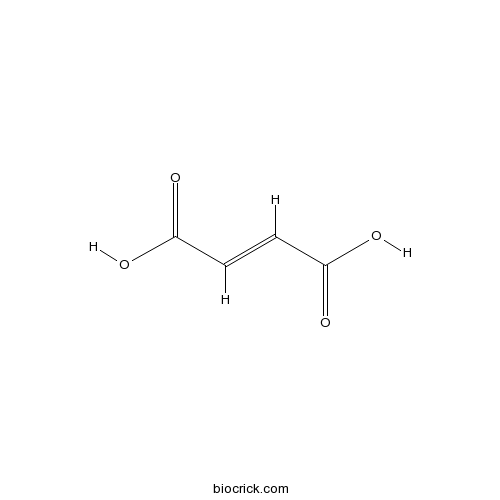
BCN5989
Fumaric acid110-17-8
Instructions
-
BCN6047
Rubiadin117-02-2
Instructions

-
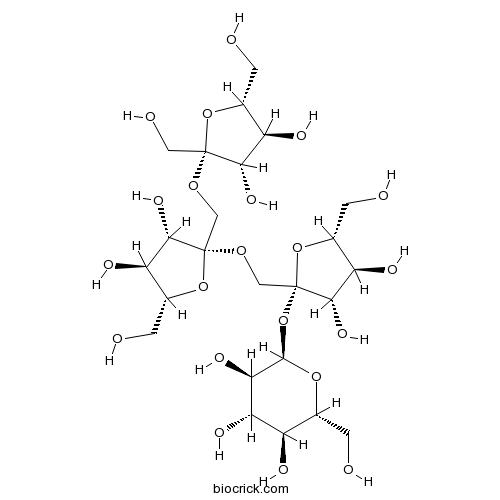
BCN5397
Nystose13133-07-8
Instructions
-
BCN6231
Asperuloside14259-45-1
Instructions
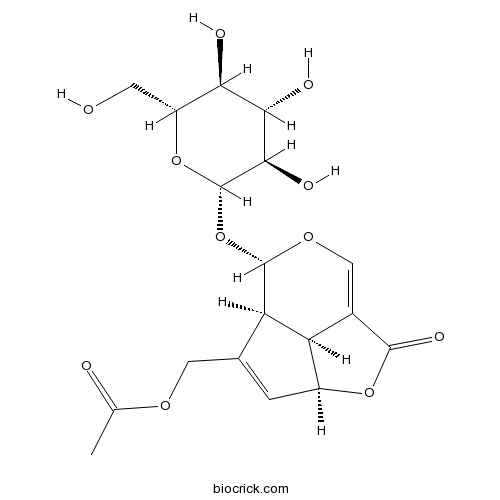
-
BCN3323
Deacetylasperulosidic acid14259-55-3
Instructions
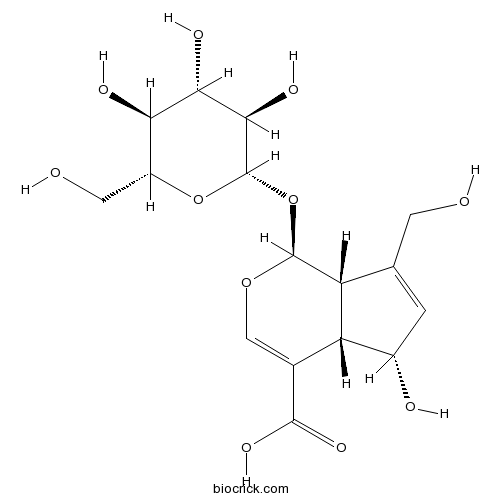
-
BCN3088
Asperulosidic acid25368-11-0
Instructions
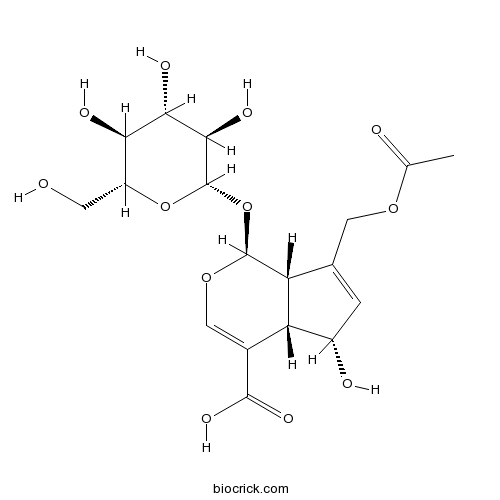
-
BCN8292
1-Kestose470-69-9
Instructions

-
BCN2327
Isofraxidin486-21-5
Instructions
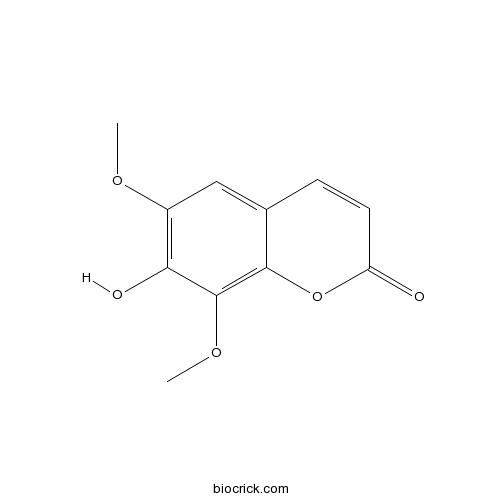
-
BCN5663
Physcion521-61-9
Instructions

-
BCN6280
Monotropein5945-50-6
Instructions
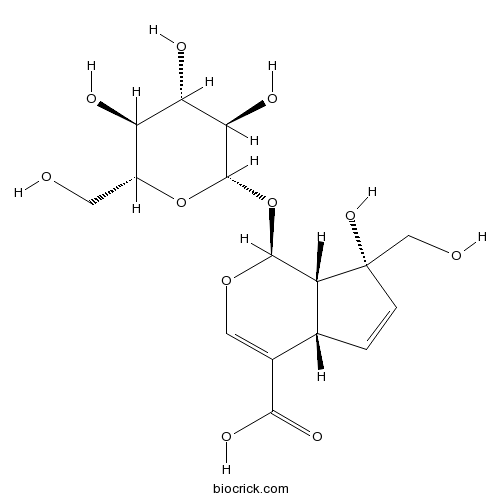
-
BCN3091
2-Hydroxy-1-methoxyanthraquinone6170-06-5
Instructions

-
BCN3478
1-Hydroxy-2-methylanthraquinone6268-09-3
Instructions
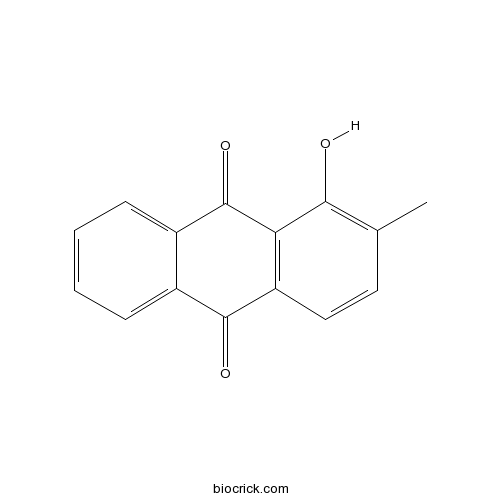
-
BCN4298
Rubiadin 1-methyl ether7460-43-7
Instructions

[Rapidly identify oligosaccharides in Morinda officinalis by UPLC-Q-TOF-MSE].[Pubmed: 29676129]
In this paper, an approach was applied for separation and identification of oligosaccharides in Morinda officinalis How by Ultra performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS) with collision energy. The separation was carried out on an ACQUITY UPLC BEH Amide C₁₈(2.1mm×100 mm,1.7 μm) with gradient elution using acetonitrile(A) and water(B) containing 0.1% ammonia as mobile phase at a flow rate of 0.2 mL·min⁻¹. The column temperature was maintained at 40 °C. The information of accurate mass and characteristic fragment ion were acquired by MSE in ESI negative mode in low and high collision energy. The chemical structures and formula of oligosaccharides were obtained and identified by the software of UNIFI and Masslynx 4.1 based on the accurate mass, fragment ions, neutral losses, mass error, reference substance, isotope information, the intensity of fragments, and retention time. A total of 19 inulin oligosaccharide structures were identified including D(+)-sucrose, 1-kestose, nystose, 1F-fructofuranosyl nystose and other inulin oligosaccharides (DP 5-18). This research provided important information about the inulin oligosaccharides in M. officinalis. The results would provide scientific basis for innovative utilization of M. officinalis.
Protective effect of MOTILIPERM in varicocele-induced oxidative injury in rat testis by activating phosphorylated inositol requiring kinase 1α (p-IRE1α) and phosphorylated c-Jun N-terminal kinase (p-JNK) pathways.[Pubmed: 29316840]
MOTILIPERM was prepared as a mixture of extracts of three medicinal herbs [roots of Morinda officinalis How (Rubiaceae), outer scales of Allium cepa L. (Liliaceae) and seeds of Cuscuta chinensis Lamark (Convolvulaceae)].
Bioassay-Guided Isolated Compounds from Morinda officinalis Inhibit Alzheimer's Disease Pathologies.[Pubmed: 28961196]
None


