cGMP Dependent Kinase Inhibitor PeptideInhibitor of protein kinases G and A CAS# 82801-73-8 |
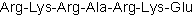
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 82801-73-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 134097 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C38H74N18O10 | M.Wt | 943.12 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | [Ala<sup>32</sup>]H2B(29-35) | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Sequence | RKRARKE | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-[[(2S)-6-amino-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-6-amino-2-[[(2S)-2-amino-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoyl]amino]hexanoyl]amino]-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoyl]amino]hexanoyl]amino]pentanedioic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(C(=O)NC(CCCN=C(N)N)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(CCC(=O)O)C(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CCCN=C(N)N)NC(=O)C(CCCCN)NC(=O)C(CCCN=C(N)N)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OUKSKNTVYYVIMZ-DUJSLOSMSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C38H74N18O10/c1-21(29(59)52-26(13-8-20-50-38(46)47)33(63)54-24(11-3-5-17-40)34(64)56-27(35(65)66)14-15-28(57)58)51-31(61)25(12-7-19-49-37(44)45)55-32(62)23(10-2-4-16-39)53-30(60)22(41)9-6-18-48-36(42)43/h21-27H,2-20,39-41H2,1H3,(H,51,61)(H,52,59)(H,53,60)(H,54,63)(H,55,62)(H,56,64)(H,57,58)(H,65,66)(H4,42,43,48)(H4,44,45,49)(H4,46,47,50)/t21-,22-,23-,24-,25-,26-,27-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Competitive inhibitor of cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG); analog of a substrate peptide corresponding to a phosphorylation site of histone H2B. Competes with synthetic substrates (Ki = 86 mM) but does not inhibit phosphorylation of intact histones by PKG. Inhibits phosphorylation of intact histones by PKA. |

cGMP Dependent Kinase Inhibitor Peptide Dilution Calculator

cGMP Dependent Kinase Inhibitor Peptide Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- H-D-HoPhe-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3239
CAS No.:82795-51-5
- Nefazodone hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7479
CAS No.:82752-99-6
- DCPIB
Catalog No.:BCC7105
CAS No.:82749-70-0
- 6,7-Dihydroxy-4-(Trifluoromethyl)Coumarin
Catalog No.:BCC8286
CAS No.:82747-36-2
- Perforatumone
Catalog No.:BCN4370
CAS No.:827319-50-6
- Danusertib (PHA-739358)
Catalog No.:BCC2172
CAS No.:827318-97-8
- Palbociclib (PD0332991) Isethionate
Catalog No.:BCC3698
CAS No.:827022-33-3
- PD 0332991 (Palbociclib) HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3680
CAS No.:827022-32-2
- Boc-Tryptophanol
Catalog No.:BCC2700
CAS No.:82689-19-8
- Picrasidine A
Catalog No.:BCN4369
CAS No.:82652-20-8
- Raloxifene HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4488
CAS No.:82640-04-8
- Zolpidem
Catalog No.:BCC9194
CAS No.:82626-48-0
- Perindopril
Catalog No.:BCC4223
CAS No.:82834-16-0
- Pingpeimine A
Catalog No.:BCN8407
CAS No.:82841-67-6
- Pingpeimine B
Catalog No.:BCN8408
CAS No.:82851-52-3
- Echinacoside
Catalog No.:BCN4953
CAS No.:82854-37-3
- Cyclo(Tyr-Leu)
Catalog No.:BCN2432
CAS No.:82863-65-8
- 2,3-Dihydroisoginkgetin
Catalog No.:BCN4035
CAS No.:828923-27-9
- (R)-(+)-Etomoxir sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7946
CAS No.:828934-41-4
- 3-Oxo-24,25,26,27-tetranortirucall-7-en-23,21-olide
Catalog No.:BCN1338
CAS No.:828935-47-3
- Fmoc-Osu
Catalog No.:BCC2804
CAS No.:82911-69-1
- 7,4'-Dihydroxy-8-methylflavan
Catalog No.:BCN6841
CAS No.:82925-55-1
- CI 898 trihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7248
CAS No.:82952-64-5
- Nafamostat Mesylate(FUT-175)
Catalog No.:BCC1228
CAS No.:82956-11-4
Synthetic peptide analogues differentially alter the binding affinities of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinases for nucleotide substrates.[Pubmed:2837278]
Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):1988-94.
Analogues of a synthetic heptapeptide substrate corresponding to the sequence around a phosphorylation site in histone H2B [Glass, D. B. & Krebs, E. G. (1982) J. Biol. Chem. 257, 1196-1200] were used to assess interactions between the peptide substrate and the ATP binding sites of cGMP-dependent protein kinase and the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. The affinity of each protein kinase for lin-benzo-ADP was determined in the absence and presence of substrate peptide by fluorescence anisotropy titrations [Bhatnagar, D., Roskoski, R., Jr., Rosendahl, M. S., & Leonard, N. J. (1983) Biochemistry 22, 6310-6317]. The Kd values of cGMP-dependent protein kinase for lin-benzo-ADP in the absence and presence of cGMP were 7.6 and 9.7 microM, respectively. Histone H2B(29-35) (Arg-Lys-Arg-Ser-Arg-Lys-Glu) had no effect on nucleotide affinity in either the absence or presence of cGMP. However, when lysine-34 located two residues after the phosphorylatable serine is replaced with an alanyl residue, the resulting [Ala34]histone H2B(29-35) and its analogue peptides interact with cGMP-dependent protein kinase and/or the nucleotide in a fashion that decreases nucleotide binding affinity approximately 3-fold. This amino acid replacement had previously been shown to cause an increase in Vmax and a decrease in the pH optimum for the phosphotransferase reaction. Replacement of positively charged residues at positions 30 and 31 of the peptide also decreased nucleotide affinity. Other analogues of histone H2B(29-35) failed to affect binding of lin-benzo-ADP to the active site of the cGMP-dependent enzyme.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Differential and common recognition of the catalytic sites of the cGMP-dependent and cAMP-dependent protein kinases by inhibitory peptides derived from the heat-stable inhibitor protein.[Pubmed:3017964]
J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12166-71.
Synthetic peptides corresponding to the active domain of the heat-stable inhibitor protein of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (Cheng, H.-C., Kemp, B. E., Pearson, R. B., Smith, A. J., Misconi, L., Van Patten, S. M., and Walsh, D. A. (1986) J. Biol. Chem. 261, 989-992) were tested as inhibitors of cGMP-dependent protein kinase. The peptides themselves were not substrates. cGMP-dependent protein kinase activity was assayed using histone H2B and two synthetic peptide substrates. Consistent with previous observations of other peptide inhibitors of this enzyme (Glass, D. B. (1983) Biochem. J. 213, 159-164), the inhibitory peptides had no effect on the phosphorylation of histone H2B, but they competitively inhibited cGMP-dependent phosphorylation of the two peptide substrates. The parent inhibitor peptide, PKI(5-24)amide, and a series of analogs had Ki (or IC50) values for cGMP-dependent protein kinase in the range of 15-190 microM. In contrast to their effects on the cAMP-dependent protein kinase, the inhibitory peptides were substantially less potent with cGMP-dependent protein kinase, and potency was reduced by the presence of the NH2-terminal residues (residues 5-13). We conclude that the two protein kinases share a recognition of the basic amino acid cluster within the pseudosubstrate region of the peptide, but that the cGMP-dependent protein kinase does not recognize additional NH2-terminal determinants that make the inhibitor protein extremely potent toward the cAMP-dependent enzyme. Even- when tested at high concentrations and with peptide substrates, the native inhibitor protein did not inhibit cGMP-dependent protein kinase under assay conditions in which the peptides derived from it were inhibitory. Thus, the native inhibitor protein appears to have structural features which block interaction with the cGMP-dependent enzyme and enhance its selectivity for cAMP-dependent protein kinase.
Differential responses of cyclic GMP-dependent and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases to synthetic peptide inhibitors.[Pubmed:6615418]
Biochem J. 1983 Jul 1;213(1):159-64.
The peptide Arg-Lys-Arg-Ala-Arg-Lys-Glu was synthesized and tested as an inhibitor of cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase. This synthetic peptide is a non-phosphorylatable analogue of a substrate peptide corresponding to a phosphorylation site (serine-32) in histone H2B. The peptide was a competitive inhibitor of cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase with respect to synthetic peptide substrates, with a Ki value of 86 microM. However, it did not inhibit phosphorylation of intact histones by cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase under any conditions tested. Arg-Lys-Arg-Ala-Arg-Lys-Glu competitively inhibited the phosphorylation of either peptides or histones by the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, with similar Ki values (550 microM) for both of these substrates. The peptide Leu-Arg-Arg-Ala-Ala-Leu-Gly, which was previously reported to be a selective inhibitor of both peptide and histone phosphorylation by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, was a poor inhibitor of cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase acting on peptide substrates (Ki = 800 microM), but did not inhibit phosphorylation of histones by cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase. The selectivity of these synthetic peptide inhibitors toward either cyclic GMP-dependent or cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases is probably based on differences in the determinants of substrate specificity recognized by these two enzymes. It is concluded that histones interact differently with cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase from the way they do with the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase.


