(R)-(+)-Bay K 8644Ca2+-channel blocker (L-type) CAS# 98791-67-4 |
- Anguizole
Catalog No.:BCC1365
CAS No.:442666-98-0
- Asunaprevir (BMS-650032)
Catalog No.:BCC1374
CAS No.:630420-16-5
- Balapiravir
Catalog No.:BCC1396
CAS No.:690270-29-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 98791-67-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6604881 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H15F3N2O4 | M.Wt | 356.3 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | (R)-(+)-Bay-K-8644; R-4407; NI-105; (+)-BAY-K-8644 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 300 mg/mL (841.99 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
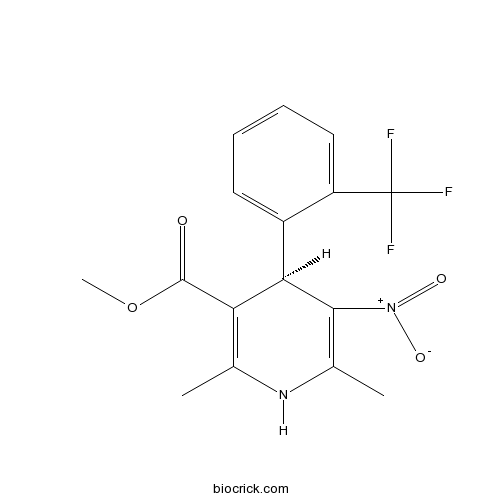
| Chemical Name | methyl (4R)-2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-4-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(C(=C(N1)C)[N+](=O)[O-])C2=CC=CC=C2C(F)(F)F)C(=O)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZFLWDHHVRRZMEI-CYBMUJFWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H15F3N2O4/c1-8-12(15(22)25-3)13(14(21(23)24)9(2)20-8)10-6-4-5-7-11(10)16(17,18)19/h4-7,13,20H,1-3H3/t13-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | L-type Ca2+-channel blocker with negative inotropic and vasodilatatory effects in vivo. Enantiomer showing opposite effects to the racemate (±)-Bay K 8644 and (S)-(-)- enantiomer. |

(R)-(+)-Bay K 8644 Dilution Calculator

(R)-(+)-Bay K 8644 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8066 mL | 14.0331 mL | 28.0662 mL | 56.1325 mL | 70.1656 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5613 mL | 2.8066 mL | 5.6132 mL | 11.2265 mL | 14.0331 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2807 mL | 1.4033 mL | 2.8066 mL | 5.6132 mL | 7.0166 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0561 mL | 0.2807 mL | 0.5613 mL | 1.1226 mL | 1.4033 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0281 mL | 0.1403 mL | 0.2807 mL | 0.5613 mL | 0.7017 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Bay-K-8644 (R)-(+)- is a calcium channel inhibitor. Bay-K-8644 (R)-(+)- inhibits Ba2+ currents (IBa) (IC50=975 nM).
In Vitro:(±)-Bay K 8644, a conventional racemic mixture of Bay K 8644, is widely used as an L-type Ca2+ channel agonist. Each optical isomer possesses opposite effects on IBa, Bay-K-8644 (R)-(+)- as an antagonist and S(-)-Bay K 8644 as an agonist. Bay-K-8644 (R)-(+)- inhibits Ba2+ currents (IBa) (IC50=975 nM). When Bay-K-8644 (R)-(+)- (0.5 μM) is applied, IBa is suppressed to 71±10% of control. In the presence of Bay-K-8644 (R)-(+)- (0.5 μM), additional application of forskolin and sodium nitroprusside (SNP) further inhibits IBa[1]. Bay-K-8644 (R)-(+)- is a calcium channel inhibitor[2].
References:
[1]. Zhu HL, et al. Antagonistic actions of S(-)-Bay K 8644 on cyclic nucleotide-induced inhibition of voltage-dependent Ba(2+) currents in guinea pig gastric antrum. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008 Dec;378(6):609-15.
[2]. Sidaway P, et al. L-type Ca2+ channel sparklets revealed by TIRF microscopy in mouse urinary bladder smooth muscle. PLoS One. 2014 Apr 3;9(4):e93803.
- 3-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)propyl tetracosanoate
Catalog No.:BCN1292
CAS No.:98770-70-8
- Reboxetine mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC4934
CAS No.:98769-84-7
- Isothymusin
Catalog No.:BCN4532
CAS No.:98755-25-0
- Latifoline N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN1979
CAS No.:98752-06-8
- Paeonilactone A
Catalog No.:BCN3967
CAS No.:98751-79-2
- Paeonilactone B
Catalog No.:BCN3963
CAS No.:98751-78-1
- Paeonilactone C
Catalog No.:BCN3964
CAS No.:98751-77-0
- Ropivacaine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4841
CAS No.:98717-15-8
- ATP disodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC5160
CAS No.:987-65-5
- Dregeoside Ga1
Catalog No.:BCN4548
CAS No.:98665-66-8
- Dregeoside Da1
Catalog No.:BCN4764
CAS No.:98665-65-7
- Ganoderic acid G
Catalog No.:BCN2915
CAS No.:98665-22-6
- FLAG tag Peptide
Catalog No.:BCC2562
CAS No.:98849-88-8
- Danshenxinkun D
Catalog No.:BCN2472
CAS No.:98873-76-8
- Pseudolaric acid B-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1291
CAS No.:98891-41-9
- Pseudolaric acid A-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1290
CAS No.:98891-44-2
- 3-Epiursolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3173
CAS No.:989-30-0
- (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate
Catalog No.:BCN6326
CAS No.:989-51-5
- Limonol
Catalog No.:BCN4533
CAS No.:989-61-7
- Fmoc-His(Fmoc)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3500
CAS No.:98929-98-7
- Fmoc-Arg(Mtr)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3074
CAS No.:98930-01-9
- 3,5-DHBA
Catalog No.:BCC7951
CAS No.:99-10-5
- Ac-DL-Leu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2977
CAS No.:99-15-0
- Prunasin
Catalog No.:BCN4535
CAS No.:99-18-3
Effects of nifedipine and Bay K 8644 on the R-PIA and caffeine-induced changes in the locomotor activity of rats.[Pubmed:8870030]
Pharmacol Res. 1996 Feb;33(2):141-4.
Possible interaction between adenosine and L type Ca2+ channel in the locomotor activity of rats was investigated. R-PIA (0.05 mg kg-1), an adenosine analogue, and caffeine (20 mg kg-1), an adenosine receptor antagonist, significantly decreased and increased locomotor activity, respectively. Ca2+ channel blocker nifedipine (5 mg kg-1) and the channel activator Bay K 8644 (0.5 mg kg-1) did not alter the locomotor activity. However, both drugs significantly potentiated the inhibitory effect of R-PIA on the locomotor activity. Additionally, caffeine induced increase in the locomotor activity was significantly blocked by nifedipine and Bay K 8644. This interaction might be due to the inhibitory effects of nifedipine and Bay K 8644 on the uptake of adenosine by rat brain.
Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic fibroblasts by Oct4 and Klf4 with small-molecule compounds.[Pubmed:18983970]
Cell Stem Cell. 2008 Nov 6;3(5):568-74.
Somatic cells can be induced into pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) with a combination of four transcription factors, Oct4/Sox2/Klf4/c-Myc or Oct4/Sox2/Nanog/LIN28. This provides an enabling platform to obtain patient-specific cells for various therapeutic and research applications. However, several problems remain for this approach to be therapeutically relevant due to drawbacks associated with efficiency and viral genome integration. Recently, it was shown that neural progenitor cells (NPCs) transduced with Oct4/Klf4 can be reprogrammed into iPSCs. However, NPCs express Sox2 endogenously, possibly facilitating reprogramming in the absence of exogenous Sox2. In this study, we identified a small-molecule combination, BIX-01294 and BayK8644, that enables reprogramming of Oct4/Klf4-transduced mouse embryonic fibroblasts, which do not endogenously express the factors essential for reprogramming. This study demonstrates that small molecules identified through a phenotypic screen can compensate for viral transduction of critical factors, such as Sox2, and improve reprogramming efficiency.
Opposite cardiac actions of the enantiomers of Bay K 8644 at different membrane potentials in guinea-pig papillary muscles.[Pubmed:1692975]
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;341(3):232-9.
The influence of membrane potential on the effects of the enantiomers and the racemate of Bay K 8644 [1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluor-methylphenyl)-p yri dine-5-carboxylate] on force of contraction and on action potentials were studied in guinea-pig papillary muscles in order to detect possible changes in the direction of drug action or in potency. Membrane potential was varied by changing the potassium concentration ([K+]o) in the bathing solution. At normal resting potential, (-)-Bay K 8644 enhanced force of contraction and prolonged the action potential duration measured at 50% of repolarization (APD) to the same extent as the racemate and with similar pD2 values. After membrane depolarization by raising [K+]o from 5.4 to 17.4 mmol/l, the (-)-enantiomer and the racemate prolonged the APD to a similar degree but enhanced force to a lesser extent. The maximum rate of depolarization of slow action potentials, Vmax, was increased at the highest concentrations (10(-5) mol/l). The effects of (+)-Bay K 8644 were more complicated. At high concentrations (10(-5) mol/l) it decreased force of contraction and APD, the pD2 values were one order of magnitude lower than for the (-)-enantiomer and the racemate. A high concentration (+)-Bay K 8644 (10(-5) mol/l) virtually abolished contractile activity at all membrane potentials, the extent of shortening in APD increased with membrane depolarization in elevated [K+]o. Vmax of slow action potentials was decreased.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Enantiomer selectivity and the development of tolerance to the behavioral effects of the calcium channel activator BAY K 8644.[Pubmed:2465070]
Brain Res Bull. 1988 Dec;21(6):865-72.
The putative behavioral effects of the enantiomers of BAY K 8644 and the behavioral responses to (+/-)-BAY K 8644 following chronic injection were assessed on motor function in mice. The interaction of the enantiomers of BAY K 8644 with mouse brain dihydropyridine binding sites was also evaluated. The calcium channel activating enantiomer (-)-S-BAY K 8644 impaired rotarod and motor activity with an ED50 value of 0.5 mg/kg. The calcium channel blocker enantiomer (+)-R-BAY K 8644 neither affected rotarod nor motor activity. (+)-R-BAY K 8644, and the structurally related dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers nifedipine and (-)-202-791 inhibited the impairment of rotarod activity by (-)-S-BAY K 8644 in a dose-dependent manner. (+/-)-BAY K 8644 produced convulsions in mice with a CD50 of 5 mg/kg. Chronic injection of (+/-)-BAY K 8644 (8 mg/kg IP once each day for four days) resulted in a significant tolerance to, and increase in recovery from, the motor deficits produced by (+/-)-BAY K 8644. Furthermore, chronic treatment with (+/-)-BAY K 8644 increased the onset time, but did not reduce the number of mice having convulsions to (+/-)-BAY K 8644. Chronic injection of nifedipine did not affect the motor deficit and convulsive activity of (+/-)-BAY K 8644. The behavioral effects of (+/-)-BAY K 8644 were observed at significant brain levels of drug. [3H]Nitrendipine binding to mouse brain dihydropyridine binding sites was unchanged in mice chronically injected with either (+/-)-BAY K 8644 or nifedipine.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
The optical isomers of the 1,4-dihydropyridine BAY K 8644 show opposite effects on Ca channels.[Pubmed:2412855]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Aug 15;114(2):223-6.
The optical isomers of the 1,4-dihydropyridine BAY K 8644 were studied in isolated rabbit aorta and heart preparations. The (-)-enantiomer has the known vasoconstricting and positive inotropic properties of the Ca agonistic compound. In contrast, its antipode shows at about 10-50 times higher concentrations the vasodilating and negative inotropic effects of Ca antagonistic drugs. It is concluded that neither simple chemical nor physical actions can be responsible for the opposite effects of Ca antagonistic and Ca agonistic dihydropyridines.


