7-HydroxycadaleneCAS# 2102-75-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 2102-75-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 608115 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H18O | M.Wt | 214.30 |
| Type of Compound | Sesquiterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
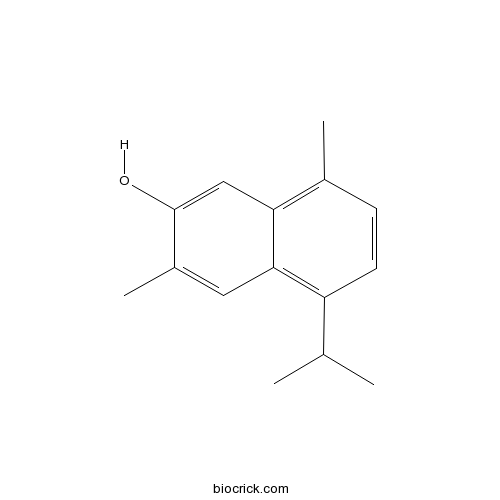
| Chemical Name | 3,8-dimethyl-5-propan-2-ylnaphthalen-2-ol | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C2C=C(C(=CC2=C(C=C1)C(C)C)C)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RIWNMJBJRPCUBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H18O/c1-9(2)12-6-5-10(3)13-8-15(16)11(4)7-14(12)13/h5-9,16H,1-4H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. 7-Hydroxycadalene shows cytotoxicity activity against HCT-15 cell line with IC50 18.89 ± 1.2 uM. |
| Targets | 5-HT Receptor |

7-Hydroxycadalene Dilution Calculator

7-Hydroxycadalene Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.6664 mL | 23.3318 mL | 46.6636 mL | 93.3271 mL | 116.6589 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9333 mL | 4.6664 mL | 9.3327 mL | 18.6654 mL | 23.3318 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4666 mL | 2.3332 mL | 4.6664 mL | 9.3327 mL | 11.6659 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0933 mL | 0.4666 mL | 0.9333 mL | 1.8665 mL | 2.3332 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0467 mL | 0.2333 mL | 0.4666 mL | 0.9333 mL | 1.1666 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 6-Formyl-1,2,9,10-tetramethoxy-6a,7-dehydroaporphine
Catalog No.:BCN6436
CAS No.:2101836-45-5
- Amarogentin
Catalog No.:BCN2661
CAS No.:21018-84-8
- Miglustat hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5186
CAS No.:210110-90-0
- 5,8,9,10,14-Pentaacetoxy-3-benzoyloxy-15-hydroxypepluane
Catalog No.:BCN1498
CAS No.:210108-91-1
- Jatrophane VI
Catalog No.:BCN7659
CAS No.:210108-90-0
- Jatrophane 5
Catalog No.:BCN1499
CAS No.:210108-89-7
- Jatrophane 4
Catalog No.:BCN1500
CAS No.:210108-88-6
- Jatrophane 3
Catalog No.:BCN1501
CAS No.:210108-87-5
- Jatrophane 2
Catalog No.:BCN1502
CAS No.:210108-86-4
- Jatrophane I
Catalog No.:BCN7658
CAS No.:210108-85-3
- Nilgirine
Catalog No.:BCN2100
CAS No.:21009-05-2
- Erythbidin A
Catalog No.:BCN6859
CAS No.:210050-83-2
- Gallein
Catalog No.:BCC7563
CAS No.:2103-64-2
- Z-DEVD-FMK
Catalog No.:BCC1137
CAS No.:210344-95-9
- Z-IETD-FMK
Catalog No.:BCC5116
CAS No.:210344-98-2
- Z-WEHD-FMK
Catalog No.:BCC1139
CAS No.:210345-00-9
- Ac-LEHD-AFC
Catalog No.:BCC2359
CAS No.:210345-03-2
- Z-LEHD-FMK
Catalog No.:BCC5117
CAS No.:210345-04-3
- Cinnamyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN4914
CAS No.:21040-45-9
- Spiradine F
Catalog No.:BCN4915
CAS No.:21040-64-2
- Odoratin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN8089
CAS No.:210413-47-1
- Sitaxentan sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4495
CAS No.:210421-74-2
- 1,11b-Dihydro-11b-hydroxymedicarpin
Catalog No.:BCN3913
CAS No.:210537-04-5
- 1,11b-Dihydro-11b-hydroxymaackiain
Catalog No.:BCN3914
CAS No.:210537-05-6
Toxicological evaluation of the natural products and some semisynthetic derivatives of Heterotheca inuloides Cass (Asteraceae).[Pubmed:26344038]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 4;175:256-65.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Heterotheca ineuloides Cass (Asteraceae), popularly known as arnica mexicana, is widely used in Mexican traditional medicine to treat bruises, dermatological problems, rheumatic pains, and other disorders as cancer. The major constituents in H. inuloides are cadinane type sesquiterpenes, flavonoids and phytosterols. Compounds with a cadinane skeleton have been proved to possess cytotoxic activity against human-tumor cell lines and brine shrimp, and display toxic effects in different animal species. Although this plant has been widely used, there is little available information on the safety and toxicity especially of pure compounds. AIM OF THIS STUDY: Evaluate the potential toxicity of the natural products isolated from H. inuloides and some semisynthetic derivatives. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The toxic aspects of the following natural products isolated from dried flowers of H. inuloides: 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydrocadalene (1), 7-Hydroxycadalene (2), 3,7-dihydroxy-3(4H)-isocadalen-4-one (3), (1R,4R)-1-hydroxy-4H-1,2,3,4- tetrahydrocadalen-15-oic acid (4), D-chiro-inositol (5), quercetin (6), quercetin-3,7,3'-trimethyl ether (7), quercetin-3,7,3',4'-tetramethyl ether (8), eriodictyol-7,4'-dimethyl ether (9), alpha-spinasterol (10), caryolan-1,9beta-diol (11) and 7-(3,3-dimethylallyloxy)-coumarin (12) as well as the toxic aspects of the semisynthetic compounds 7-acetoxy-3,4-dihydrocadalene (13), 7-benzoxy-3,4-dihydrocadalene (14), 7-acetoxycadalene (15), 7-benzoxycadalene (16), quercetin pentaacetate (17), 7-hydroxycalamenene (18), 3,8-dimethyl-5-(1-methylethyl)-1,2-naphthoquinone (19), and 4-isopropyl-1,6-dimethylbenzo[c]oxepine-7,9-dione (20). Toxic activities of compounds were determined by sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay, Artemia salina assay, RAW264.7 macrophage cells. Additionally, the acute toxicity in mouse of compound 1, the major natural sesquiterpene isolated from the acetone extract, was evaluated. RESULTS: The best cytotoxicity activity was observed for mansonone C (19) on K562 cell line with IC50 1.45 +/- 0.14 muM, for 7-Hydroxycadalene (2) on HCT-15 cell line with IC50 18.89 +/- 1.2 muM, and for quercetin pentaacetate (17) on MCF-7 cell line with IC50 22.57 +/- 2.4 muM. Sesquiterpenes mansonone C (19) and 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydrocadalene (1) caused the strongest deleterious effects against A. salina with IC50 39.4 +/- 1.07, and 45.47 +/- 1.74 muM, respectively. The number of viable RAW 264.7 cells was reduced with sesquiterpenes 1 and 2 by more than 90%. In addition, the acute study of 1 revealed no lethal effects at 300 mg/kg body weight, however, a reduction in the body weight of mice, morphological changes in the tissues of the liver and kidney and toxic signs were observed at very high doses (2000 mg/kg). CONCLUSION: The results provided evidence for the cytotoxicity of Mexican arnica (H. inuloides) metabolites and may be correlated with one of the popular uses of this plant, in traditional Mexican medicine, as anticancer remedy. Among the active compounds contained in the acetone extract, the cytotoxic activity is mainly ascribable to cadinene type sesquiterpenes. In addition, evidence of acute toxicity suggests that 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydrocadalene (1) may lead to toxicity at very high doses.
Antinociceptive effect of 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydrocadalin isolated from Heterotheca inuloides: role of peripheral 5-HT(1) serotonergic receptors.[Pubmed:20863828]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2010 Dec 15;649(1-3):154-60.
The purpose of this study was to investigate the possible antinociceptive effect of Heterotheca inuloides in inflammatory pain and to identify the main compounds involved in this effect. Dose-response curves were obtained for hexane, dichlorometane, ethyl acetate and methanol extracts from Heterotheca inuloides inflorescences in the formalin test. Hexane extract was more potent and effective than other extracts. Bio-guided fractionation was performed to determine the main antinociceptive compounds of the plant. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry technique demonstrated the composition of the most active fraction from hexane extract revealing the presence of caryophyllene oxide, cedrene, 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydrocadalin, 7-Hydroxycadalene and a compound not identified. The isolated compounds were individually evaluated in the formalin test in a preliminary dose of 100 mug/paw and only 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydrocadalin showed a significant antinociceptive effect. Dose-response curves were then obtained for 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydrocadalin and diclofenac, a prototypical analgesic drug. Both drugs were equieffective and equipotent in the second phase of the formalin test, but 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydrocadalin was more effective and potent in the first phase than diclofenac. In addition, 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydrocadalin reduced carrageenan-induced mechanical hyperalgesia and inflammation in a dose-dependent manner. Finally, in mechanistic studies, the antinociceptive effect of 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydrocadalin in the formalin test was prevented by methiothepin, WAY100635, SB224289 and BRL15572 but not by naltrexone. Results support the use of H. inuloides inflorescences as analgesic in the Mexican traditional medicine. Moreover, data indicate that 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydrocadalin is partly responsible of this pharmacological activity, and suggest that 5-HT(1A), 5-HT(1B), and 5-HT(1D) serotonergic, but not opioid, receptors participate in the antinociceptive effect of this drug.


