AM 92016 hydrochloridePotassium channel blocker CAS# 133229-11-5 |
- MLN2238
Catalog No.:BCC2092
CAS No.:1072833-77-2
- MG-115
Catalog No.:BCC1237
CAS No.:133407-86-0
- Salinosporamide A (NPI-0052, Marizomib)
Catalog No.:BCC2094
CAS No.:437742-34-2
- Gliotoxin
Catalog No.:BCN3894
CAS No.:67-99-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 133229-11-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 45073415 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H25Cl3N2O4S | M.Wt | 483.84 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 260 mg/mL (537.37 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
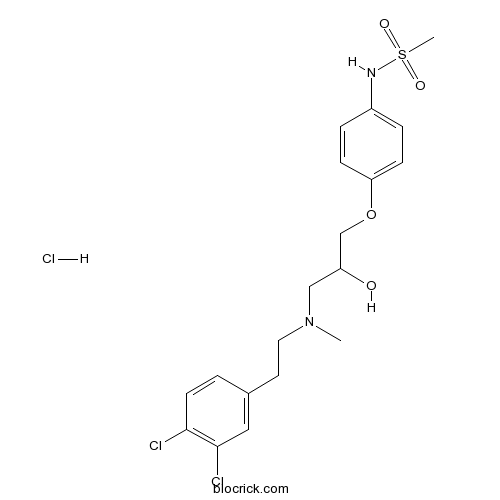
| Chemical Name | N-[4-[3-[2-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl-methylamino]-2-hydroxypropoxy]phenyl]methanesulfonamide;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CN(CCC1=CC(=C(C=C1)Cl)Cl)CC(COC2=CC=C(C=C2)NS(=O)(=O)C)O.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | TXOARFPCQOBODS-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H24Cl2N2O4S.ClH/c1-23(10-9-14-3-8-18(20)19(21)11-14)12-16(24)13-27-17-6-4-15(5-7-17)22-28(2,25)26;/h3-8,11,16,22,24H,9-10,12-13H2,1-2H3;1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | A specific blocker of the time dependent delayed rectifier potassium current, devoid of any β-adrenoceptor blocking activity. Exhibits proarrhythmic and prohypertensive activity in vivo. |

AM 92016 hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

AM 92016 hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0668 mL | 10.334 mL | 20.668 mL | 41.336 mL | 51.67 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4134 mL | 2.0668 mL | 4.1336 mL | 8.2672 mL | 10.334 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2067 mL | 1.0334 mL | 2.0668 mL | 4.1336 mL | 5.167 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0413 mL | 0.2067 mL | 0.4134 mL | 0.8267 mL | 1.0334 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0207 mL | 0.1033 mL | 0.2067 mL | 0.4134 mL | 0.5167 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
AM 92016 hydrochloride is a specific inhibitor of delayed rectifier potassium current [1].
Potassium channel is an ion channel and acts to reset the resting potential and shapes the action potential. Delayed rectifier potassium channel (IK) is activated by the influx of Na+ and discharges K+, which repolarizes the membrane. IK restricts the duration of the nerve impulse.
AM 92016 hydrochloride is a specific iK inhibitor. In guinea-pig and rabbit ventricular cells, AM 92016 significantly increased action potential duration with 20% and 90% repolarization levels, respectively. Also, AM 92016 (1 μM) inhibited IK activated by step depolarizations in a time-dependent way [1]. In rabbit sino-atrial node cells, AM 92016 (50 nM) significantly inhibited IK with IC50 value of 40 nM in a concentration-dependent way [2]. In vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC), AM92016 hydrochloride inhibited NO-induced ERK1/2 dephosphorylation [3].
In guinea-pigs, AM 92016 (1-5 mg/kg) significantly increased heart rate, left ventricular systolic pressure, systolic arterial blood pressure and the contractile index dp dtmax. AM 92016 exhibited proarrhythmic activity [4].
References:
[1]. Connors SP, Gill EW, Terrar DA. Actions and mechanisms of action of novel analogues of sotalol on guinea-pig and rabbit ventricular cells. Br J Pharmacol, 1992, 106(4): 958-965.
[2]. Lei M, Brown HF. Inhibition by Compound II, a sotalol analogue, of delayed rectifier current (iK) in rabbit isolated sino-atrial node cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 1998, 357(3): 260-267.
[3]. Palen DI, Belmadani S, Lucchesi PA, et al. Role of SHP-1, Kv.1.2, and cGMP in nitric oxide-induced ERK1/2 MAP kinase dephosphorylation in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res, 2005, 68(2): 268-277.
[4]. Hagerty MJ, Wainwright CL, Kane KA. The in-vivo cardiovascular effects of a putative class III anti-arrhythmic drug, AM 92016. J Pharm Pharmacol, 1996, 48(4): 417-421.
- PI3k-delta inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC1861
CAS No.:1332075-63-4
- Fmoc-Thr(Trt)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3554
CAS No.:133180-01-5
- Fmoc-Cit-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3180
CAS No.:133174-15-9
- Oxypeucedan hydrate
Catalog No.:BCN8372
CAS No.:133164-11-1
- GR 73632
Catalog No.:BCC5801
CAS No.:133156-06-6
- Epimedin B1
Catalog No.:BCN8199
CAS No.:133137-58-3
- Flutamide
Catalog No.:BCC4364
CAS No.:13311-84-7
- Darifenacin HBr
Catalog No.:BCC4567
CAS No.:133099-07-7
- Darifenacin
Catalog No.:BCC1516
CAS No.:133099-04-4
- 3PO
Catalog No.:BCC5616
CAS No.:13309-08-5
- Crassifoline methine
Catalog No.:BCN1793
CAS No.:133084-00-1
- Fmoc-D-Lys(Boc)-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3527
CAS No.:133083-36-0
- Heliangin
Catalog No.:BCN6487
CAS No.:13323-48-3
- 4-O-Methylbutein
Catalog No.:BCN6677
CAS No.:13323-67-6
- GSK2194069
Catalog No.:BCC8053
CAS No.:1332331-08-4
- KPT-185
Catalog No.:BCC4444
CAS No.:1333151-73-7
- TRPC6 inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC4199
CAS No.:1333207-63-8
- 10-Deacetylyunnanxane
Catalog No.:BCN7338
CAS No.:1333323-17-3
- Imbricataflavone A
Catalog No.:BCN8025
CAS No.:133336-96-6
- CHR-6494
Catalog No.:BCC1479
CAS No.:1333377-65-3
- Lactacystin
Catalog No.:BCN1841
CAS No.:133343-34-7
- Lydicamycin
Catalog No.:BCN1843
CAS No.:133352-27-9
- Daturataturin A
Catalog No.:BCN6179
CAS No.:133360-51-7
- DV 7028 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6202
CAS No.:133364-62-2
Role of SHP-1, Kv.1.2, and cGMP in nitric oxide-induced ERK1/2 MAP kinase dephosphorylation in rat vascular smooth muscle cells.[Pubmed:15967421]
Cardiovasc Res. 2005 Nov 1;68(2):268-77.
OBJECTIVE: Nitric oxide (NO) elicits relaxation in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) that is associated with guanylate cyclase (GC) and K(+) channel activation. In this study we determined the mechanisms that lead to ERK1/2 MAP kinase dephosphorylation in response to NO. METHODS: VSMC were treated with the NO donor SNAP or sodium nitroprusside (SNP), and ERK1/2, Src homology (SH) 1 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase (SHP-1), and Kv.1.2 phosphorylation were assessed by immunoprecipitation and Western blot analysis. RESULTS: NO decreased basal ERK1/2 phosphorylation in a dose- and time-dependent manner. NO-induced ERK1/2 dephosphorylation was detected at 1 min and sustained for 30 min. Pre-treatment with the GC inhibitor ODQ or the protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor I prevented ERK1/2 dephosphorylation induced by SNAP. The inhibition of protein phosphatase 1A/2A had no effect on ERK1/2 dephosphorylation induced by SNAP. Treatment with cromakalim A, a nonspecific K(+) channel activator, also induced ERK1/2 dephosphorylation, while blockade of Kv.1.2 K(+) channels (AM92016 hydrochloride) prevented NO-induced ERK1/2 dephosphorylation. In addition, SNAP induced SHP-1 phosphorylation, and the Kv.1.2 dephosphorylation increase and SHP-1 phosphorylation was blocked by ODQ or AM92016. The basal interaction between ERK1/2 and SHP-1 was decreased in response to SNAP stimulation. SHP-1 also interacted with Kv.1.2 under basal conditions and participates in Kv.1.2 activation. Using the mouse mesenteric resistance artery, we found that ERK1/2 MAP kinase is involved in regulation of myogenic tone. CONCLUSION: Thus, our study provides the first evidence that NO controls basal ERK1/2 phosphorylation by a signaling cascade that involves a dynamic signaling complex between cGMP, Kv.1.2 and SHP-1.
Inhibition by Compound II, a sotalol analogue, of delayed rectifier current (iK) in rabbit isolated sino-atrial node cells.[Pubmed:9550297]
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1998 Mar;357(3):260-7.
The effects of Compound II, a sotalol analogue, on spontaneous electrical activity and on three membrane currents (the delayed rectifier current, iK, the long-lasting inward calcium current, i(Ca,L) and hyperpolarization activated inward current, i(f)) were investigated in rabbit isolated sino-atrial node cells by whole cell clamp with amphotericin-permeabilised patches. A submaximal concentration of Compound II (50 nM) had a significant effect on the time and voltage dependent activation of iK and caused a positive shift of the iK activation curve. As well as blocking i(Kr), it caused some degree of block of i(Ks). Block of iK by Compound II was found to be concentration dependent with an IC50 of approximately 40 nM. 1 microM Compound II nearly completely blocked iK without significantly affecting the peak current or I/V relationships of i(Ca,L) or i(f). 50 nM Compound II caused a significant prolongation of APD100 and of cycle length. It also decreased diastolic depolarization rate without significantly affecting MDP and action potential amplitude. It is concluded that Compound II, a sotalol analogue, slows spontaneous activity of isolated rabbit SA node cells through a selective inhibition of iK.
The in-vivo cardiovascular effects of a putative class III anti-arrhythmic drug, AM 92016.[Pubmed:8794994]
J Pharm Pharmacol. 1996 Apr;48(4):417-21.
AM 92016 (1-(4-methanesulphonamidophenoxy)- 3-(N-methyl-3-4-dichlorophenethylamino)-2-propanol benzoic acid salt), an oxypropanolamine analogue of sotalol, has been shown to possess Class III anti-arrhythmic properties in-vitro at concentrations showing 1000 times more potency than sotalol. The aim of this study was to characterize the effects of AM 92016 in-vivo. When administered to anaesthetized guinea-pigs, AM 92016 (10 micrograms kg-1 -5 mg kg-1) significantly increased heart rate, systolic arterial blood pressure, left ventricular systolic pressure and the contractile index dp dtmax. AM 92016 also significantly decreased the QT interval of the electrocardiogram from 135 +/- 10 to 105 +/- 4 ms (5 mg kg-1). The time to onset of the first arrhythmia and ventricular fibrillation, induced by intravenous infusion of ouabain, was shortened in the presence of AM 92016. Ouabain-induced ventricular fibrillation occurred at 18 +/- 5 and 12 +/- 3 min (P < 0.05) in control and AM 92016-(1 mg kg-1) treated guinea-pigs, respectively. An infusion of AM 92016 (2.5 micrograms kg-1 min-1) to anaesthetized pigs significantly increased the total number of arrhythmias occurring following coronary artery occlusion from 266 +/- 26 in control pigs to 535 +/- 148 (P < 0.05) in those receiving AM 92016. The time to onset of ventricular fibrillation was also significantly reduced in anaesthetized pigs from 24 +/- 1 to 18 +/- 3 min in the presence of AM 92016. The drug did not change haemodynamics in the anaesthetized pig. We conclude that AM 92016 exhibited proarrhythmic rather than antiarrhythmic activity when administered in-vivo to either guinea-pigs or pigs.
Actions and mechanisms of action of novel analogues of sotalol on guinea-pig and rabbit ventricular cells.[Pubmed:1393293]
Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;106(4):958-65.
1. The actions and mechanisms of action of novel analogues of sotalol which prolong cardiac action potentials were investigated in guinea-pig and rabbit isolated ventricular cells. 2. In guinea-pig and rabbit cells the compounds significantly prolonged action potential duration at 20% and 90% repolarization levels without affecting resting membrane potential. In guinea-pig but not rabbit cells there was an increase in action potential amplitude and in rabbit cells there was no change in the shape or position of the 'notch' in the action potential. 3. Possible mechanisms of action were studied in more detail in the case of compound II (1-(4-methanesulphonamidophenoxy)-3-(N-methyl 3,4 dichlorophenylethylamino)-2-propanol). Prolongation of action potential duration continued to occur in the presence of nisoldipine, and calcium currents recorded under voltage-clamp conditions were not reduced by compound II (1 microM). Action potential prolongation by compound II was also unaffected in the presence of 10 microM tetrodotoxin. 4. Compound II (1 microM) did not influence IK1 assessed from the current during ramp changes in membrane potential (20 mV s-1) over the range -90 to -10 mV. 5. Compound II (1 microM) blocked time-dependent delayed rectifier potassium current (IK) activated by step depolarizations and recorded as an outward tail following repolarization. When a submaximal concentration (50 nM) was applied there was no change in the apparent reversal potential of IK.6. Submaximal concentrations of compound II were without effect on activation of IK with time at a membrane potential of + 40 mV, and no changes were detected in the time constants of the two components of IK decay over the range of potentials - 60 to 0 mV. Compound 11 (50 nM) appeared to cause a small shift in the activation of IK with membrane potential (an apparent shift of approximately 10mV in the depolarizing direction at the mid-point of the curve).7. Log dose-response curves for action potential prolongation and for blockade of IK by compound II were similar. The IC50 for compound II was approximately 30 nM.8. It is concluded that this novel series of compounds prolongs action potential duration, and that in the case of compound II the evidence supports a potent selective effect on the time-dependent potassium current IK, an effect which can account for this prolongation.


