CHR-6494Haspin inhibitor,potent ands selective CAS# 1333377-65-3 |
- Celastrol
Catalog No.:BCN5986
CAS No.:34157-83-0
- BMS-345541
Catalog No.:BCC1423
CAS No.:547757-23-3
- Bay 65-1942 free base
Catalog No.:BCC1408
CAS No.:600734-02-9
- Bay 65-1942 HCl salt
Catalog No.:BCC1409
CAS No.:600734-06-3
- Bay 65-1942 R form
Catalog No.:BCC1410
CAS No.:758683-21-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1333377-65-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 70679308 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H16N6 | M.Wt | 292.34 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 50 mg/mL (171.03 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
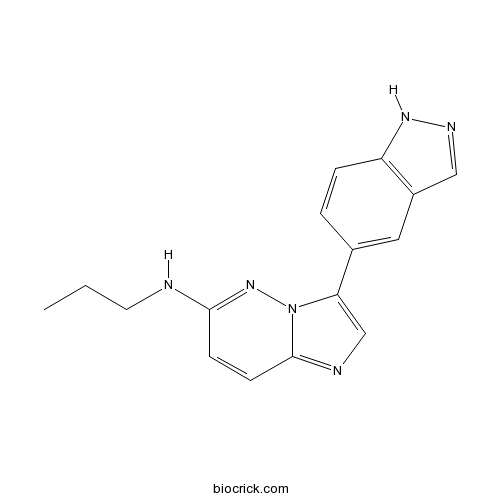
| Chemical Name | 3-(1H-indazol-5-yl)-N-propylimidazo[1,2-b]pyridazin-6-amine | ||
| SMILES | CCCNC1=NN2C(=NC=C2C3=CC4=C(C=C3)NN=C4)C=C1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CZZCAOGIEGXMBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H16N6/c1-2-7-17-15-5-6-16-18-10-14(22(16)21-15)11-3-4-13-12(8-11)9-19-20-13/h3-6,8-10H,2,7H2,1H3,(H,17,21)(H,19,20) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | CHR-6494 is a potent inhibitor of haspin, inhibiting histone H3T3 phosphorylation, with an IC50 of 2 nM.In Vitro:CHR-6494 is a potent inhibitor of haspin, inhibiting histone H3T3 phosphorylation, with an IC50 of 2 nM. CHR-6494 does not modify H3S10 and H328 phosphorylation levels, and shows no significantly inhibitory effects on other protein kinases such as Aurora B kinase. CHR-6494 dose-dependently inhibits the growth of cancer cells, such as HCT-116, HeLa, MDA-MB-231, and Wi-38 cell, with IC50s of 500 nM, 473 nM, 752 nM and 1059 nM, respectively. CHR-6494 (500 nM) produces a mitotic catastrophe with abnormal morphology of the mitotic spindle and centrosome amplification, and upregulates the spindle assembly checkpoint protein BUB1 and the marker of mitotic arrest cyclin B1[1]. CHR-6494 exhibits inhibitory activities against melanoma cell lines, including BRAFV600E mutants, NRAS mutants, and wild type cells, with IC50s ranging from 396 nM to 1229 nM. CHR-6494 (300 nM and 600 nM) induces apoptosis, increases caspase 3/7 activity by 3- and 6-fold, respectively in COLO-792 cells, and to 8.5- and 16-fold in RPMI-7951 cells. CHR-6494 in combination with MEK inhibitors synergistically inhibits viability of melanoma cells, enhances apoptosis in melanoma cells, modulates cell cycle progression independently by arresting melanoma cells at different phases, and suppresses migration of melanoma cells[2].In Vivo:CHR-6494 (50 mg/kg, i.p.) inhibits the growth of tumor and cuases no obvious body weight change in nude mice bearing HCT-116 human colorectal cancer cells[1]. References: | |||||

CHR-6494 Dilution Calculator

CHR-6494 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4207 mL | 17.1034 mL | 34.2067 mL | 68.4135 mL | 85.5169 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6841 mL | 3.4207 mL | 6.8413 mL | 13.6827 mL | 17.1034 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3421 mL | 1.7103 mL | 3.4207 mL | 6.8413 mL | 8.5517 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0684 mL | 0.3421 mL | 0.6841 mL | 1.3683 mL | 1.7103 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0342 mL | 0.171 mL | 0.3421 mL | 0.6841 mL | 0.8552 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Haspin is a serine/threonine kinase that phosphorylates Thr-3 of histone H3 in mitosis that has emerged as a possible cancer therapeutic target. CHR-6494 is a first-in-class Haspin inhibitor with a wide spectrum of anticancer effects. Recent research showed that CHR-6494 reduces H3T3ph levels in a dose-dependent manner and causes a mitotic catastrophe characterized by metaphase misalignment, spindle abnormalities and centrosome amplification. From the cellular standpoint, the identified small-molecule Haspin inhibitor causes arrest in G2/M and subsequently apoptosis. Importantly, ex vivo assays also demonstrate its anti-angiogenetic features; in vivo, it shows antitumor potential in xenografted nude mice without any observed toxicity.
- Imbricataflavone A
Catalog No.:BCN8025
CAS No.:133336-96-6
- 10-Deacetylyunnanxane
Catalog No.:BCN7338
CAS No.:1333323-17-3
- TRPC6 inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC4199
CAS No.:1333207-63-8
- KPT-185
Catalog No.:BCC4444
CAS No.:1333151-73-7
- GSK2194069
Catalog No.:BCC8053
CAS No.:1332331-08-4
- 4-O-Methylbutein
Catalog No.:BCN6677
CAS No.:13323-67-6
- Heliangin
Catalog No.:BCN6487
CAS No.:13323-48-3
- AM 92016 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6825
CAS No.:133229-11-5
- PI3k-delta inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC1861
CAS No.:1332075-63-4
- Fmoc-Thr(Trt)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3554
CAS No.:133180-01-5
- Fmoc-Cit-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3180
CAS No.:133174-15-9
- Oxypeucedan hydrate
Catalog No.:BCN8372
CAS No.:133164-11-1
- Lactacystin
Catalog No.:BCN1841
CAS No.:133343-34-7
- Lydicamycin
Catalog No.:BCN1843
CAS No.:133352-27-9
- Daturataturin A
Catalog No.:BCN6179
CAS No.:133360-51-7
- DV 7028 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6202
CAS No.:133364-62-2
- Fmoc-His(MMt)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3503
CAS No.:133367-33-6
- 4-Hydroxy-11,12,13-trinor-5-eudesmen-7-one
Catalog No.:BCN6627
CAS No.:133369-42-3
- Fmoc-β-Homo-D-Tyr(tBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2620
CAS No.:133373-24-7
- Brandioside
Catalog No.:BCN6770
CAS No.:133393-81-4
- 3-MPPI
Catalog No.:BCC6705
CAS No.:133399-65-2
- (+)-Aflavazole
Catalog No.:BCN7339
CAS No.:133401-09-9
- MG-132
Catalog No.:BCC1227
CAS No.:133407-82-6
- MG-115
Catalog No.:BCC1237
CAS No.:133407-86-0
Dynamics of histone H3 phosphorylation at threonine 3 during meiotic maturation in mouse oocytes.[Pubmed:25645018]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Mar 6;458(2):280-6.
Various histone residues are post-translationally modified during the cell cycle. Among these, histone H3 phosphorylation at threonine 3 (H3T3ph) is newly characterized and has been considered to be crucial for chromosome dynamics during mitosis. However, little is known about the role of H3T3ph during mouse oocyte maturation. In the present study, we examined H3T3ph expression and localization during oocyte meiosis. Our results showed that H3T3ph was tightly associated with condensed chromosomes during meiotic maturation. H3T3ph along the chromosome arms was dissociated at anaphase/telophase I, but centromeric H3T3ph remained intact. Moreover, the inhibition of H3T3ph with the small molecule inhibitors CHR-6494 and 5-Itu impaired segregation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis. Partial inhibition of H3T3ph revealed that centromeric Aurora B/C kinase is sufficient to complete meiosis I, but Aurora B/C kinase along the chromosome arms is required to ensure accurate homologous chromosome segregation. Therefore, our results demonstrate that H3T3ph is a universal regulator of chromosome dynamics during oocyte meiosis and mitosis.
Anti-Melanoma Activities of Haspin Inhibitor CHR-6494 Deployed as a Single Agent or in a Synergistic Combination with MEK Inhibitor.[Pubmed:28928884]
J Cancer. 2017 Aug 25;8(15):2933-2943.
Background: Melanoma is a heterogeneous malignancy that presents an immense challenge in therapeutic development. Recent approaches targeting the oncogenic MAP kinase pathways have shown tremendous improvement in the overall survival of patients with advanced melanoma. However, there is still an urgent need for identification of new strategies to overcome drug resistances and to improve therapeutic efficacy. Haspin (Haploid Germ Cell-Specific Nuclear Protein Kinase) belongs to a selected group of mitotic kinases and is required for normal mitosis progression. In contrast to inhibitors of other mitotic kinases, anti-tumor potential of haspin inhibitors has not been well explored. Herein, we aim to examine effects of CHR-6494, a small molecule inhibitor of haspin, in melanoma cells. Methods: Anti-tumor activities of the haspin inhibitor CHR-6494 were tested in a number of melanoma cell lines either as a single agent or in combination with the MEK inhibitor Trametinib (GSK1120212). Experiments are based on: 1) Cell viability determined by the crystal violet staining assay; 2) apoptotic responses measured by the caspase 3/7 activity assay and western blot analysis for the level of cleaved PARP (Poly ADP-Ribose Polymerase); 3) cell cycle analysis conducted using flow cytometry; and 4) cell migratory ability assessed by the scratch assay and the transwell migration assay. Results: We have found that CHR-6494 alone elicits a dose dependent inhibitory effect on the viability of several melanoma cell lines. This growth inhibition is accompanied by an increase in apoptotic responses. More importantly, CHR-6494 appears to synergize with the MEK inhibitor Trametinib in suppressing cell growth and enhancing apoptosis in both wild type and BRAFV600E mutant melanoma cell lines. Administering of these two small molecules as a combination is also capable of suppressing cell migration to a greater extent than the individual agent. Conclusion: These results suggest that haspin can be considered as a viable anti-melanoma target, and that concomitant inhibition of haspin and MEK activities with small molecules could represent a novel therapeutic strategy with improved efficacy for treatment of melanoma.
Antitumor activity of a small-molecule inhibitor of the histone kinase Haspin.[Pubmed:21804608]
Oncogene. 2012 Mar 15;31(11):1408-18.
The approval of histone deacetylase inhibitors for treatment of lymphoma subtypes has positioned histone modifications as potential targets for the development of new classes of anticancer drugs. Histones also undergo phosphorylation events, and Haspin is a protein kinase the only known target of which is phosphorylation of histone H3 at Thr3 residue (H3T3ph), which is necessary for mitosis progression. Mitotic kinases can be blocked by small drugs and several clinical trials are underway with these agents. As occurs with Aurora kinase inhibitors, Haspin might be an optimal candidate for the pharmacological development of these compounds. A high-throughput screening for Haspin inhibitors identified the CHR-6494 compound as being one promising such agent. We demonstrate that CHR-6494 reduces H3T3ph levels in a dose-dependent manner and causes a mitotic catastrophe characterized by metaphase misalignment, spindle abnormalities and centrosome amplification. From the cellular standpoint, the identified small-molecule Haspin inhibitor causes arrest in G2/M and subsequently apoptosis. Importantly, ex vivo assays also demonstrate its anti-angiogenetic features; in vivo, it shows antitumor potential in xenografted nude mice without any observed toxicity. Thus, CHR-6494 is a first-in-class Haspin inhibitor with a wide spectrum of anticancer effects that merits further preclinical research as a new member of the family of mitotic kinase inhibitors.


