PI3k-delta inhibitor 1PI3k-delta inhibitor CAS# 1332075-63-4 |
- PF-04691502
Catalog No.:BCC3837
CAS No.:1013101-36-4
- A66
Catalog No.:BCC3715
CAS No.:1166227-08-2
- IC-87114
Catalog No.:BCC1161
CAS No.:371242-69-2
- PIK-93
Catalog No.:BCC2519
CAS No.:593960-11-3
- CAL-101 (Idelalisib, GS-1101)
Catalog No.:BCC1270
CAS No.:870281-82-6
- PIK-294
Catalog No.:BCC4995
CAS No.:900185-02-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1332075-63-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 53378051 | Appearance | Powder |
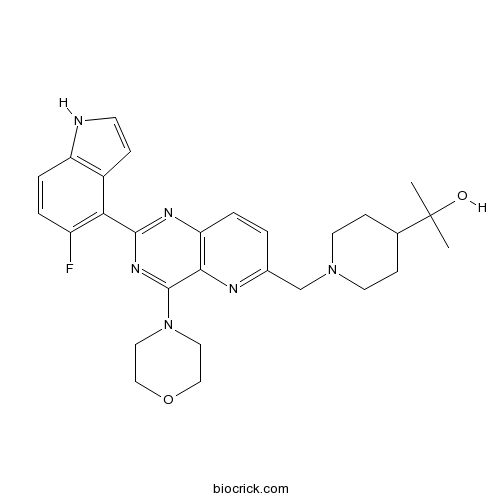
| Formula | C28H33FN6O2 | M.Wt | 504.6 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-[1-[[2-(5-fluoro-1H-indol-4-yl)-4-morpholin-4-ylpyrido[3,2-d]pyrimidin-6-yl]methyl]piperidin-4-yl]propan-2-ol | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)(C1CCN(CC1)CC2=NC3=C(C=C2)N=C(N=C3N4CCOCC4)C5=C(C=CC6=C5C=CN6)F)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ONEJEIKQLAZPNN-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C28H33FN6O2/c1-28(2,36)18-8-11-34(12-9-18)17-19-3-5-23-25(31-19)27(35-13-15-37-16-14-35)33-26(32-23)24-20-7-10-30-22(20)6-4-21(24)29/h3-7,10,18,30,36H,8-9,11-17H2,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | PI3kδ inhibitor 1 is a potent and selective PI3Kδ inhibitor with an IC50 of 3.8 nM.In Vitro:PI3kδ inhibitor 1 (Compound 3) is a potent inhibitor of PI3Kδ that is 200-400 fold selective for all three remaining Class I PI3K isoforms and extremely selective relative to 239 kinases tested in SelectScreen service (0/239 kinases showing >50% inhibition when tested at 1 μM; mTOR, DNA-PK, VPS34, PI4Kα and PI4Kβ are inhibited at 10% or less when tested at 1 μM; PIKC2A and PIKC2B are inhibited at 11% and 42%, respectively, at this same concentration and show less than 10% inhibition when tested at 0.1 μM; the PIKK family kinases ATM and ATR are not assessed)[1].In Vivo:The pharmacokinetic properties of PI3kδ inhibitor 1 (Compound 3) are evaluated in mice and rats when dosed IV and orally. Good plasma exposures and reasonable half-lives are observed upon oral dosing, a reflection of high oral bioavailability (80% and 90% at a low dose for mouse and rat, respectively), moderate volume of distribution, and moderate clearance. PI3kδ inhibitor 1 has moderate terminal elimination half-life (t1/2=2.6 h, 2.9 h, 5 h, 2.6, 3.8 and 4.8 h for mouse (5 mg/kg, po), mouse (20 mg/kg, po), mouse (40 mg/kg, po), rat (5 mg/kg, po), rat (10 mg/kg, po), rat (30 mg/kg, po)). Plasma exposures and Cmax levels increase with dose in both mice and rats, important in that inflammatory disease models utilize these two species. Plasma protein binding for PI3kδ inhibitor 1 ranges from 80-88% in rodents and is consistent with values obtained in human plasma (86%)[1]. References: | |||||

PI3k-delta inhibitor 1 Dilution Calculator

PI3k-delta inhibitor 1 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9818 mL | 9.9088 mL | 19.8177 mL | 39.6354 mL | 49.5442 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3964 mL | 1.9818 mL | 3.9635 mL | 7.9271 mL | 9.9088 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1982 mL | 0.9909 mL | 1.9818 mL | 3.9635 mL | 4.9544 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0396 mL | 0.1982 mL | 0.3964 mL | 0.7927 mL | 0.9909 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0198 mL | 0.0991 mL | 0.1982 mL | 0.3964 mL | 0.4954 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
PI3kδ inhibitor 1; useful for inhibiting the delta isoform of PI3K, and for treating disorders mediated by lipid kinases such as inflammation, immunol. disorders, and cancer.
- Fmoc-Thr(Trt)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3554
CAS No.:133180-01-5
- Fmoc-Cit-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3180
CAS No.:133174-15-9
- Oxypeucedan hydrate
Catalog No.:BCN8372
CAS No.:133164-11-1
- GR 73632
Catalog No.:BCC5801
CAS No.:133156-06-6
- Epimedin B1
Catalog No.:BCN8199
CAS No.:133137-58-3
- Flutamide
Catalog No.:BCC4364
CAS No.:13311-84-7
- Darifenacin HBr
Catalog No.:BCC4567
CAS No.:133099-07-7
- Darifenacin
Catalog No.:BCC1516
CAS No.:133099-04-4
- 3PO
Catalog No.:BCC5616
CAS No.:13309-08-5
- Crassifoline methine
Catalog No.:BCN1793
CAS No.:133084-00-1
- Fmoc-D-Lys(Boc)-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3527
CAS No.:133083-36-0
- BIM 23052
Catalog No.:BCC5945
CAS No.:133073-82-2
- AM 92016 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6825
CAS No.:133229-11-5
- Heliangin
Catalog No.:BCN6487
CAS No.:13323-48-3
- 4-O-Methylbutein
Catalog No.:BCN6677
CAS No.:13323-67-6
- GSK2194069
Catalog No.:BCC8053
CAS No.:1332331-08-4
- KPT-185
Catalog No.:BCC4444
CAS No.:1333151-73-7
- TRPC6 inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC4199
CAS No.:1333207-63-8
- 10-Deacetylyunnanxane
Catalog No.:BCN7338
CAS No.:1333323-17-3
- Imbricataflavone A
Catalog No.:BCN8025
CAS No.:133336-96-6
- CHR-6494
Catalog No.:BCC1479
CAS No.:1333377-65-3
- Lactacystin
Catalog No.:BCN1841
CAS No.:133343-34-7
- Lydicamycin
Catalog No.:BCN1843
CAS No.:133352-27-9
- Daturataturin A
Catalog No.:BCN6179
CAS No.:133360-51-7
Idelalisib may have the potential to increase radiotherapy side effects.[Pubmed:28659152]
Radiat Oncol. 2017 Jun 28;12(1):109.
INTRODUCTION: Idelalisib is approved for the treatment of relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia together with Rituximab and for monotherapy of follicular B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and small lymphocytic lymphoma. It is a potent and selective phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-delta (PI3K-delta) inhibitor. PI3K-delta primarily is expressed in B-cells and prevents effectively proliferation in malignant B-cells. METHODS: We provide a detailed report on treatment history and photo documentation of acute adverse effects of radiation therapy with simultaneous Idelalisib medication in one case of B-CLL. Radiosensitivity tests were performed for the index patient under Idelalisib and after the addition of Idelalisib to healthy individuals' blood. Radiosensitivity in human lymphocytes was analyzed with a three color in situ hybridization assay. Primary skin fibroblasts were studied after a treatment with Idelalisib for apoptosis, necrosis and cell cycle using flow cytometry. DNA double-strand break repair was analyzed by gammaH2AX immunostaining. RESULTS: The index patient presented a strong grade 2 radiodermatitis and grade 3 mucositis after irradiation with 20 Gy and a simultaneous intake of Idelalisib. Irradiations without Idelalisib medication were well tolerated and resulted in not more than grade 1 radiodermatitis. The index patient under Idelalisib had a radiosensitivity of 0.62 B/M which is in the range of clearly radiosensitive patients. A combined treatment of lymphocytes with 2 Gy and 10 nmol/l Idelalisib showed a tendency to an increased radiosensitivity. We found a clear increase of apoptosis as a result of the combined treatment in the Idelalisib dose range of 1 to 100 nmol/l compared to solely irradiated cells or solely Idelalisib treated cells (p = 0.05). CONCLUSION: A combined Idelalisib radiotherapy treatment has an increased risk of side effects. However, combined therapy seems to be feasible when patients are monitored closely.
Anti-tumor activity of PI3K-delta inhibitor in hematologic malignant cells: Shedding new light on resistance to Idelalisib.[Pubmed:28254430]
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2017 Apr;85:149-158.
Genetic and laboratory experiments have brought remarkable advances in management of human malignancies, which not only revolutionized the understanding of the disease, but also led to development of novel and effective targeted therapies against specific deregulated pathways. This study aimed to investigate anti-cancer effects of Idelalisib, a potent PI3K-delta inhibitor, in a panel of hematological cell lines. The resulting data showed that Idelalisib decreased cell survival in all the tested cell lines; however, as compared to NB4, viability of other cell lines, irrespective of their molecular characteristics or even the compensatory activation of MEK/ERK pathway, was inhibited at higher concentrations. This study suggests for the first time that there is a significant correlation between relative response to Idelalisib and basal expression levels of anti-apoptotic genes, in particular survivin and MCL-1. Intriguingly, we found that Idelalisib-induced apoptosis in NB4, as the most sensitive cell line with the lowest expression level of the aforementioned genes, is executed probably via alteration in the transcriptional level of apoptosis-related genes coupled with p21-mediated caspase-3 activation. Moreover, the lower concentrations of Idelalisib combined with arsenic trioxide (ATO) produced synergistic anti-cancer effect in APL-derived NB4 cells. Overall, due to the pharmacologic safety of Idelalisib and its broad clinical effectiveness in chronic lymphoproliferative disorders, our study suggests that this inhibitor is a promising agent for the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia, either as single agent or in a combined-modality strategy.
Current Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.[Pubmed:28185174]
Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2017 Jan;18(1):5.
OPINION STATEMENT: A number of new treatment options have recently emerged for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients, including the Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) delta isoform inhibitor idelalisib combined with rituximab, the Bcl-2 antagonist venetoclax, and the new anti-CD20 antibodies obinutuzumab and ofatumumab. Most of these agents are already included into treatment algorithms defined by international practice guidelines, but more clinical investigations are needed to answer still remaining questions. Ibrutinib was proven as a primary choice for patients with the TP53 gene deletion/mutation, who otherwise have no active treatment available. Idelalisib with rituximab is also an active therapy, but due to increased risk of serious infections, its use in first-line treatment is limited to patients for whom ibrutinib is not an option. A new indication for ibrutinib was recently approved for older patients with comorbidities, as an alternative to the already existing indication for chlorambucil with obinutuzumab. The use of kinase inhibitors is already well established in recurrent/refractory disease. Immunochemotherapy with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, rituximab (FCR) remains a major first-line option for many CLL patients without the TP53 gene deletion/mutation, and who have no significant comorbidities or history of infections, and is particularly effective in patients with favorable features including mutated IGHV status. There are a number of issues regarding novel therapies for CLL that need further investigation such as optimum duration of treatment with kinase inhibitors, appropriate sequencing of novel agents, mechanisms of resistance to inhibitors and response to class switching after treatment failure, along with the potential role of combinations of targeted agents.
Design of Selective Benzoxazepin PI3Kdelta Inhibitors Through Control of Dihedral Angles.[Pubmed:28947940]
ACS Med Chem Lett. 2017 Aug 25;8(9):936-940.
A novel selective benzoxazepin inhibitor of PI3Kdelta has been discovered. Beginning from compound 3, an alphaPI3K inhibitor, we utilized structure-based drug design and computational analysis of dihedral torsion angles to optimize for PI3Kdelta isoform potency and isoform selectivity. Further medicinal chemistry optimization of the series led to the identification of 24, a highly potent and selective inhibitor of PI3Kdelta.
Silencing c-Myc translation as a therapeutic strategy through targeting PI3Kdelta and CK1epsilon in hematological malignancies.[Pubmed:27784673]
Blood. 2017 Jan 5;129(1):88-99.
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and the proteasome pathway are both involved in activating the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR). Because mTOR signaling is required for initiation of messenger RNA translation, we hypothesized that cotargeting the PI3K and proteasome pathways might synergistically inhibit translation of c-Myc. We found that a novel PI3K delta isoform inhibitor TGR-1202, but not the approved PI3Kdelta inhibitor idelalisib, was highly synergistic with the proteasome inhibitor carfilzomib in lymphoma, leukemia, and myeloma cell lines and primary lymphoma and leukemia cells. TGR-1202 and carfilzomib (TC) synergistically inhibited phosphorylation of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E)-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1), leading to suppression of c-Myc translation and silencing of c-Myc-dependent transcription. The synergistic cytotoxicity of TC was rescued by overexpression of eIF4E or c-Myc. TGR-1202, but not other PI3Kdelta inhibitors, inhibited casein kinase-1 epsilon (CK1epsilon). Targeting CK1epsilon using a selective chemical inhibitor or short hairpin RNA complements the effects of idelalisib, as a single agent or in combination with carfilzomib, in repressing phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and the protein level of c-Myc. These results suggest that TGR-1202 is a dual PI3Kdelta/CK1epsilon inhibitor, which may in part explain the clinical activity of TGR-1202 in aggressive lymphoma not found with idelalisib. Targeting CK1epsilon should become an integral part of therapeutic strategies targeting translation of oncogenes such as c-Myc.


