Auristatin FCAS# 163768-50-1 |
- Pioglitazone
Catalog No.:BCC4927
CAS No.:111025-46-8
- GW501516
Catalog No.:BCC2268
CAS No.:317318-70-0
- WY-14643 (Pirinixic Acid)
Catalog No.:BCC2265
CAS No.:50892-23-4
- L-165041
Catalog No.:BCC1687
CAS No.:79558-09-1
- Sodium 4-amiropparaty Hyalrate
Catalog No.:BCC3855
CAS No.:94-16-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 163768-50-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 67472795 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C40H67N5O8 | M.Wt | 745.99 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 56 mg/mL (75.07 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
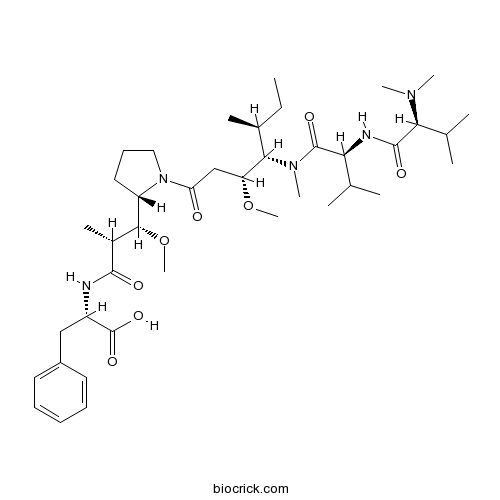
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-[[(2R,3R)-3-[(2S)-1-[(3R,4S,5S)-4-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-(dimethylamino)-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]-methylamino]-3-methoxy-5-methylheptanoyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl]-3-methoxy-2-methylpropanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCC(C)C(C(CC(=O)N1CCCC1C(C(C)C(=O)NC(CC2=CC=CC=C2)C(=O)O)OC)OC)N(C)C(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)N(C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LGNCNVVZCUVPOT-FUVGGWJZSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C40H67N5O8/c1-13-26(6)35(44(10)39(49)33(24(2)3)42-38(48)34(25(4)5)43(8)9)31(52-11)23-32(46)45-21-17-20-30(45)36(53-12)27(7)37(47)41-29(40(50)51)22-28-18-15-14-16-19-28/h14-16,18-19,24-27,29-31,33-36H,13,17,20-23H2,1-12H3,(H,41,47)(H,42,48)(H,50,51)/t26-,27+,29-,30-,31+,33-,34-,35-,36+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Auristatin F Dilution Calculator

Auristatin F Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.3405 mL | 6.7025 mL | 13.405 mL | 26.81 mL | 33.5125 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2681 mL | 1.3405 mL | 2.681 mL | 5.362 mL | 6.7025 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1341 mL | 0.6703 mL | 1.3405 mL | 2.681 mL | 3.3513 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0268 mL | 0.1341 mL | 0.2681 mL | 0.5362 mL | 0.6703 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0134 mL | 0.067 mL | 0.1341 mL | 0.2681 mL | 0.3351 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Auristatin F is a cytotoxic tubulin modifier with potent and selective antitumor activity; MMAF analog and cytotoxin in Antibody-drug conjugates.
References:
[1]. Temming K, et al. Improved efficacy of alphavbeta3-targeted albumin conjugates by conjugation of a novel auristatin derivative. Mol Pharm. 2007 Sep-Oct;4(5):686-94.
[2]. Doronina SO, et al. Enhanced activity of monomethylauristatin F through monoclonal antibody delivery: effects of linker technology on efficacy and toxicity. Bioconjug Chem. 2006 Jan-Feb;17(1):114-24.
- WIN 64338 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6914
CAS No.:163727-74-0
- Pazufloxacin mesilate
Catalog No.:BCC9114
CAS No.:163680-77-1
- Kadsulignan L
Catalog No.:BCN3627
CAS No.:163660-06-8
- Evofolin C
Catalog No.:BCN4695
CAS No.:163634-05-7
- Fmoc-D-Trp(Boc)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3561
CAS No.:163619-04-3
- Kadsulignan N
Catalog No.:BCN3631
CAS No.:163564-58-7
- Vilazodone
Catalog No.:BCC2040
CAS No.:163521-12-8
- Vilazodone Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2041
CAS No.:163521-08-2
- Triptoquinonide
Catalog No.:BCN1724
CAS No.:163513-81-3
- Flufenamic acid
Catalog No.:BCC9162
CAS No.:530-78-9
- Fmoc-Met(O2)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3531
CAS No.:163437-14-7
- 2',4'-Di-O-(E-p-coumaroyl)afzelin
Catalog No.:BCN6512
CAS No.:163434-73-9
- YM 90709
Catalog No.:BCC7149
CAS No.:163769-88-8
- 7beta-Hydroxyrutaecarpine
Catalog No.:BCN6500
CAS No.:163815-35-8
- Salvianolic acid Y
Catalog No.:BCN8123
CAS No.:1638738-76-7
- Androstenediol-3-acetate
Catalog No.:BCC8829
CAS No.:1639-43-6
- 8(17),12E,14-Labdatrien-20-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7396
CAS No.:1639257-36-5
- 12E,14-Labdadien-20,8beta-olide
Catalog No.:BCN7395
CAS No.:1639257-37-6
- Kaempferol-3-O-(6''-O-cis-coumaryl)glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1538
CAS No.:163956-16-9
- Longiferone B
Catalog No.:BCN7378
CAS No.:1639810-67-5
- Clerodenoside A
Catalog No.:BCN1725
CAS No.:164022-75-7
- LY 311727
Catalog No.:BCC7728
CAS No.:164083-84-5
- AM630
Catalog No.:BCC1353
CAS No.:164178-33-0
- Phosphoramidon Disodium Salt
Catalog No.:BCC5484
CAS No.:164204-38-0
Native intact mass determination of antibodies conjugated with monomethyl Auristatin E and F at interchain cysteine residues.[Pubmed:22384990]
Anal Chem. 2012 Mar 20;84(6):2843-9.
We present here a method for the rapid determination of the intact mass of noncovalently associated antibody heavy chains (HC) and light chains (LC) which result from the attachment of drug conjugates to interchain cysteine residues. By analyzing the antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) using native desalting conditions, we maintain the intact bivalent structure of the ADC, which ordinarily would decompose as a consequence of denaturing chromatographic conditions typically used for liquid chromatographic-mass spectrometric (LC-MS) analysis. The mass of the desalted ADC is subsequently determined using standard desolvation and ionization conditions. Methods presented previously in the literature for analyzing interchain cysteinyl-linked ADCs are either not amenable to online mass spectrometry or result in the denaturing dissociation of conjugated HC and LC during chromatographic separation and subsequent mass measurement. We have avoided this outcome with our method and have successfully and routinely obtained intact mass measurement of IgG1 mAbs conjugated with maleimidocaproyl-monomethyl Auristatin F (mcMMAF) and valine-citrulline-monomethyl Auristatin E (vcMMAE) at interchain cysteine residues. Our results thus represent the first reported direct measurement of the intact mass of an ADC conjugated at interchain cysteine residues.
The efficient elimination of solid tumor cells by EGFR-specific and HER2-specific scFv-SNAP fusion proteins conjugated to benzylguanine-modified auristatin F.[Pubmed:27502168]
Cancer Lett. 2016 Oct 28;381(2):323-30.
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) combine the potency of cytotoxic drugs with the specificity of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). Most ADCs are currently generated by the nonspecific conjugation of drug-linker reagents to certain amino acid residues in mAbs, resulting in a heterogeneous product. To overcome this limitation and prepare ADCs with a defined stoichiometry, we use SNAP-tag technology as an alternative conjugation strategy. This allows the site-specific conjugation of O(6)-benzylguanine (BG)-modified small molecules to SNAP-tag fusion proteins. To demonstrate the suitability of this system for the preparation of novel recombinant ADCs, here we conjugated SNAP-tagged single chain antibody fragments (scFvs) to a BG-modified version of Auristatin F (AURIF). We used two scFv-SNAP fusion proteins targeting members of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family that are frequently overexpressed in breast cancer. The conjugation of BG-AURIF to EGFR-specific 425(scFv)-SNAP and HER2-specific alphaHER2(scFv)-SNAP resulted in two potent recombinant ADCs that specifically killed breast cancer cell lines by inducing apoptosis when applied at nanomolar concentrations. These data confirm that SNAP-tag technology is a promising tool for the generation of novel recombinant ADCs.
A Novel Platinum(II)-Based Bifunctional ADC Linker Benchmarked Using 89Zr-Desferal and Auristatin F-Conjugated Trastuzumab.[Pubmed:27872093]
Cancer Res. 2017 Jan 15;77(2):257-267.
Greater control is desirable in the stochastic conjugation technology used to synthesize antibody-drug conjugates (ADC). We have shown recently that a fluorescent dye can be stably conjugated to a mAb using a bifunctional platinum(II) linker. Here, we describe the general applicability of this novel linker technology for the preparation of stable and efficacious ADCs. The ethylenediamine platinum(II) moiety, herein called Lx, was coordinated to Desferal (DFO) or Auristatin F (AF) to provide storable "semifinal" products, which were directly conjugated to unmodified mAbs. Conjugation resulted in ADCs with unimpaired mAb-binding characteristics, DAR in the range of 2.5 to 2.7 and approximately 85% payload bound to the Fc region, presumably to histidine residues. To evaluate the in vivo stability of Lx and its effect on pharmacokinetics and tumor targeting of an ADC, Lx-DFO was conjugated to the HER2 mAb trastuzumab, followed by radiolabeling with (89)Zr. Trastuzumab-Lx-DFO-(89)Zr was stable in vivo and exhibited pharmacokinetic and tumor-targeting properties similar to parental trastuzumab. In a xenograft mouse model of gastric cancer (NCI-N87) or an ado-trastuzumab emtansine-resistant breast cancer (JIMT-1), a single dose of trastuzumab-Lx-AF outperformed its maleimide benchmark trastuzumab-Mal-AF and FDA-approved ado-trastuzumab emtansine. Overall, our findings show the potential of the Lx technology as a robust conjugation platform for the preparation of anticancer ADCs. Cancer Res; 77(2); 257-67. (c)2016 AACR.


